We are stepping into a world where innovation meets efficiency, and the synergy of human ingenuity and cutting-edge artificial intelligence (AI) technology drives the future of manufacturing.
The numbers don’t lie: recent AI in manufacturing statistics project remarkable transformations. But AI in manufacturing isn’t just a trend; it’s a strategic necessity that can reshape businesses and invigorate economies.
AI in Manufacturing Statistics Highlights
- The global AI in the manufacturing market reached $6.7 billion and is expected to grow at a CAGR of 45.6%, projecting it to reach $20.8 billion by 2028.
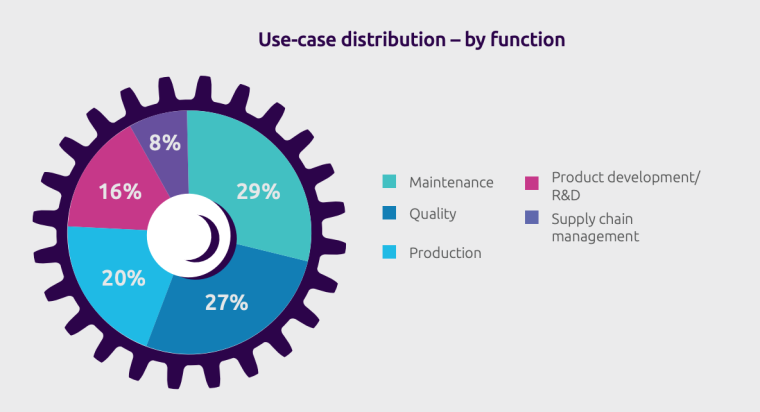
- Maintenance is the primary application of AI in the manufacturing sector.
- As of 2024, 63% of manufacturing companies are using AI for quality control, with expanded applications in predictive maintenance and real-time process optimization.
- AI in manufacturing will increase labor productivity by 38% by 2035.
- By 2040, 47% of current job tasks could be automated using AI, including advanced robotics and AI-driven automation systems.
AI in Manufacturing: What You Should Keep in Mind
- Enhanced Productivity and Efficiency: AI drives significant improvements in manufacturing productivity and operational efficiency through automation, predictive maintenance, and quality control systems.
- Innovation and Competitiveness: The use of AI in manufacturing not only spurs innovation in product development and production processes but also helps companies maintain a competitive edge in a rapidly evolving industry.
- Investment in AI Capabilities: The increasing investment in AI technologies reflects a broader industry trend towards high-tech, efficient production systems. This shift is crucial for companies looking to reduce costs, improve product quality, and accelerate time-to-market in their manufacturing processes.
Types of AI in Manufacturing
Picture factories that operate with intelligence and respond to data that predict future patterns, optimizing processes with a precision that surpasses human capability. This fusion of artificial intelligence (AI) and manufacturing isn’t just smarter production; it’s a symphony of possibilities, orchestrating increased productivity, enhanced product quality, and cost efficiency, all contributing to economic growth.
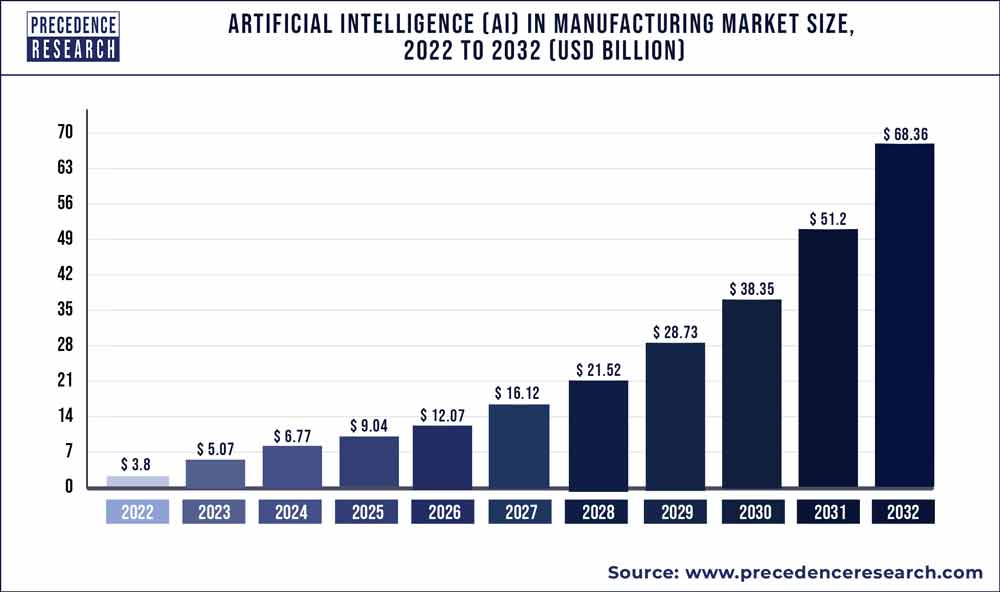
In 2022, AI in the manufacturing market reached $6.7 billion worldwide.
