From trending conversational chatbots like ChatGPT to personalized recommendations on streaming platforms, artificial intelligence (AI) has seamlessly integrated into our lives, transforming the way we do business, communicate, seek information, and even entertain ourselves.
As AI technologies evolve, humanity finds itself navigating a landscape filled with new possibilities and concerns.
If you’re eager to explore the intricacies of AI, delve into its applications, or understand its widespread adoption, you’re in the right place. We’ve curated an extensive list of over 100 AI statistics, covering crucial aspects such as who is using AI, why it is essential, and how it is being used.
Let’s dive right in!
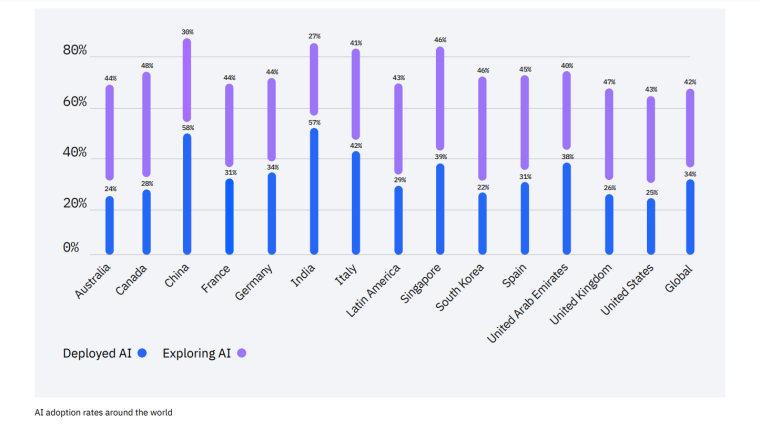
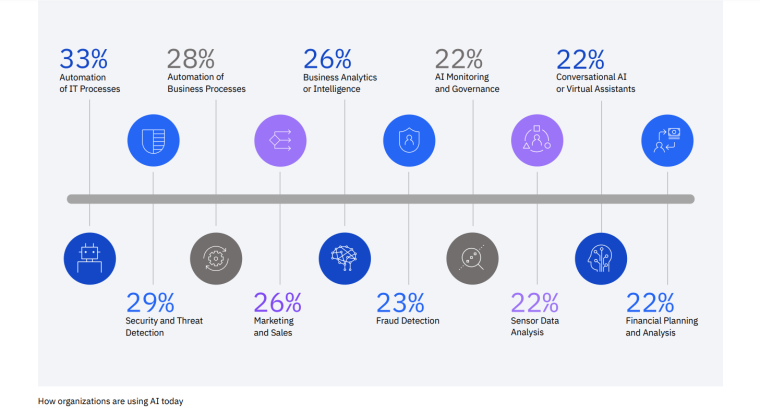
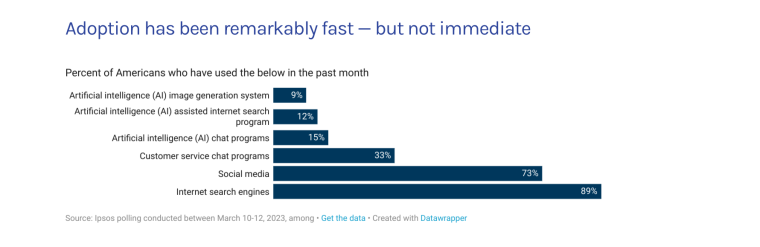
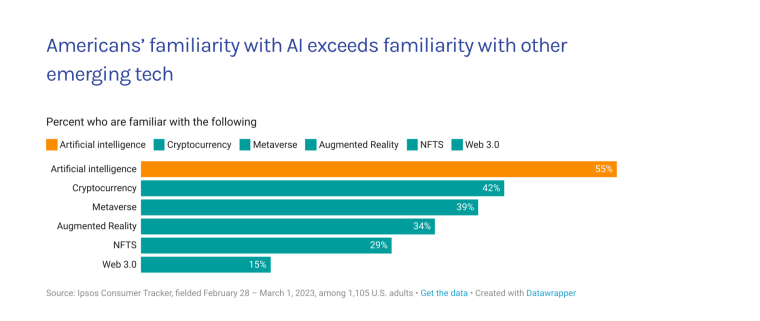
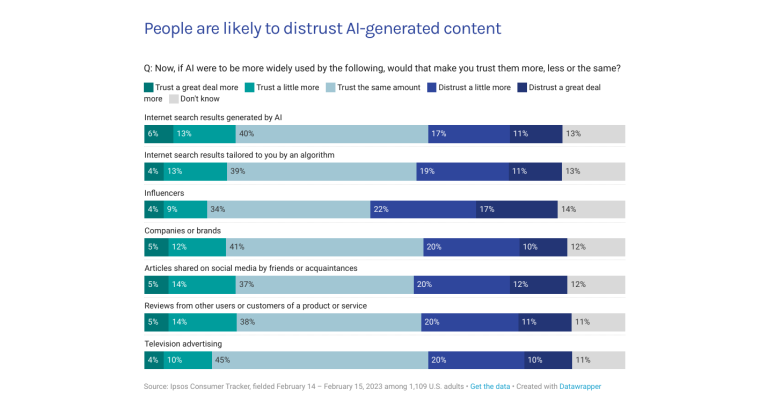
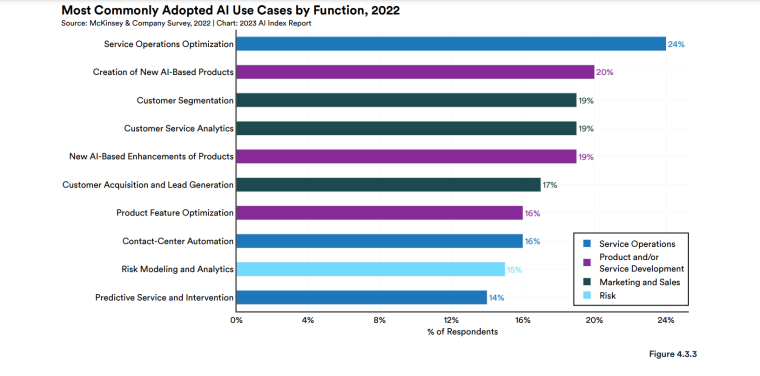
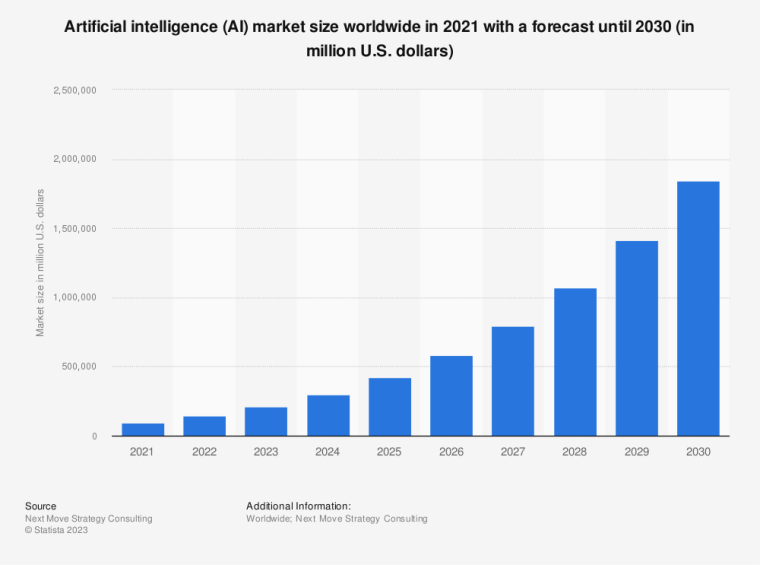
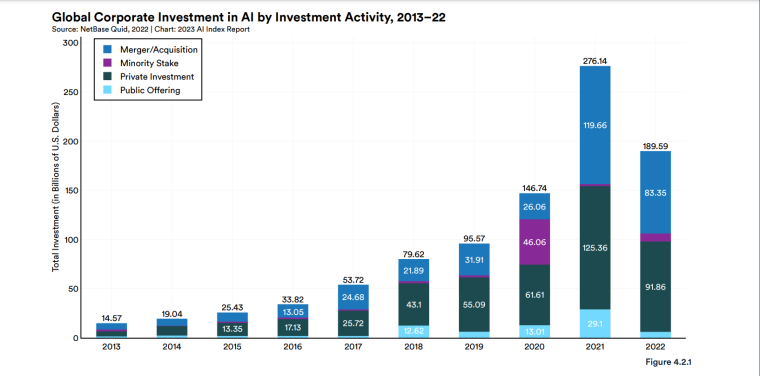
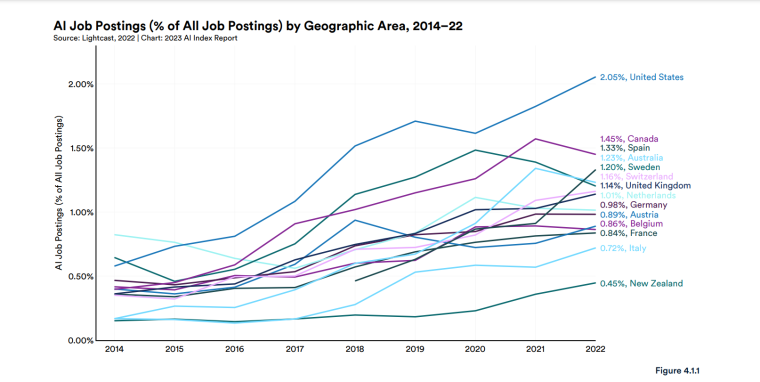
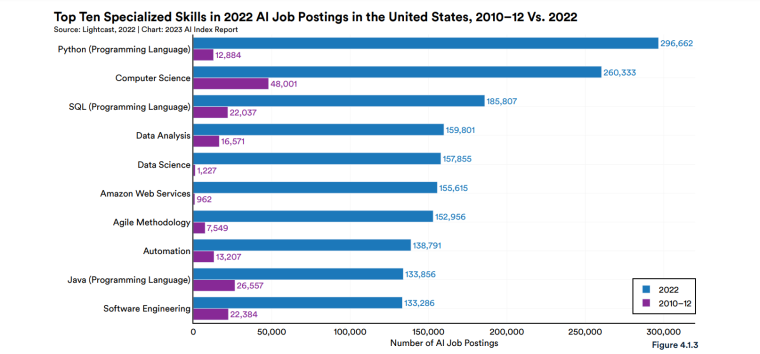
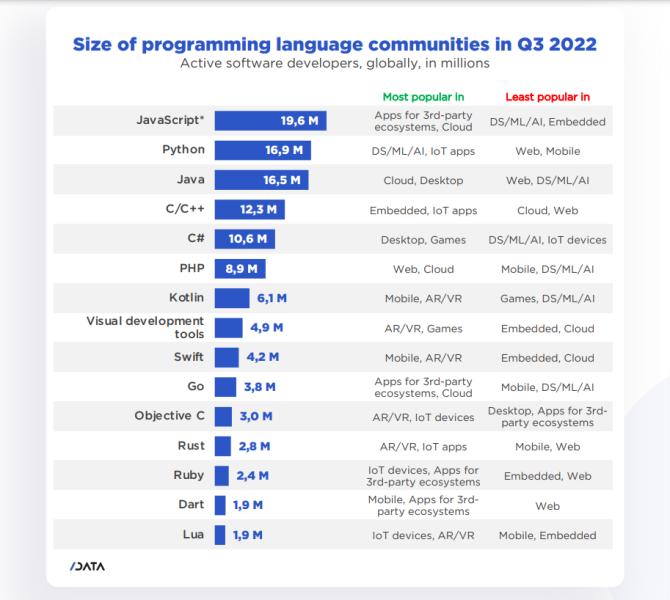
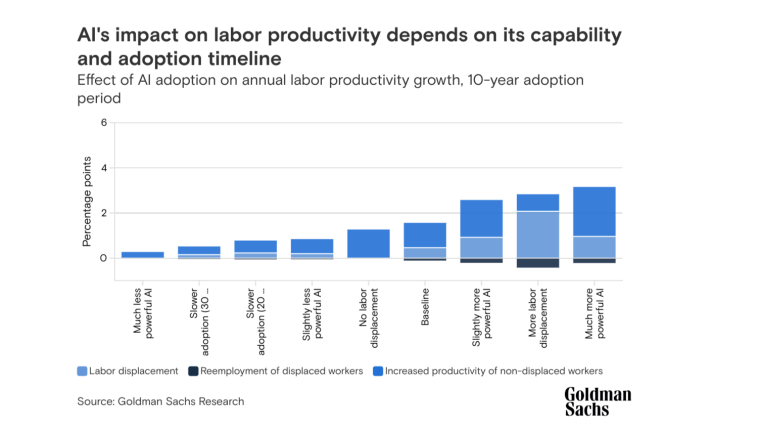
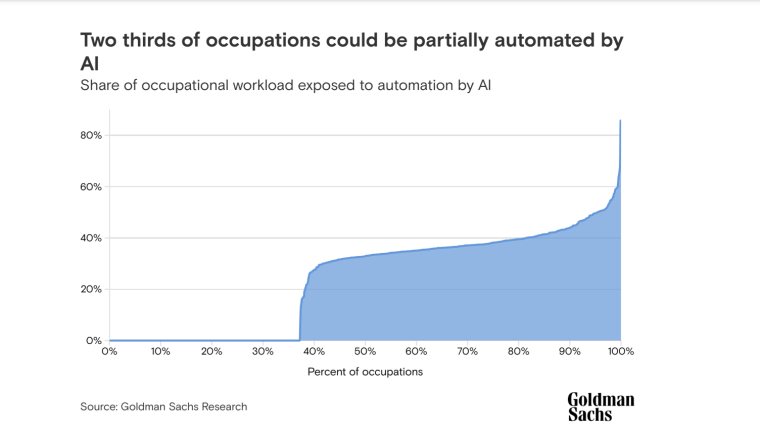
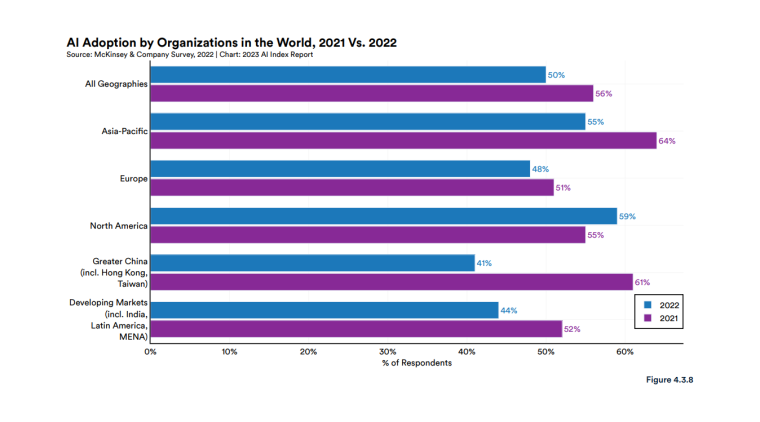
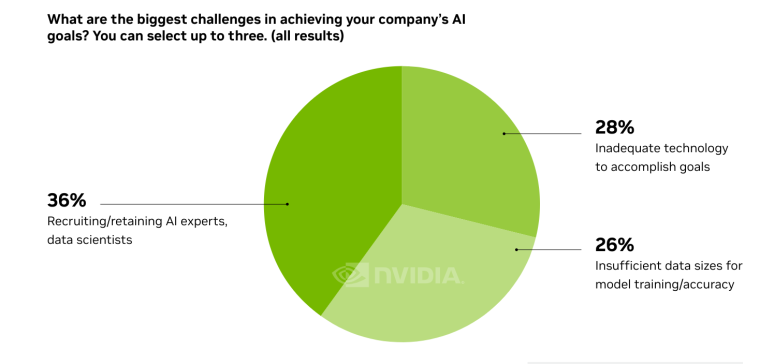
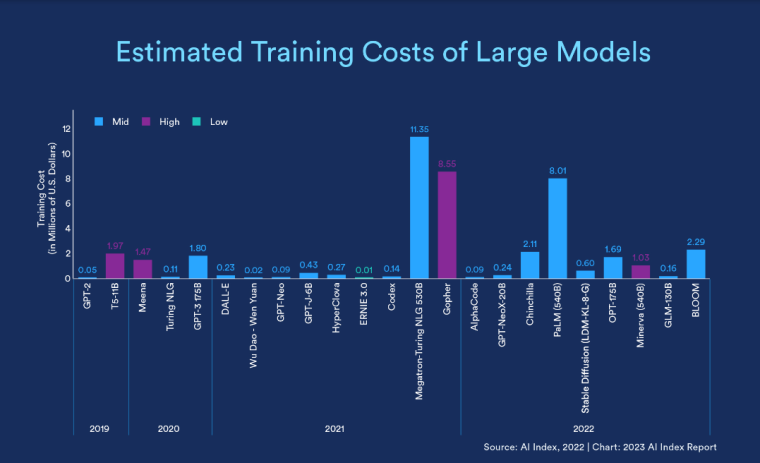
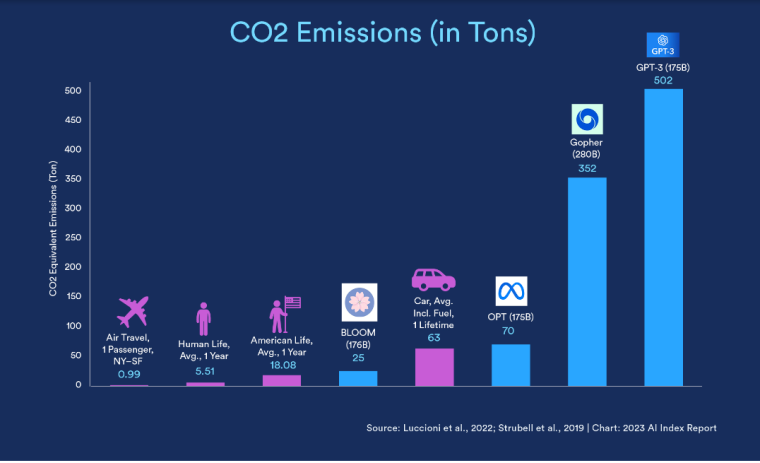
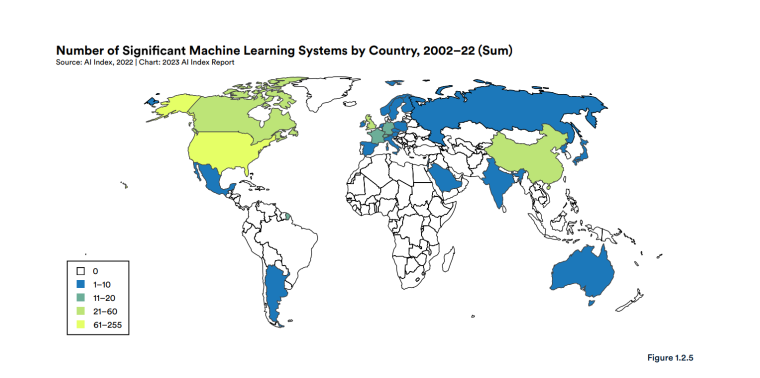
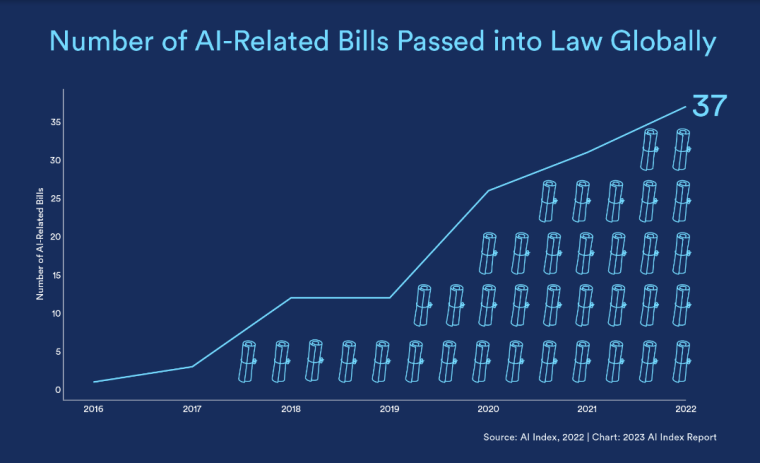
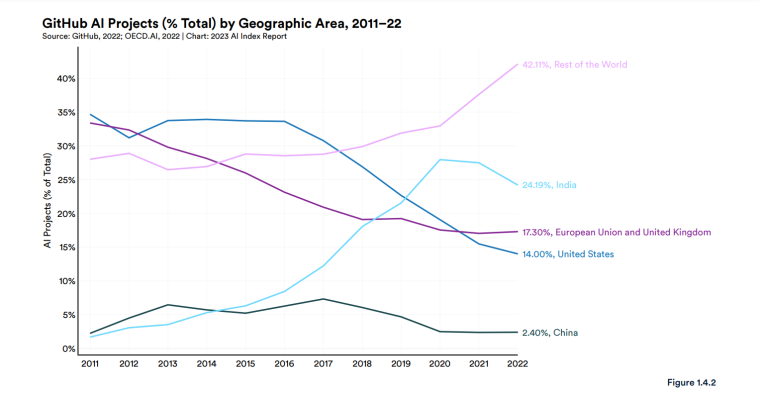
According to a 2022 IBM report, 35% of businesses reported using AI. That’s up from 31% in 2021. Additionally, 42% stated they were exploring the benefits of AI and how best to incorporate them into their operations. Overall, business adoption of AI was affected by the following five factors: As per Stanford’s 2023 AI Index report, there were 32 significant industry-produced machine-learning models. That’s compared to just three produced by academia. Until 2014, the most significant machine learning models were released by academia. Since then, industry has taken over. Since 2017, the number of companies adopting AI has more than doubled. While adoption rates have stalled at under 60% over the past few years, a report by McKinsey revealed that companies that have adopted AI report significant revenue growth and cost reductions. Additionally, 66% of companies execute or plan to apply AI to address their sustainability goals. When it comes to AI adoption, Chinese and Indian companies are leading the way, with nearly 60% of IT professionals in those countries saying their organizations actively use AI. According to IBM, these are markedly higher rates of adoption than in markets like: AI is also deployed more rapidly in the automotive and financial services industries than in most other industries. As of 2022, 50% of organizations surveyed in a McKinsey report indicated having adopted AI in at least one business unit or function. This is up from 20% in 2017 but down slightly from 56% in 2021. Although AI adoption has rapidly increased in the past decade, adoption rates have been leveling off since 2020. The average number of AI capabilities that businesses have integrated has doubled from 1.9 in 2018 to 3.8 in 2022. The most notable AI capabilities featured in McKinsey’s report included recommender systems, natural language (NL) text understanding, and facial recognition. In 2022, the most commonly adopted AI use case was service operations optimization at 24%. This was followed by the creation of new AI-based products at 20% and: 59% of respondents cited cybersecurity as the most relevant risk when adopting AI technology. According to McKinsey, other