Geotargeting (or location targeting) allows you to only show ads to people in the locations that matter to your business so you don’t waste money on clicks that will never convert.
Aside from controlling who does/doesn’t see your ads, geotargeting also allows you to prioritise campaigns for the most important locations to your business by managing bids, based on where the bulk of your customers come from or where your highest spenders typically live.
In this guide, we run through the core essentials of geotargeting in Google Ads, how to apply it to your campaigns and how Facebook’s location targeting options are different.
What is geotargeting?
Geotargeting delivers ads to users based on their location data, typically using GPS data from mobile devices or account data. Google uses a combination of techniques for geotargeting, including GPS data, account location settings and search interest in locations – all of which we’ll explain in more detail shortly.
Here’s what Google has to say about location targeting:
“Location targeting allows you to serve ads to users in a particular geographical region. For example, assume you’re advertising for a chain of supermarkets. Without location targeting, your ads would show in all regions worldwide, and your ads might receive clicks from users in regions where you have no supermarket locations. This generates cost while providing no possibility of a return on the investment.”
Google goes on to explain that “with location targeting, your campaigns show ads only in regions where you have open supermarkets”.
The most important use of geotargeting is to prevent your ads from showing to people in locations that are no use to your business. For example, if you operate in the UK, you don’t want to be spending money on ad clicks from the US or other countries.
Likewise, if your business operates in fixed business locations across the country, you may only want people within certain distances of your branches to see your ads (or certain ads).
For example, if your business sells online and offline, you might create ad campaigns specifically for store visits and offline sales. Geotargeting allows you to ensure people within travelling distance see your ads and prevent users who are more likely to order online from seeing them.
Taking this one step further, you can also set location targeting to campaigns and then manage bids to prioritise users in specific locations – for example, if you want to bid more on locations that generate high volumes of customers, areas where high-spending customers are known to live or areas where specific products or services are particularly popular.
Let’s say a roofing company wants to maximise sales of specific roofing tiles. They can create campaigns for used clay reds, concrete ridge tiles or double Romans and apply location targeting to show the relevant ad to people living in areas where houses typically use the same type of tiles.
How does geotargeting work?
Google uses location data from users’ devices, account settings and search interest in locations to provide a range of targeting options in Google Ads.
“Location targeting is based on a variety of signals, including users’ settings, devices, and behaviouryou on our platform, and is Google’s best effort to serve ads to users who meet your location settings. Because these signals vary, 100% accuracy is not guaranteed in every situation. As always, you should check your overall performance metrics to help ensure your settings are meeting your advertising goals and change them accordingly.”
This allows you to specify locations where people see your ads and you can also exclude locations to prevent people in specific places from seeing your ads.
By using Google’s physical location data (from devices and account settings), you can target users who are currently or frequently in your specified locations – in other words, people who likely live or work in your targeted locations.
However, you can also use location targeting in Google Ads to target users who demonstrate an interest in specific locations, such as people researching for their next holiday.
You can find out more about geotargeting in Google Ads on this documentation page for advanced location options.
How to use geotargeting
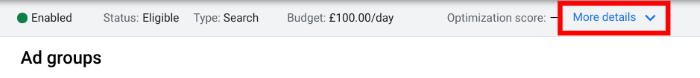
To apply geotargeting settings in Google Ads, open up the campaign you want to work with and then click on the More details tab at the top of the screen.
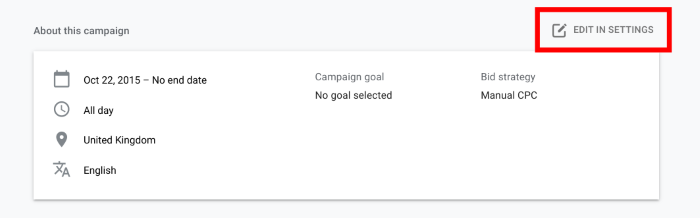
This opens a dropdown menu with a preview of your campaign settings – click the Edit In Settings icon to the top-right of the menu.