It is projected to grow at a CAGR of 33.5% from 2023 to 2032, reaching approximately $68.36 billion by 2032.
Manufacturers are already employing different AI technology and techniques like machine learning (ML) to enhance manufacturing processes, providing advanced analysis and control capabilities.
Various aspects of artificial intelligence are reshaping the manufacturing industry and driving significant changes. They collectively contribute to increased productivity, cost savings, improved product quality, and sustainability in the manufacturing industry.
Intelligent Maintenance
Maintenance experts report that the main reasons behind unscheduled equipment downtime include the following:
- Aging machinery (34%)
- Mechanical malfunctions (20%)
- Operator mistakes (11%)
- Insufficient maintenance time (9%)
- Poor equipment design (8%)
Maintenance stands out as a primary application of AI in machinery.
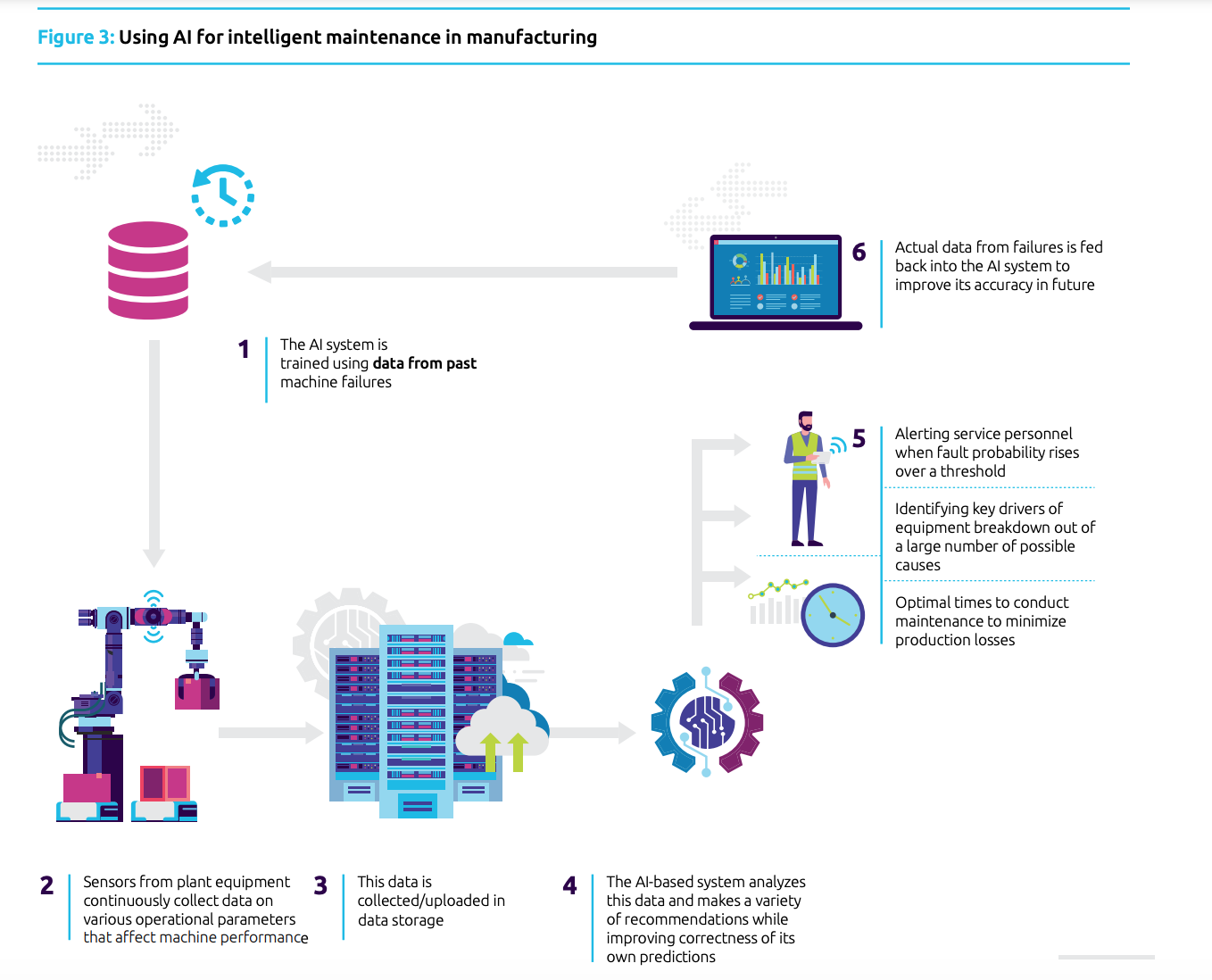
AI-powered intelligent maintenance reduces downtime but also lowers maintenance expenses and enhances productivity. Implementing intelligent maintenance is relatively straightforward, provided there is access to high-quality data and the expertise to analyze it within a business context.