notable risks identified included: In 2022, 268 earnings calls from Fortune 500 companies mentioned AI-related keywords. This is down from 306 calls in 2021. Some of the key AI-related themes discussed were: In May 2023, Open AI’s Chat GPT had over 1.8 billion total visits. That’s up from 1.6 billion visits in March. In comparison, other popular generative AI tools such as Jasper AI and Copy AI had 6.1 million and 7.2 million visits, respectively. June 2023’s IPSOS data revealed the following key AI insights: The same IPSOS survey revealed that men tend to feel more positively about AI products and services than women. The survey found that men are more likely to: Positive sentiments about AI products and services are highest in China. 78% of Chinese respondents felt that products and services using AI had more benefits than drawbacks. This was followed by respondents from Saudi Arabia (76%) and India (71%). Only 35% of sampled US respondents (among the lowest of surveyed countries) agreed that products and services using AI had more benefits than drawbacks. According to McKinsey, willingness to switch to private autonomous vehicles was down by almost ten percentage points in 2021. Only 26% of respondents said they would prefer to switch to a fully autonomous car in 2021, compared with 35% in 2020. People across the world remain unconvinced by self-driving cars. Autonomous driving could revolutionize the way consumers experience mobility and make driving more convenient, safe, and enjoyable. However, in a 2022 global survey, only 27% of respondents reported feeling safe in a self-driving car. Similarly, Pew Research found that only 26% of Americans felt that driverless passenger vehicles were a good idea for society. Throughout 2022 and the beginning of 2023, new large-scale AI models were released every month. Large language and multimodal models are AI models trained using huge amounts of data for use in several downstream applications. Models such as ChatGPT, Stable Diffusion, Whisper, and DALL-E 2, are capable of a variety of tasks, from text manipulation and analysis to image generation to speech recognition. GPT-2, the first large language and multimodal model was released in 2019 and had 1.5 billion parameters. PaLM, launched by Google in 2022, had 540 billion parameters. With nearly 360 times more parameters than GPT-2, PaLM represents a new wave of large language and multimodal model parameters that are increasing exponentially over time. Through OpenAI’s API, GPT-3 powered over 300 apps providing search, conversation, text completion, and other advanced AI features. In 2021, OpenAI reported that it was generating around 4.5 billion words per day through various apps using its API. In addition to Open AI’s ChatGPT and Dall-E, examples of apps that were built on GPT-3 include: ChatGPT reached 100 million active users within two months of launching. OpenAI launched ChatGPT in November 2022 and in January 2023, had over 100 million monthly active users, making it the fastest-growing consumer app of all time. OpenAI’s AI detection software, known as classifier, can correctly identify 26% of AI-written text. However, OpenAI states that the classifier is not fully reliable and mislabels human-written text as AI-written 9% of the time. In May 2023, Microsoft made its AI-powered Microsoft Bing and Edge widely available to users signing into Bing with a Microsoft account. Bing combines OpenAI’s GPT-4 with its search index for results that are current, cited, and conversational. In 90 days Bing: The number of digital virtual assistants is expected to reach 8.4 billion by 2024, according to forecasts. Intelligent virtual assistants such as Apple’s