China has emerged as a dominant force in the electric vehicle (EV) market, especially when it comes to EV battery production. The global shift towards sustainable transportation heavily relies on China’s contribution, with the country playing a crucial role in shaping the EV landscape.
This report delves into the significance of China’s influence on worldwide EV battery production and its implications for the EV market as a whole.
As part of its efforts to reduce pollution from automobiles, the Biden administration in the United States has put forth new regulations. According to reports, these regulations would mandate that up to two-thirds of all new vehicles sold in the country by 2032 must be electric.
This ambitious proposal would signify a remarkable tenfold surge compared to the present sales figures of electric vehicles.
To speed up the shift to electric vehicles, the European Union (EU) plans to ban the sale of new gasoline and diesel cars within its borders starting in 2035. This action aims to encourage the widespread use of EVs as part of the EU’s effort to fight climate change and cut emissions.
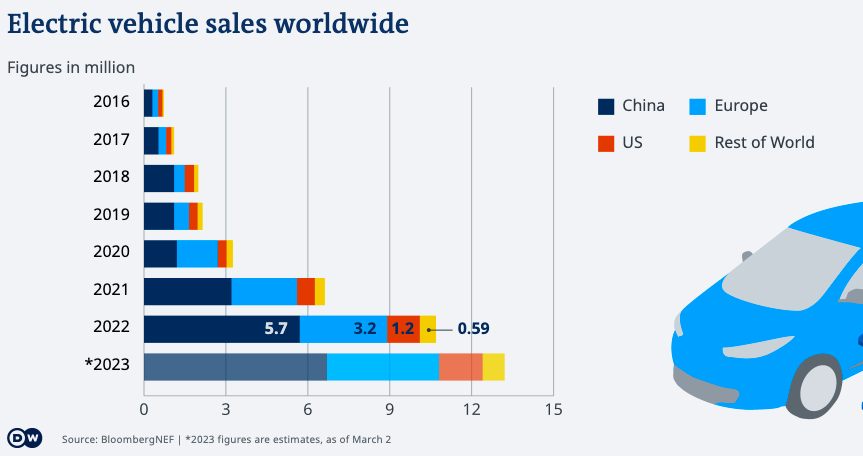
In 2022, global EV sales reached 10.5 million units, up 60% from 2021. China accounted for 60% of global EV sales in 2022, followed by Europe (23%) and the United States (10%). Battery electric vehicles (BEVs) accounted for 87% of global EV sales in 2022, while plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs) accounted for the remaining 13%.
The average selling price of an EV in 2022 was $50,000, up from $40,000 in 2021. BloombergNEF expects global EV sales to reach 22 million units in 2025 and 700 million units by 2040.
EV Battery Demand Set To Soar
The demand for electric vehicle (EV) batteries is expected to rise sharply in the next few years. Major car manufacturers around the globe are anticipated to invest about $1.2 trillion (€1.08 trillion) in EVs and batteries by 2030, according to Reuters. The International Energy Agency forecasts that the share of battery-powered cars in total global auto sales will jump from around 10% in 2021 to over 60% by 2030.
With tens of millions of EVs expected to hit the roads, the demand for batteries will be substantial. Batteries represent the most expensive component in an electric vehicle, constituting around 30-40% of its cost. In anticipation of this surge, governments and companies are racing to secure sufficient battery supplies.
Attempts To Establish Local Supply Chains Will Not Completely Eradicate Reliance On China
As the demand for EV batteries surges, countries are striving to enhance self-sufficiency and establish domestic supply chains. China currently holds a dominant position in the global battery industry, securing the top spot in BNEF’s Global Lithium-Ion Battery Supply Chain Ranking. It commands over 50% of battery-grade metals refining capacity across key materials, with substantial investments in mining assets worldwide.