Examining underlying causes and pinpointing factors responsible for machine downtime can avert future breakdowns proactively. Furthermore, analyzing reasons for machine downtime to prevent future breakdowns is a major use of AI in manufacturing.
The cost of just one minute of downtime for companies like General Motors can reach up to $20,000. General Motors spotted 72 component failures in 7,000 robots in a test, preventing costly production line stoppages. The automotive company used image analysis from cameras on assembly robots to catch signs of failing robotic parts, helping avoid unplanned outages.
Connecting the effects of events and problems to machine performance and breakdowns is a key AI role in manufacturing.
For instance, Volvo employs a vast dataset in its Early Warning System. The system examines over a million weekly events during machine operations, like temperature changes or unusual pressure readings. This helps Volvo understand how these events affect breakdowns and failures, all aimed at minimizing production losses and maximizing overall equipment effectiveness (OEE).
AI systems can eliminate defects and unused equipment in manufacturing, continuously improving efficiency through learning and adaptation. By implementing rapid prototyping and smart resource allocation, substantial reductions in time-to-market and costs can be achieved, resulting in a remarkable 39% increase in profit shares for the sector.
For example, AI tools like Elementum can offer advanced alerts about potential issues and suggest alternative remedies.
With the ability to analyze over 10 million incidents daily and track products worth $25 trillion in real time, Elementum is a popular choice for renowned corporations to optimize their supply chains. Some notable customers include Siemens, Starbucks, Dyson, and Vitamix. This platform monitors isolated incidents, traces transportation, and logs manufacturing outputs, granting live visibility into supply chains.
AI for Improving OEE in Manufacturing
Using AI in overall equipment effectiveness (OEE) can help monitor shortages or quality issues, triggering automatic failure alerts in production control.
OEE signifies the efficiency of equipment utilization. It has emerged as the primary KPI across numerous manufacturing sectors, owing to its incorporation of three pivotal indicators:
- Availability: percentage of time that equipment can operate.
- Quality: percentage of goods produced.
- Performance: percentage of maximum operation speed used.
By using advanced AI technologies, manufacturers can gain valuable OEE insights that improve decision-making and address various needs in manufacturing.
Quality Control with AI
AI transforms manufacturing quality control by swiftly analyzing data, spotting defects, and maintaining product consistency. It monitors in real time, detects deviations, and improves product quality while cutting costs.
An MIT report revealed that 63% of companies in the manufacturing industry utilize AI for quality control.
The following prominent applications of AI in manufacturing trailed closely behind:
- Inventory management: 44%
- Monitoring and diagnostics: 32%
- Customer care: 29%
- Personalization of products and services: 22%
- Asset maintenance: 22%
Additional research conducted by Capgemini indicates that 27% of manufacturers prioritize quality control in implementing AI after maintenance.
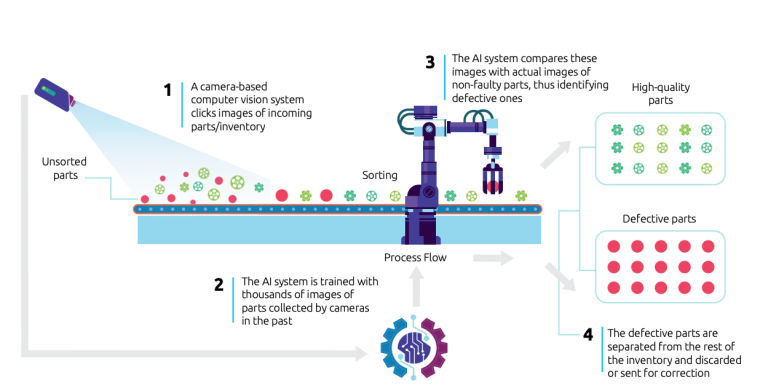
In manufacturing, computer vision uses AI to process visual data from cameras and sensors, enhancing quality control.
Using AI-powered computer vision transforms quality control in manufacturing by introducing efficiency, accuracy, and real-time monitoring. Its ability to identify defects and anomalies early in production enhances product quality, reduces costs, and supports overall operational excellence.
Utilizing AI in the Production Process
AI in manufacturing revolutionizes the production processes in several ways:
- Process optimization
- Line balancing
- Product development and design
- Process parameter optimization
- Production planning and decision support
There are three stages in product life management (PLM):
- Product design
- Product management
- Product service
AI plays a pivotal role in the PLM journey within manufacturing. It optimizes the design phase by analyzing vast data, leading to smarter decisions and innovative concepts. AI monitors processes, predicts maintenance needs, and enhances quality control during production, ensuring a smoother and more efficient product lifecycle from conception to market.
AI in Product Research & Design in Manufacturing
Manufacturers are challenged to efficiently navigate complex information to speed up the time it takes to bring products to market.
According to experts at Nanyang Technological University, this has sparked a growing interest in using AI technology to streamline designing and developing products. This trend has given birth to a fresh design approach known as AI-empowered product design.