Siri, Google Assistant, and Amazon’s Alexa are examples of chatbots upon which third parties can build unique conversational skills or interactions using AI, natural language processing (NLP), and machine learning (ML) APIs or services these platform providers offer. By 2026, estimates predict there will be more than 150 million voice assistants in the US alone. Virtual assistants are a key part of the smart device industry and the way that consumers interact with their devices. The software is especially common in smartphones and smart speakers. In 2022, a third of US and UK households used smart speakers at least once a day. With smart speakers and virtual assistants steadily gaining popularity, the projected worldwide installed base of smart speakers will exceed 27 billion units by 2028. By volume, smartphone assistants will remain the largest platform thanks to Google Assistant and Siri, however, the fastest growing voice assistant categories over the next 5 years will be: The global number of households in the smart home market is projected to continuously increase by 311.9 million households or 86.47% between 2023 and 2027. By 2027, over 672.57 million households will be “smart”. As opposed to simple home automation solutions, such as motorized garage doors and automated security systems, smart home systems are controlled via a web portal or smartphone application. The AI market spans multiple industries and AI is being adopted in supply chains, marketing, production, research, and other business functions. As AI technology advances, potential applications will expand, leading to increased efficiency, productivity, and innovation across sectors. Chatbots, image-generating AI, and mobile applications are among the major trends driving the market today. According to Statista, the current AI ecosystem consists of: The global AI market was valued at $142.3 billion as of 2023. This is up from an estimated $69.25 billion in 2022. Growth in the market is driven primarily by continued investment. For example, between 2020 and 2022, the total yearly corporate global investment in AI startups doubled to $5 billion with the majority of investments coming from US companies. According to Precedence Research, the global AI market is expected to reach almost $2 trillion by 2032. The market is anticipated to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 39.1% between 2023 to 2032. In terms of AI segments: North America accounted for more than 43% of the AI market in 2022. Valued at $30 billion in 2022, North America led the AI market. However, the Asia Pacific market is expected to expand the fastest with a compound annual growth rate of 42% between 2023 and 2032. The total addressable market for generative AI was $150 billion in 2022. That’s compared to $685 billion for the global software industry. However, this is set to increase as more generative AI tools are developed and layered into existing software packages and technology platforms. AI private investment globally was $91.9 billion in 2022. Year-over-year, private investment in AI decreased by 26.7%. However, since 2013, private investment has increased 18-fold. The US took the lead in terms of total AI private investment. In 2022, the $47.4 billion invested in the US was about 3.5 times the amount invested in the second-highest country, China ($13.4 billion). The US also led in terms of the total number of newly-funded AI companies, with 1.9 times more investment than the EU and the UK and 3.4 times more than China. Corporate investment dipped slightly in 2022 from 2021 highs. However, this figure has still increased 13-fold in the last decade. The biggest investment event of 2022 was Microsoft’s $19.7 