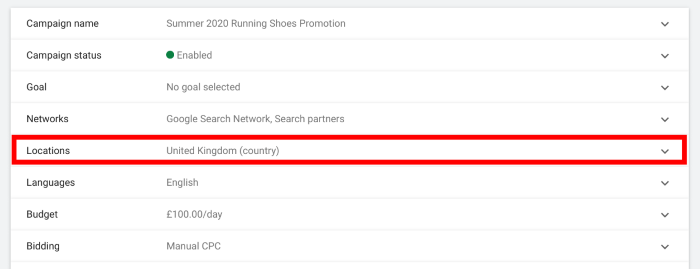
Next, click on the Locations tab in the list of settings on the next page.
This opens up your location targeting options and your account location should be selected by default.
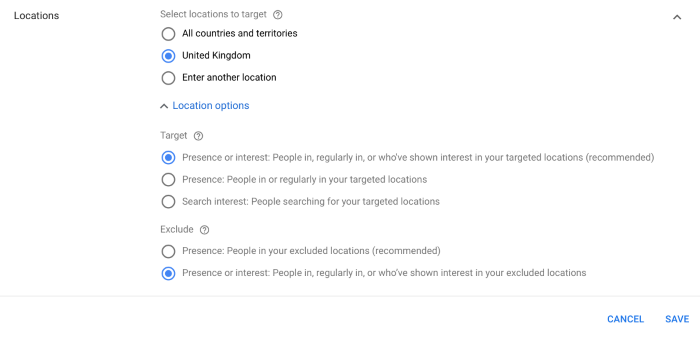
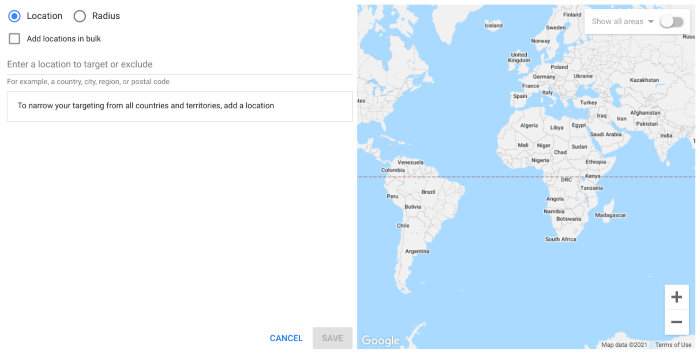
In the first section, you can select which locations you want to target for this campaign. You can select All countries and territories (not recommended), stick with the default account location, which is the United Kingdom in this case, or choose to Enter another location to specify specific countries, cities, regions or postcodes.
You can simply type in the locations you want to target or click on Advanced search to add locations in bulk or use radius targeting.
Here, you can choose to target your specified locations, target the nearby areas or exclude locations to prevent people in specific areas from seeing your ads.
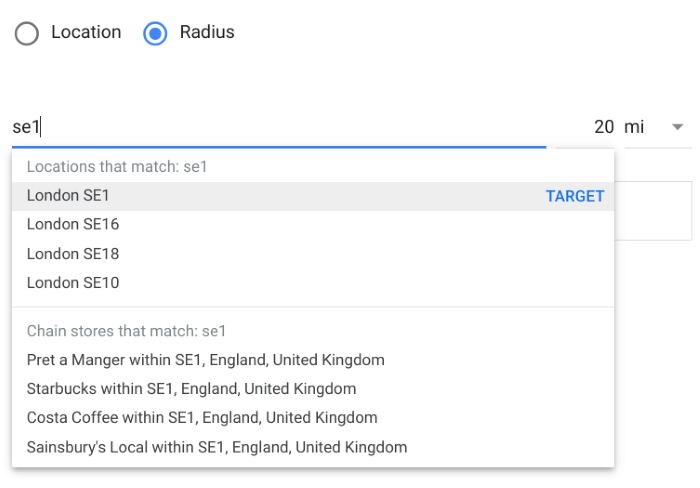
With radius targeting, you can limit geotargeting to specific areas so that, for example, people within walking or driving distance only see your ads. This can be invaluable for local campaigns and ad formats, such as local inventory ads.