The infusion of AI into the product development process (PDP) boosts the design process’s smarts, skillfully handles vast amounts of data, and accomplishes specific goals and tasks by adapting flexibly.
Generative AI can be used to assist in designing and creating prototypes in manufacturing.
While the physical act of prototyping typically involves creating a tangible model or representation of a design concept, generative AI can play a role in various aspects of the prototyping process, from creating initial design ideas to optimizing and refining prototypes.
Here are some ways generative AI design can be applied in creating prototypes in the manufacturing industry:
- Product and innovation
- Lightweighting and material optimization
- 3D printing
Generative AI design enables rapid iteration and prototyping, allowing manufacturers to explore numerous design options quickly. This accelerates the product development cycle and helps identify the most suitable designs early on.
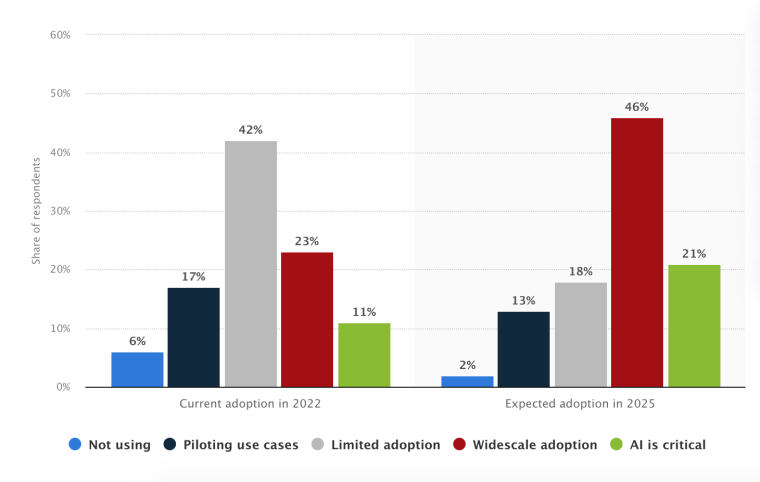
By 2025, ~49% of global manufacturers are expected to fully adopt AI technologies across product development, maintenance, and production optimization. This is a remarkable leap from a mere 23% back in 2022.
AI Tests in Manufacturing
AI speeds up product development and research by shortening test times and extracting valuable insights from customer data and demands.
For example, a Turkish home appliance company, Arçelik, harnessed AI to enhance performance tests.
By utilizing an in-house AI and ML-based decision system, they effectively improved cooling tests under varying climatic conditions, leading to a 15.3% decrease in service call rates.
- Test capacity grew by 17.8%, with test times reduced from 80 to 65 minutes
- Energy savings per unit reached 17.8% in the long performance test (LPT) system
- They achieved a 16.7% reduction in warranty costs per unit
Generative AI in Manufacturing Statistics
According to an interview with an AWS Senior Advisor by Hubspot, generative AI can help convert customer feedback into data.
Generative AI can convert unstructured feedback into organized datasets that offer valuable insights for businesses to comprehend preferences, concerns, and trends by processing and deciphering customer reviews, comments, and messages.
McKinsey research suggests generative AI could boost the global economy by around $3.2 trillion and $4.8 trillion annually across industries, with significant contributions in product development and design in manufacturing.
Additionally, generative AI can increase labor productivity by 0.1% to 0.6% annually until 2040, based on how quickly technology is adopted and shifts worker time to different tasks. When combined with other technologies, work automation could boost productivity growth by 0.2 % to 3.3% annually.
AI-enabled Robotics
The AI industrial robotics market is forecast to experience substantial growth, with a CAGR of 14.2% from 2024 to 2030, driven by higher adoption rates in sectors such as automotive, electronics, and food & beverage manufacturing.
This expansion is driven by the increased adoption of industrial robots in sectors like automotive, electronics, and food and beverage, alongside market advancements in the Asia-Pacific region.
AI is used to make advanced robots understand and act independently in complex environments. Furthermore, machine learning can help robots learn from their experiences and improve over time.
Workplace accidents in the manufacturing industry are anticipated to substantially decrease as AI robots assume human roles and manage routine and risky responsibilities. Advancing into the domain of AI results in a decreased reliance on human labor for hazardous and excessively demanding tasks.
AI-enabled robotics can be used for piece picking in manufacturing, enabling them to adeptly grasp random objects without necessitating specific training or intricate programming.
Piece picking is considered one of the simplest warehouse tasks; however, it is often highly costly and primarily relies on manual labor. The advent of AI-enabled robotics has the potential to transform this scenario.
“Robots by themselves cannot learn human behavior, but through technology, they can achieve capabilities to do so,” Eugen Solowjow, leading the research group at Siemens, envisions that equipping AI robots with human-like learning abilities could significantly transform conventional manufacturing methods.
Experts at the University of Maribor believe that as robots advance in intelligence, they will inevitably take over the roles of factory employees.