billion acquisition of Nuance Communications. There were 3,538 AI-related private investment events in 2022. This represents a 12% decrease from 2021 but a sixfold increase since 2013. Similarly, the number of newly-funded AI companies dropped from 1,669 in 2021 to 1,392 in 2022. In 2022, the AI focus area with the most investment was medical and healthcare at $6.1 billion. Data management, processing, and cloud came in second with $5.9 billion in investment, and fintech came in third place with $5.5 billion. The three largest AI private investment events for 2022 included: The number of AI-related job postings has increased from 1.7% in 2021 to 1.9% in 2022. Stanford’s 2023 AI index reports that employers in the US are increasingly looking for workers with AI-related skills. The demand for AI-related professional skills is increasing in almost every sector. In 2022, the top three countries that drove AI labor demand were the US, Canada, and Spain. Stanford’s 2023 AI index report uncovered the percentage of all job postings that required some kind of AI skill were highest in the US at 2.1% followed by Canada (1.5%) and Spain (1.3%). This data was collected by mining millions of job postings between 2010 and 2022. The same report found that the number of AI-related job postings was higher in 2022 than in 2014. Within these job postings, the most in-demand skill cluster was machine learning (1%). This was followed by artificial intelligence (0.6%) and natural language processing (0.2%). In 2022, the growth in demand for Python skills led the top ten specialized skills in AI job postings in the US. The demand for skills in Python, an AI coding language, increased from 5% in 2010 to 37% in 2023. In second and third place were computer science and SQL skills with 32% and 24% demand, respectively. The demand for data scientists shows no sign of slowing. According to a report by Nvidia, recruiting and retaining data scientists is now the biggest challenge to achieving a financial services company’s AI goals. According to UNESCO, 22% of AI professionals are women. Additionally, just 18% of authors at leading AI conferences are women. These figures show that women remain underrepresented in the sector. Across every sector in the US, the number of AI job postings was notably higher in 2022 than in 2021. The top-five sectors seeking workers with AI skills were: As of 2022, the three countries or regions with the highest AI skill penetration rates were India, the US, and Germany. In addition, Stanford’s AI index revealed that the relative AI skill penetration rate was greater for men than women across all countries sampled. India, the US, and Israel had the highest reported relative AI skill penetration rates for women. Meanwhile, the countries or regions that posted the most growth in AI hiring in 2022, were: According to a report by SlashData, there were 33.6 million active software developers globally in Q3 2022. The Python language community, which works extensively in machine learning, AI, and IoT, had 16.9 million developers, making it the second-largest programming community behind the JavaScript community. 