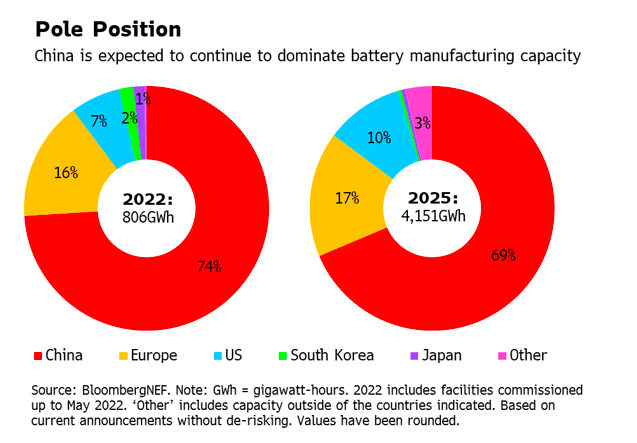
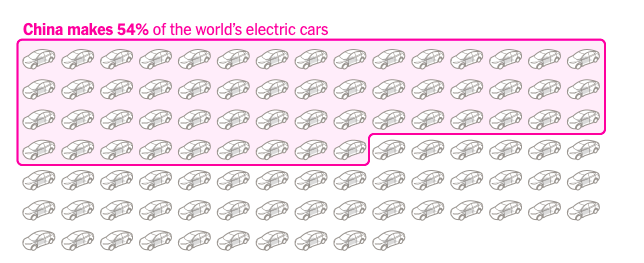
Additionally, China stands out as a formidable battery manufacturing powerhouse, accounting for nearly 75% of the total commissioned capacity. While Europe and the US are making progress in this market, China is projected to maintain its leading position, with an expected 69% share of global manufacturing capacity by 2025, according to BNEF.
According to The New York Times, China maintains control over every stage of the lithium-ion battery production process, encompassing the extraction of raw materials and the manufacturing of vehicles. These advantages are expected to endure for the foreseeable future.
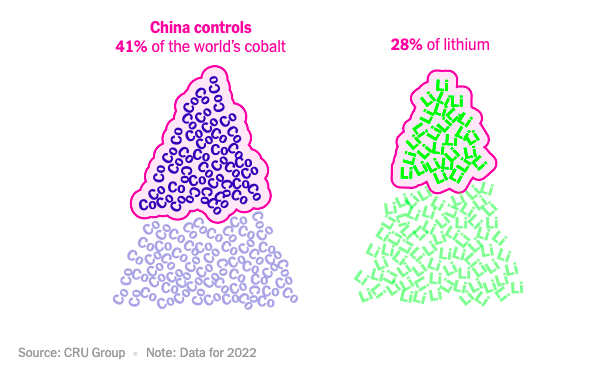
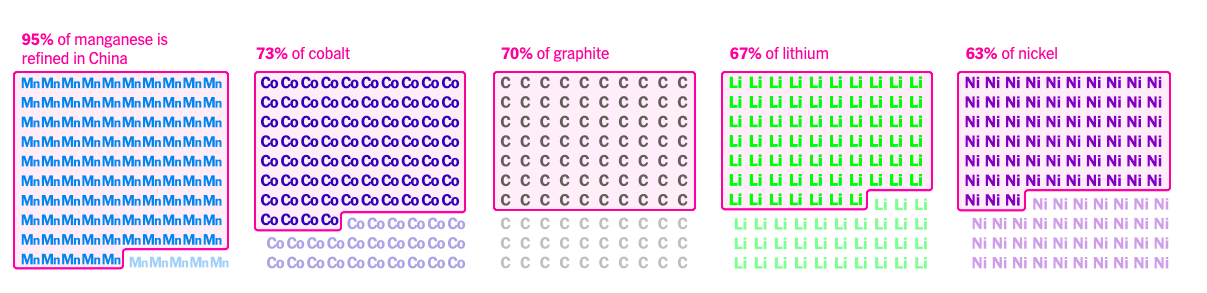
First, China controls essential rare minerals. China, lacking domestic resources, has strategically acquired stakes in mining companies worldwide to ensure a steady supply of essential battery ingredients. It controls 41% of global cobalt mining and dominates lithium mining.
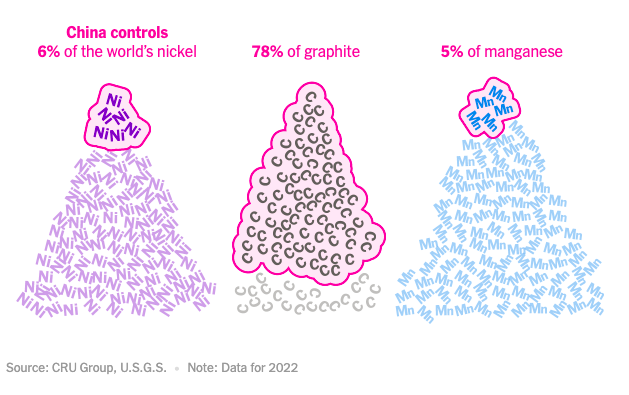
Second, China plays a crucial role in mineral processing for the world. China dominates the mineral refining industry, regardless of the source of the mined minerals. The refining process is energy-intensive and generates significant waste and pollution. Chinese companies benefit from government support, lower costs, and less stringent environmental regulations.