This is because sensors closely watch each step, sharing data with AI and analytics software. This speeds up output, detects defects, takes quick corrective action, and makes the production process more efficient.
Who is Using AI in Manufacturing?
Several distinguished international companies are integrating artificial intelligence into their manufacturing operations.
| Company | Use of AI in Manufacturing |
| Intel |
|
| Bridgestone |
|
| Danone |
|
| General Motors |
|
| L’Oreal |
|
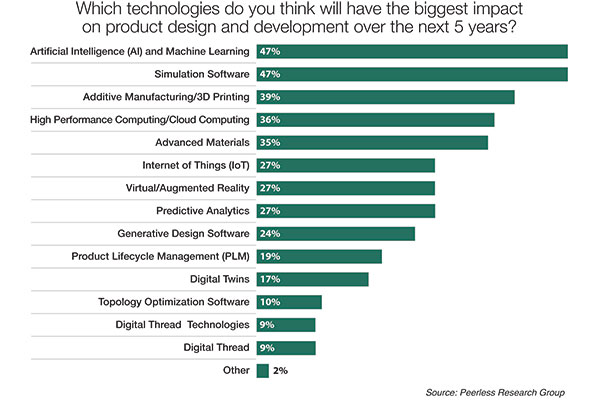
In a survey conducted by Peerless Research Group in 2021, involving 330 participants, 47% of respondents anticipated that artificial intelligence and machine learning would have the most significant influence on product design and development between 2021 and 2026.
Among the surveyed participants, the leading group identified their primary roles as:
- Product or system design engineering: 24%
- Engineering management: 13%
- Corporate management: 10%
- Research and development: 10%
- Consultant/service provider: 10%
AI in the Automotive Industry
AI has become a valuable player across the automotive spectrum, contributing to design, manufacturing, sales, and product maintenance. Additionally, studies indicate that AI contributes to optimizing processes, parameters, and quality evaluation for manufactured automotive products.
No exploration of AI’s impact on manufacturing within the automotive world would be complete without delving into the trailblazing world of Tesla, the undisputed champion of AI integration in vehicles.
According to the Wall Street Journal, Elon Musk, has often depicted Tesla as more than just an automaker – he’s painted it as an artificial intelligence powerhouse. Tesla’s comprehensive integration of AI technology underscores its commitment to innovation, safety, and user satisfaction.
Tesla employs AI in manufacturing through various applications and processes:
| AI Application | Result |
| Robotic Assembly | AI-powered robots are utilized in assembly lines for welding, painting, and component assembly, enhancing efficiency and precision. |
| Quality Control | AI-driven computer vision systems inspect and analyze products in real time, identifying defects and inconsistencies and ensuring high product quality. |
| Predictive Maintenance | AI algorithms monitor machinery and equipment, predicting maintenance needs and preventing unplanned downtime. |
| Supply Chain Optimization | AI assists in optimizing supply chain operations by analyzing data to predict demand, manage inventory, and improve logistics. |
| Process Optimization | AI algorithms analyze production data to identify bottlenecks, inefficiencies, and opportunities for process enhancement. |
| Customization /Configuration | AI enables the customization of manufacturing processes based on specific product requirements, optimizing resource allocation. |
| Energy Management | AI optimizes energy consumption in manufacturing facilities, reducing costs and environmental impact. |
| Cobots | AI-powered collaborative robots work alongside human workers, assisting with tasks that require precision and repetitive actions. |
| Data Analysis | AI analyzes historical data to extract insights, allowing for continuous improvement in manufacturing processes. |
Use of AI in Pharmaceutical Manufacturing
Artificial intelligence in drug development and discovery emerges as a frontrunner among cutting-edge technologies, unleashing a world of potential within the pharmaceutical sector.
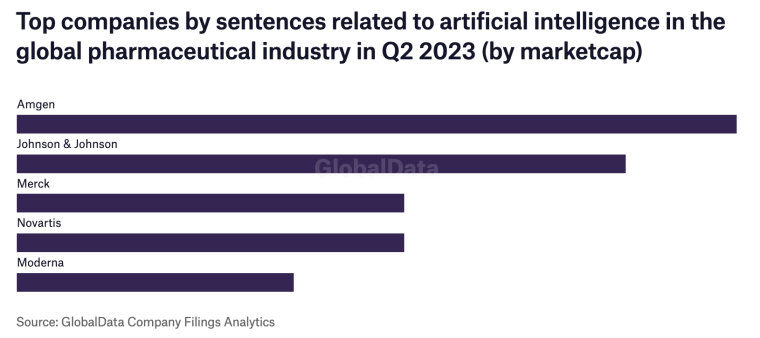
Among major pharmaceutical companies, Amgen saw the highest rise in references to AI in Q2 2023.
Pharmaceutical technology specialists shared noteworthy discoveries from a GlobalData study: they uncovered 13 sentences related to AI in Amgen’s filings, comprising 0.6% of all sentences, indicating a remarkable 333% surge compared to Q2 2022.