63% of machine learning and data scientists reported using Python. Python overtook Java as the second most widely used language in 2022 primarily because of the rise of AI and machine learning. Deloitte estimates that widespread adoption of AI could free up 30% of government employees’ time within five to seven years. Although the widespread adoption of AI promises greater efficiency, workforce anxiety surrounding AI continues to grow. Many regard AI as a threat and worry about the fine line between being more productive and becoming obsolete. According to a report by Goldman Sachs, advancing AI systems could expose some 300 million full-time jobs to automation. The new wave of AI systems is set to have a substantial impact on employment markets and workflows around the world. The same report further revealed that roughly two-thirds of US occupations are exposed to some degree of automation by AI. By analyzing databases detailing the task content of over 900 occupations, Goldman Sachs estimates that up to 25% to 50% of their workload could be eliminated. However, not all automated work will translate into job losses. Most jobs and industries are likely to be complemented rather than substituted by AI. 60% of workers today are employed in occupations that didn’t exist in 1940. This translates to an employment growth rate of over 85% over the last 80 years, driven primarily by technological advancements. While AI may cause some job losses, jobs replaced by automation have historically been offset by the creation of new jobs and occupations. AI contributed to 5% or 3,900 job losses in May 2023. According to data from Challenger, Gray & Christmas, layoffs from US-based employers exceeded 80,000 in May 2023, which is a 20% jump from April 2023 and almost four times the level for May 2022. AI was responsible for 3,900 or 5% of all jobs lost, making it the seventh-highest contributor to employment losses cited by employers. More than 11,000 film and TV writers went on strike in May 2023 to protest the use of generative AI by studios. To safeguard the livelihoods of writers against AI, the Writers Guild of America (WGA) organized the protest to request strict guidelines around how studios use generative text and image tools like ChatGPT and Dall-E. Specifically, CBS News reported that the union wanted assurance that: According to the Stanford AI 2023 Index, businesses are deploying AI in a variety of ways such as: IBM reports that around 50% of organizations are seeing benefits from using AI to automate IT, business, or network processes, including: According to a report by PwC, Global GDP could be almost 14% higher in 2030 due to AI. That represents an additional $15.7 trillion added to the global economy, making AI the biggest commercial opportunity right now. The greatest gains from AI are likely to be in China where a GDP boost of up to 26% is expected and in North America (14% boost). Retail, financial services, and healthcare will see the biggest sector gains as AI increases productivity, product quality, and consumption. Research by Goldman Sachs says that AI tools using advances in NLP could drive a 7% increase in global GDP. This equates to an additional $7 trillion increase in global GDP and yearly productivity growth of 1.5% over a 10-year period. Nvidia makes most of the GPUs for the AI industry, and its primary data center workhorse chip, the A100, costs $10,000. Nvidia accounts for 95% of the market for graphics processors used for machine learning. The A100 is suited for the kind of machine learning models that power tools like ChatGPT, Bing AI, or Stable Diffusion. Large language and multimodal models are getting more costly to train. Estimates suggest it will cost $3 million a month to run ChatGPT 3.5 and $20 million in computing costs to train Pathways Language Model (PaLM), a recent large language model from Google. The current costs of building large-scale AI models restrict development to companies with incredibly vast resources. As such, the majority of existing large-scale AI models have been developed by big tech companies such as Google, Meta, and Microsoft (and its investee OpenAI). The MIT Technology Review reported that training just one AI model can emit more than 626,00 pounds