With your locations set, you can also choose how Google applies these targeting options by selecting from the following three options in the Target section:
- Presence or interest: People currently in, regularly in or showing interest in your targeted locations (recommended).
- Presence: People in or regularly in your targeted locations.
- Search interest: People searching for your targeted locations.
While Google recommends the first setting, it’s important to understand that people showing an interest in your location (eg: tourists) may see your ad, even though they don’t live in your area and this isn’t ideal for a lot of business types.
Unless you specifically want to target people in your area and people showing interest in visitors at a later date, you might be better off with choosing one of the other targeting methods. Also, keep in mind that you can create separate campaigns for Presence and Search interest with relevant messages for both audience types.
Finally, you can also set your exclusion settings with two options to choose from:
- Presence: People in your excluded locations (recommended).
- Presence or interest: People in, regularly in, or who’ve shown interest in your excluded locations.
Once, you’ve set your targeting options, click Save and these will be applied across all ad groups in your campaign.
Geotargeting on Facebook
Geotargeting in Google Ads gives you plenty of control but Facebook’s location targeting options takes things to an entirely different level. Facebook Advertising offers advanced location targeting options that are also available for Instagram and, thanks to a wealth of mobile data, Facebook is able to determine the difference between where people live and the places they visit.
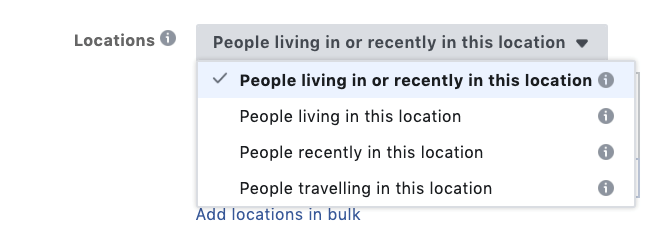
This allows you to target users based on the following location options:
- People living or recently in this location (default)
- People living in this location
- People recently in this location
- People travelling in this location
So you can target people who live in specific locations, knowing that people who recently visited or regularly visit won’t see your ads. Likewise, you can target people who recently visited specific locations and even target people who are currently travelling in your target locations.
This makes Facebook’s location targeting options invaluable for businesses that want to target tourists currently in their locations.
Best of all, you can combine Facebook geotargeting with a plethora of other targeting options, such as interests and behaviours to target people with a proven interest in your business in every location of your choice.
To find out more about Facebook targeting, take a look at our extensive guide.
Geotargeting best practices
Getting started with geotargeting is relatively straightforward but there are plenty of steps you can take to maximise the impact of location targeting.
1. Start small & scale
Geotargeting allows you to get pretty granular with location targeting but you don’t want to get too carried away and narrow your audiences to the point where you’re not getting enough impressions, clicks or traffic.
Start with the basics by specifying the locations where your business operates and ruling out any locations that aren’t useful to you. Run with that for a while and measure campaign performance before you test more granular targeting options.
2. Do your audience location research
If you want to get more advanced with your location targeting you’re going to need data to make informed decisions, such as which locations most of your customers are coming from, and the ability to attribute other KPIs, such as purchase value or lifetime customer value to locations.
Eventually, you want enough insights to know where your most profitable locations are, compare location performance against previous years and spot emerging trends where new locations become more important to your business.
3. Adjust your bids for priority locations
Naturally, you want to increase your bids for your most profitable locations where KPIs like ROAS and revenue are highest. You also want to attribute performance differences to something more tangible than location alone – for example, travelling distance from your business location or the average household income for certain areas.
These insights will help you adapt your bids accordingly but also optimise your campaigns to make them more relevant to audiences across different locations.
4. Combine geotargeting with other targeting options
Geotargeting works best when combined with other targeting options to maximise performance, such as ad scheduling to show ads in specific locations at the most effective times for each area. This is especially important if you’re operating in multiple countries where time differences are directly linked with locations.
That said, even within the same country, you may find the most effective time to run ads varies across different times of the day, week, year, etc. and purchase habits can vary wildly depending on regional weather patterns, environmental factors and other local characteristics.