Other countries lack processing capabilities, and building refineries is time-consuming. Sustainable processing methods increase costs. The United States and Australia have faced challenges in establishing their own refineries.
Third, The majority of battery components are manufactured in China. China’s rise as the largest battery producer is attributed to its efficient and cost-effective manufacturing of battery components. One crucial component is the cathode, which has traditionally used nickel, cobalt, and manganese. However, China has successfully invested in an alternative cathode called LFP (lithium iron phosphate), using iron and phosphate instead.
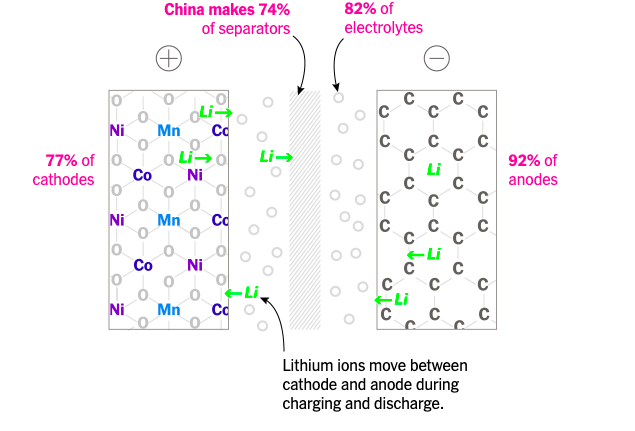
LFP cathodes have gained significant market share, providing an opportunity for Western countries to diversify their mineral supply. However, China currently dominates LFP production. Chinese companies also lead in the production of anodes, separators, and electrolytes, making them key players in the global battery component market.
Western companies interested in LFP must collaborate with experienced Chinese manufacturers to access this technology.
Finally, China has emerged as the leading producer of both batteries and cars in the world. China dominates the electric car market with its own batteries, thanks to policies that favored domestic manufacturers and restricted foreign competition.
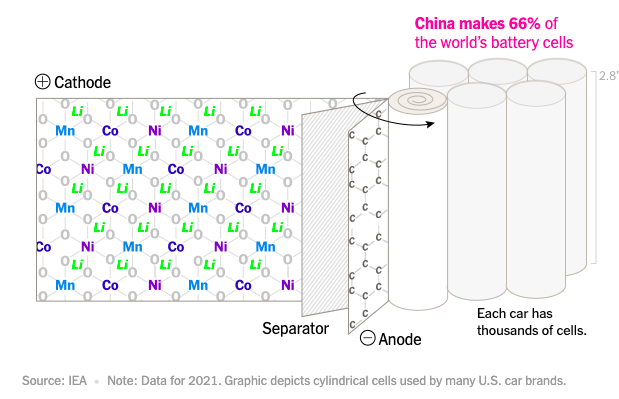
Chinese companies like CATL and BYD have become global leaders, leaving Japanese and South Korean rivals behind. Now, the Biden administration is seeking to catch up by supporting battery development in the United States.
However, China’s significant advantage in experience, state funding, and lower costs gives it a head start in the complex process of battery assembly. China’s ability to build battery factories at a much lower cost contributes to its industry dominance.
According to The New York Times, American investors remain cautious about investing in electric vehicles due to the continued profitability of traditional cars, the need to train American workers in new skills, and the uncertainty of future government incentives. In contrast, China has invested over $130 billion in research incentives, contracts, and subsidies, allowing it to lead in production, equipment, and design.
Experts believe it is nearly impossible for any country to achieve self-reliance in the battery supply chain without partnering with Chinese manufacturers. Cooperation with China is seen as essential for success in the electric vehicle industry.
Related News
- 15+ Best Crypto To Buy Now
- Spotify Expected to Finally Add High-Fidelity Subscription Tier This Year
- $1,000 in $PEPE Could Have Made You a Crypto Millionaire – $1,000 of This Memecoin Could Be Worth Even More Soon
What's the Best Crypto to Buy Now?
- B2C Listed the Top Rated Cryptocurrencies for 2023
- Get Early Access to Presales & Private Sales
- KYC Verified & Audited, Public Teams
- Most Voted for Tokens on CoinSniper
- Upcoming Listings on Exchanges, NFT Drops