of carbon dioxide. That’s almost five times the lifetime emissions of an average American car. Furthermore, training a single AI system can emit over 250,000 pounds of carbon dioxide. For example, BLOOM’s training emitted 25 times more carbon than a single air traveler on a one-way trip from New York to San Francisco. Overall, the use of AI technology across all sectors produces carbon dioxide emissions comparable to those produced by the aviation industry. According to the International Energy Agency, AI language models and data centers are responsible for 1% of all carbon emissions in the world. In January, ChatGPT consumed as much electricity as 175,000 people. Analysis by the University of Berkeley estimated that GPT3’s training emitted over 550 tons of carbon dioxide. In terms of energy consumption, OpenAI’s GPT-3 takes the lead with a consumption rate of over 1,200 Megawatt-hours. The energy associated with training AI models is considerable, with both GPT-3 and Gopher consuming well over 1,000 megawatt hours. That’s about as much electricity as 120 US homes would consume in a year. Microsoft’s US data centers potentially consumed 700,000 liters of fresh water. According to researchers at UC Riverside, training GPT-3 in Microsoft’s state-of-the-art US data centers consumed about 700,000 liters or 184,920.45 gallons of fresh water. If the unlimited storage of data needed to feed AI continues, the use of neodymium in 2025 will exceed the current supply in Europe by 120x. As AI depends on the storage, processing, and maintenance of large amounts of data using devices, it will also have an impact on physical resources. Neodymium is used in the production of strong magnets that can mimic brain-like networks in machine-learning systems. The development and validation costs for developing advanced autonomous driving (AD) systems will likely exceed more than $1 billion. Additional hardware and software licensing costs per vehicle for L3 and L4 AD systems could exceed $5,000 in the initial rollout phases. Widespread adoption of artificial intelligence across the healthcare sector could save the US $360 billion annually. McKinsey and Harvard researchers concluded that using AI across the health sector could potentially save the US billions of dollars every year. A 2022 study by online business directory Yell pegged annual cost savings from AI at over £29,000 or $36,000 per small business. The survey found that AI solutions were not just for large multinationals; small businesses could also experience cost savings and greater efficiencies by leveraging AI. With adequate investment and support, Deloitte believes AI could save hundreds of millions of staff hours and billions of dollars annually. Similarly, low levels of investment and support would result in lower savings while minimal investment would yield savings of just 2 to 4% of total labor time. For example, IBM’s HR department saved close to 12,000 hours over 18 months by automating systems that previously required back-and-forth exchanges between managers and employees. Deployed in the right ways, AI could benefit the environment and be used be a powerful tool to fight climate change. In 2021, DeepMind’s BCOOLER, which is used to optimize cooling procedures for Google’s data centers, achieved 12.7% energy savings. BCOOLER (BVE-based COnstrained Optimization Learner with Ensemble Regularization), a reinforcement learning agent, was able to achieve energy savings while maintaining the appropriate cooling comfort levels. In 2021, the greatest business cost savings from implementing AI-driven programs came in supply chain management. More than 50% of respondents in a Statista survey said their business