According to the FDA, AI opens up a domain of possibilities in pharmaceuticals, offering a toolbox of smart solutions.
It helps fine-tune processes, keep a watchful eye on operations, and detect trends that lead to constant improvement.
| AI Application | Outcome |
| Process Design and Scale-up |
|
| Advanced Process Control (APC) |
|
| Process Monitoring and Fault Detection |
|
| Trend Monitoring |
|
In pharmaceutical manufacturing, AI offers the potential to shorten operational cycle times while simultaneously increasing quality and/or reducing overall costs and raw material consumption.
It provides a solid basis for greater automation and knowledge expansion, enabling better, faster decision-making in the pharmaceutical industry.
AI in Manufacturing Apparel and Textiles
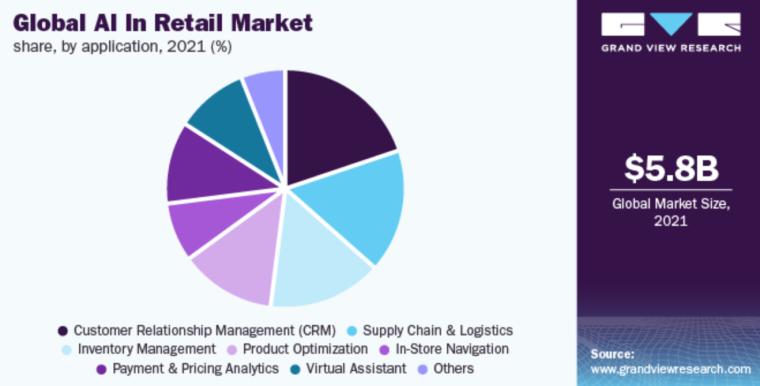
In 2021, the worldwide AI in the retail market was valued at $5.79 billion. It is projected to grow significantly, with a CAGR surpassing 23.9% from 2022 to 2030.
The supply chain and logistics sector commanded a notable portion of the market’s revenue. Leading companies incorporate this application into manufacturing and operations to enhance efficiency and streamline business processes.
The machine learning sector led the AI in the apparel market in 2021, securing a 30.2% revenue share. Machine learning swiftly derives insights from data, enabling personalized customer experiences. It also boosts inventory efficiency, helping retailers improve supply chains and demand forecasts.
AI-driven robots in apparel manufacturing tackle tasks too repetitive or hazardous for humans, like cutting and sewing fabrics. This not only enhances worker safety but also trims production expenses.
Furthermore, AI marks its spot within the textile industry, lending its capabilities to tasks such as color matching and pattern creation in visual inspections.
Jeffrey Joines, who leads the Department of Textile Engineering, Chemistry, and Science at North Carolina State University’s Wilson College of Textiles, says AI and machine learning can be employed within textile machinery to ensure precise cutting of garments and other products, minimizing fabric wastage.
According to sustainable fashion experts, clothing and textiles comprise at least 7% of the total waste in global landfills. In the United States, 66% of clothing and textiles are in landfills. Moreover, globally, 92 million tons of textile waste is generated annually.
AI-powered solutions not only revolutionize the process of clothing design, manufacturing, and market introduction but also do so in an environmentally sustainable way.
Take H&M, for instance – with AI analyzing RFID and other data, it makes precise supply forecasts, benefiting its finances and the environment.
On average, online shoppers return 15-40% of their purchases, compared to 5-10% for in-store purchases. Addressing this concern, H&M is developing digital twin technology to let customers “try on” clothes before buying and promote waste-free design.
AI digital twin tech generates virtual replicas of objects/processes via AI and data analytics. They offer real-time monitoring, prediction, and optimization in manufacturing.
AI in Aerospace & Defense Manufacturing
The aerospace industry continues to explore and develop new applications for AI, leading to advancements that enhance various aspects of manufacturing, operations, and safety within the sector.
The AI and robotics in aerospace and defense market is anticipated to grow from $29.67 billion in 2023 to $42.60 billion by 2028. This represents a CAGR of 7.50% during the forecast period.
In the aerospace and defense sector, advanced AI-driven robotic technologies can enhance overall equipment efficiency (OEE) and elevate first-pass yield during production processes. Prominent participants in the aerospace and defense artificial intelligence and robotics market include
- The Boeing Company
- Lockheed Martin Corporation
- Airbus SE
- IBM Corporation
- Thales Group
AI software helps aerospace manufacturers improve quality control efficiency and lower production costs simultaneously. AI-powered computer vision systems can analyze and inspect components, structures, and assemblies with high precision and speed. This helps detect defects, anomalies, or inconsistencies in real time, ensuring the production of high-quality and reliable aerospace parts.
In the aerospace and defence manufacturing sector, the current application of artificial intelligence involves the automatic programming of tasks and processes and predictive maintenance capabilities. Moreover, the emerging applications of AI focus on developing advanced safety features in aircraft. These include utilizing AI for CT scanners, analyzing biometric data, replacing human co-pilots with robots, and creating autonomous aircraft.
