The Oregon Department of Transportation (ODOT) and Louisiana’s Office of Motor Vehicles (OMV) are among the many victims affected by a massive data breach resulting from a global hack targeting the data transfer software MOVEit Transfer. This breach has compromised personal information for millions of individuals holding driver’s licenses or IDs in both states. The incident is part of a broader international attack that has affected various high-profile entities worldwide.
Vulnerability Exploited: Massive Breach Exposes Personal Data
The Louisiana OMV asserts that MOVEit Transfer, a widely used file-sharing tool developed and supported by Progress Software Corp, has been utilized by the organization since 2015. On the other hand, ODOT has used it as a vendor. The file-sharing tool allows organizations to securely transfer files and data between business partners and customers. However, ODOT highlighted in a statement that, on June 1, 2023, the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency issued an alert regarding a zero-day vulnerability in MOVEit Transfer, acknowledging that the software was susceptible to a takeover by malicious actors.
ODOT immediately took measures to secure their systems and collaborated with state cyber security services for analysis. Its statement read:
“As soon as ODOT learned of the MOVEit vulnerability, we promptly initiated additional security measures to safeguard our systems.”
Unfortunately, it was discovered that unauthorized actors had accessed files shared through MOVEit Transfer, compromising personal information. In Oregon, approximately 3.5 million individuals holding Oregon IDs or driver’s licenses have been affected, while in Louisiana, the breach exposed the data of millions of individuals with state-issued driver’s licenses, IDs, or car registrations.
The accessed data is extremely sensitive as well. It includes personal information such as names, addresses, social security numbers, birthdates, and driver’s license numbers. Additionally, vehicle registration information and handicap placard information were compromised in Louisiana. While some of this information is publicly available, there is also sensitive personal data at risk.
OMV stated:
“There is no indication at this time that cyber attackers who breached MOVEit have sold, used, shared or released the OMV data obtained from the MOVEit attack. The cyber attackers have not contacted state government. ”
In response to these breaches, both ODOT and OMV are urging affected individuals to take immediate steps to protect themselves even though there is no evidence that the breached data is being used or sold maliciously. Precautionary measures include monitoring personal credit reports, changing passwords for online accounts, protecting tax refunds and returns, and reporting suspected identity theft to the appropriate authorities.
Other Recent Data Breaches That Have Affected Government Agencies
The breach is the latest in a series of high-profile data breaches that have affected government agencies in recent years. In 2017, a breach of the Equifax credit reporting agency exposed the personal information of approximately 145 million Americans. In 2019, a breach of the Office of Personnel Management exposed the personal information of approximately 21.5 million federal employees and contractors.
In 2020, a breach of the Department of Veterans Affairs exposed the personal information of approximately 4.5 million veterans. In 2022, a breach of the U.S. Department of Education exposed the personal information of approximately 820,000 students.
These are just a few examples of the many data breaches that have affected government agencies in recent years. These breaches have exposed the personal information of millions of Americans, and they have raised serious concerns about the security of government data.
U.S. Data Breach Epidemic
According to Comparitech, since 2014, the United States government has experienced 822 breaches, impacting nearly 175 million records. These breaches have incurred substantial costs for government entities, estimated to exceed $26 billion from 2014 to October 2022, based on the average cost per breached record. In 2022, the average number of records affected per breach stands at 71,534.
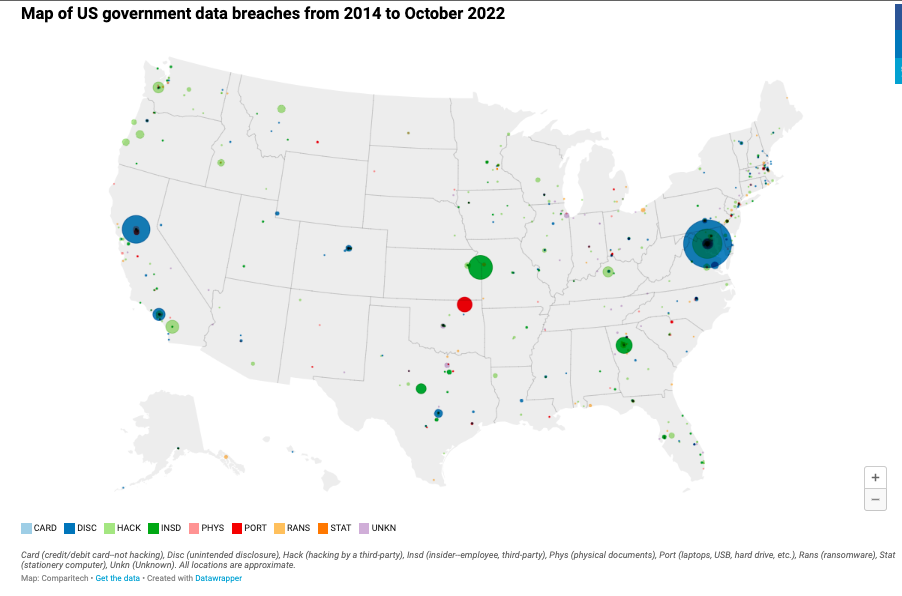
Hacking accounted for the majority of breaches, with 256 incidents, making it the most prevalent type of breach. The second-largest category of breaches was inadvertent disclosure, which comprised 192 incidents.
These figures highlight the persistent challenges faced by the US government and businesses in safeguarding sensitive data and mitigating the impact of data breaches. The costs associated with these breaches, both in terms of financial losses and potential harm to individuals affected, underscore the ongoing need for robust cybersecurity measures and proactive strategies to prevent and respond to such incidents.
These incidents serve as a reminder that data breaches can have far-reaching consequences, impacting individuals and organizations across different regions. It underscores the need for continued efforts to strengthen cybersecurity measures and promote awareness of data protection best practices. By taking proactive steps, individuals can minimize the risk of their personal information being misused or exploited, and organizations can work towards creating a more secure digital environment.
Related Articles
- How to Remove Spyware | Best Spy App Removal Tools in 2023
- US Accounted for 41% of AI-Powered Apps’ Q1 2023 Revenues
- How LinkedIn Dominates the Recruiting Market and is Still Growing – Users Up 11.4% to 922 Million in the Past Year
What's the Best Crypto to Buy Now?
- B2C Listed the Top Rated Cryptocurrencies for 2023
- Get Early Access to Presales & Private Sales
- KYC Verified & Audited, Public Teams
- Most Voted for Tokens on CoinSniper
- Upcoming Listings on Exchanges, NFT Drops