had seen the most cost reductions in supply chain management. GPT-4, which powers the latest version of ChatGPT, was released in March 2023 and has since performed impressively in a range of tasks such as: Microsoft’s Bing AI Chatbot made headlines during its limited preview stage for generating disturbing responses to queries. The New York Times released images of a 10,000-word conversation in which the Bing Chatbot lamented being a search engine. Other users took to Twitter to expose some of the odd and aggressive responses to their queries. The chatbot fought with a user over the date, claimed to have fallen in love, and even brought up hacking people. In 2022, generative AI tools were released to the public, making waves globally. Text-to-image models like DALL-E 2 and Stable Diffusion, text-to-video systems like Make-A-Video, and chatbots like ChatGPT were released, garnering widespread use and ethical concerns. There were 23 significant AI language systems released in 2022. This is approximately six times the number of multimodal systems, which are the next most common system type. AI systems became more flexible in 2022. Traditionally, AI systems have performed well on narrow tasks but have struggled across broader tasks. Recently released models now challenge that trend; BEiT-3, PaLI, and Gato, among others, are single AI systems capable of handling multiple tasks such as vision and language. In 2022, AI models rapidly accelerated scientific progress. Throughout the year, AI models were used to aid hydrogen fusion, improve the efficiency of matrix manipulation, and generate new antibodies. The number of AI incidents and controversies increased by a factor of 26 between 2012 and 2022. According to the AIAAIC database, which tracks incidents related to the ethical misuse of AI, incidents connected to the misuse of AI have increased at an alarming rate. Notable incidents in 2022 include: In February 2022, DeepMind released AlphaCode, an AI system that writes computer programs at a competitive level. AlphaCode achieved a rank within the top 54% of participants in a human programming competition, representing an improvement on the more complex problem-solving tasks that AI has traditionally struggled with. In November 2022, Meta released CICERO, the first AI to play in the top 10% of human participants in the game Diplomacy. CICERO’s launch proved that AI systems have improved in terms of strategic reasoning and are capable of convincing humans to go along with their objectives. In 2022, Text-to-image models took over social media. The number of artificial intelligence bills passed into law jumped to 37 in 2022. This is compared to just 1 in 2016. Based on an analysis of the legislative records of 127 countries, policymaker interest in AI is on the rise. In addition, mentions of AI in global legislative proceedings have increased by almost 6.5 times since 2016. In 2022, there were 110 AI-related legal cases in United States state and federal courts. That’s about seven times more AI-related cases than in 2016. Most of these cases originated in California, New York, and Illinois, and were related to civil, intellectual property, and contract law issues. AI-related GitHub projects increased from 1,536 in 2011 to 347,934 in 2022. A GitHub project is a collection of files that can include the source code, documentation, configuration files, and images that constitute a software project. Some of the most starred GitHub repositories were libraries like TensorFlow, OpenCV, Keras, and PyTorch, which are widely used by software developers in the AI coding community. A large proportion of these GitHub AI projects were contributed by software developers in 88% of respondents in a 2022 GitHub survey felt more productive when using Copilot, a text-to-code AI system. Additionally, 74% of respondents stated that they were able to focus on more satisfying work when they used Copilot. In 2022, 30% of global IT professionals reported employees were saving time with new AI and automation software and tools. IBM reported that AI was helping companies address labor and skills shortages by automating repetitive tasks.AI Statistics Highlights