Benefits of AI in Manufacturing
AI integration in manufacturing yields numerous advantages, including heightened production efficiency, data-driven decision-making, and streamlined automation. By harnessing AI’s capabilities, manufacturers can optimize resource allocation, enhance product quality, and swiftly adapt to market dynamics, fostering competitive advantage.
61% of manufacturing companies that adopted AI in 2021 increased their revenue. Further:
- 10% achieved revenue growth of more than 10%
- 18% experienced revenue growth between 6-10%
- 33% saw an increase of less than 5%
Manufacturing is among the top leading sectors which are adopting AI. According to MITT’s tech review survey, manufacturers point to their main achievements with AI as:
- Improved supply chain speed and transparency
- Streamlined production operations
- Accelerated and innovative product development
Additionally, regarding maintenance in manufacturing, AI brings several benefits, driving industries to new levels of efficiency and excellence, including:
- High uptime and availability, leading to high overall equipment effectiveness
- Low maintenance costs
- Avoiding loss of production
- Low spare part inventory
AI technologies come with key characteristics that can be summed up as intelligence, systematization, and automation, as researchers at the University of Tehran pointed out in their studies.
Think of it like the brainy, organized, and automated superhero of the tech world. This dynamic duo of machine learning and deep learning will shake up industries worldwide, promising exciting changes ahead.
Machine Learning Advantages
Machine learning is a subset of AI that involves training computers to learn from data and improve their performance on a specific task over time without being explicitly programmed.
It enables machines to recognize patterns, make predictions, and adapt their actions based on the information they process. Machine learning offers multiple benefits to manufacturing, including:
- Product R&D
- Production
- Inventory management
- Process and quality control
- Predictive maintenance
Labour Productivity with AI
Artificial intelligence in industrial production is forecast to increase labor productivity by 38% by 2035.
AI enhances labor productivity in manufacturing by automating repetitive tasks, allowing human workers to focus on more complex and value-added activities. Additionally, AI-driven data analysis provides insights for optimized decision-making, leading to efficient resource allocation and process improvements.
AI can enhance manufacturing processes, effectively reducing takt and improving throughput. Takt time is when a product or process must be completed to meet customer demand while maintaining a consistent production flow. It helps ensure that work is evenly distributed and aligned with customer needs.
For example, Mitsubishi Electric utilizes AI to optimize industrial robot parameters such as rate, speed, and acceleration. This innovation has led to an impressive time reduction, condensing the process to just 1/10th of the conventional method.
AI might double yearly economic growth rates by 2035 by transforming work dynamics and establishing a new human-machine relationship where technology adapts to our needs while we remain in control.
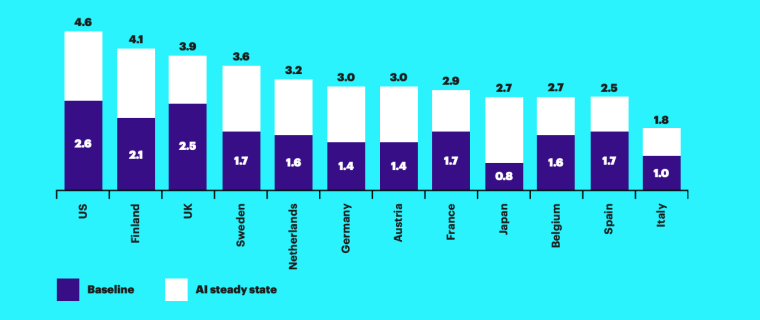
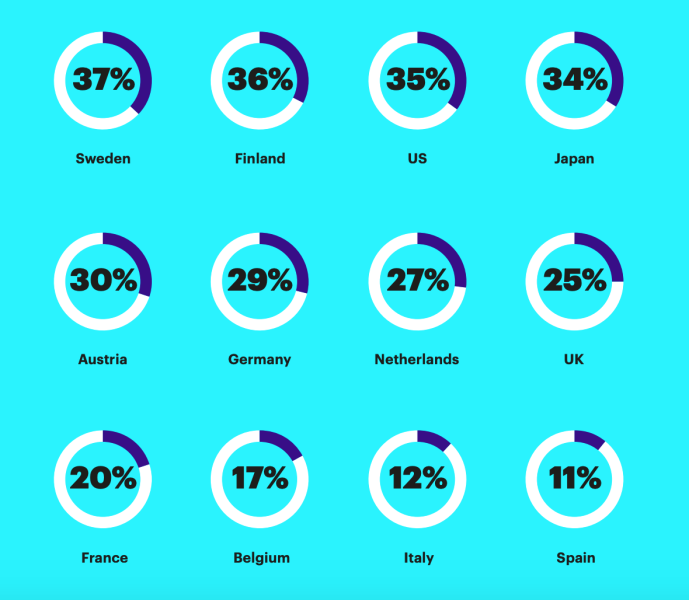
In the US, AI has the potential to amplify labor productivity by 35%. Yet, the horizon shines even brighter for Sweden and Finland, where AI is projected to ignite a staggering near-40% surge in labor productivity.