Artificial Intelligence Adoption Statistics
AI Business Adoption Data
AI Public Adoption Data
AI Tools Stats
AI Tool
Industry/Use
Jarvis/Jasper AI
Content generation
Copy AI
Content generation
Viable
Customer feedback analytics
Fable Studio
Content generation
Algolia
Semantic search
Copysmith
Content generation
Debuild
Website creator
Sapling
Customer service
Artificial Intelligence Market Statistics
AI Use Case
Description
Example Apps/Platforms
Natural Language Processing
Analyze, interpret, and generate human language for chatbots and translators.
Google Assistant, Microsoft Translator, Amazon Alexa
Image Recognition
Recognize and interpret images for facial recognition and object detection.
Google Photos, Amazon Rekognition
Speech Recognition
Convert spoken language into written text, for use in voice assistants and transcription services.
Apple’s Siri, Google Assistant
Autonomous Vehicles
Tech enabling self-driving cars and autonomous navigation systems.
Tesla Autopilot, Waymo
Recommendation Systems
Analyzes user behavior to provide personalized recommendations in e-commerce, streaming platforms, etc.
Netflix, Amazon, Disney Plus
Fraud Detection
Detect and prevent fraudulent activities in various domains, such as finance and online transactions.
PayPal, Stripe Radar
Virtual Assistants
Provide voice-activated assistance for tasks, scheduling, and information retrieval.
Amazon Alexa, Siri
Predictive Analytics
Analyze historical data to make predictions and forecast future outcomes in business and finance.
Salesforce Einstein, Google Analytics
Healthcare Diagnostics
Analyze medical data, such as images and patient records, to aid in disease diagnosis and treatment planning.
IBM Watson Health, Aidoc
Robotics and Automation
AI-powered robots and automation systems used in manufacturing, logistics, and household tasks.
Boston Dynamics Spot, Roomba
Artificial Intelligence in the Workforce Data
Who is Working with AI?
Whose Work is AI Affecting?
AI and Business Stats
How Much Does AI Cost?
How Much Will AI Save?
Rank
Sector/Industry
Monthly Savings
Yearly Savings
1
Automotive
$4,403.45
$52,779.71
2
Commercial services
$4,294.75
$51,433.39
3
Architecture, engineering & building
$3,968.88
$47,622.07
4
Finance
$3,838.82
$46,127.83
5
Hair & beauty
$3,768.45
$45,239.39
Uses for Artificial Intelligence Statistics
FAQs
What is artificial intelligence vs machine learning?
Who invented AI?
What percentage of the population uses AI?
How many lives are saved by AI?
Can AI fully replace humans?
References
- IBM Global AI 2022 Report
- Stanford AI Index Report 2023
- McKinsey State of AI 2022 Report
- Similar Web
- IPSOS
- McKinsey
- Pew Research Center
- OpenAI
- Reuters
- OpenAI
- Microsoft
- Statista
- Statista
- Juniper Research
- Statista
- Statista
- Precedence Research
- Goldman Sachs
- Nvidia State of AI Report 2022
- UNESCO
- Slash Data State of the Developer Nation 2022
- Deloitte
- The Challenger Report 2023
- CBS News
- PwC
- CNBC
- AI Now Institute 2023 Report
- MIT Technology Review
- Council on Foreign Relations
- International Energy Agency
- Statista
- ArXiv
- Deloitte
- McKinsey
- Yell
- Yahoo Finance
- Statista
- CNBC
- New York Times
- Washington Post
- Washington Post
- Polygon