The Challenges of AI in Manufacturing
A common issue with using AI and machine learning in manufacturing is getting accurate data, according to specialists from West Virginia University. Furthermore, the quality and composition of available manufacturing data greatly affects how well machine learning algorithms perform.
A significant and growing challenge with AI in manufacturing involves selecting the right ML technique and algorithm.
Despite efforts to define general ML approaches, the varying problems and requirements emphasize the necessity for specialized algorithms, each with strengths and weaknesses. The increasing focus on ML in manufacturing has led to a wide array of algorithms and variations, catering to practitioners and researchers in the field.
AI in Manufacturing Workforce Shift
By 2040, 47% of current job tasks could be automated using AI, including advanced robotics and AI-driven automation systems. Generative AI has the potential to significantly enhance overall labor productivity. To realize this, investing in aiding workers as they transition their work tasks or job roles is crucial.
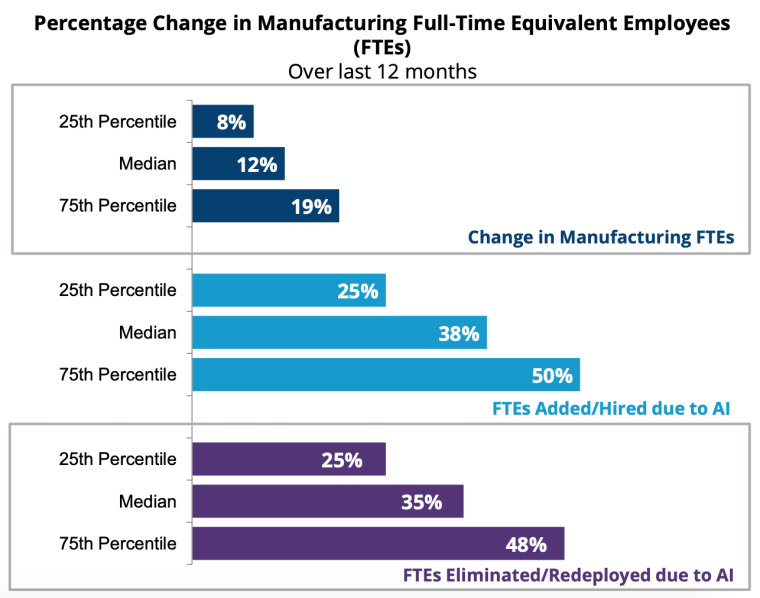
Companies have experienced shifts in their manufacturing workforce, with a median of 12% turnover due to AI, according to a 2021 AI in manufacturing survey report. The report also noted:
- 35% of FTEs were eliminated or redeployed
- 38% or more FTEs were added
Nonetheless, findings indicated that the transition isn’t about substituting people for AI but signifies a transformation in the necessary skills.
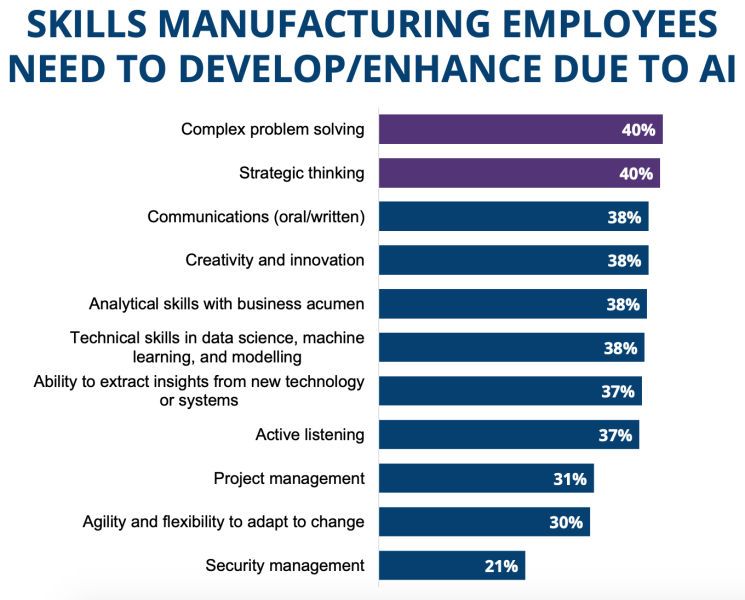
AI needs manufacturing staff who prioritize critical and strategic thinking to tackle organizational challenges rather than focusing solely on technical skills.
Cost Concerns of AI in Manufacturing Statistics
Implementing AI technologies can involve substantial upfront costs, including infrastructure, software development, and training. Manufacturers must carefully evaluate the potential return on investment (ROI) and long-term benefits of AI adoption.
AI software expenses can span from no cost to $300,000 for different companies. However, custom AI solutions might incur expenses ranging between $6,000 to well over $300,000, encompassing development and implementation.
When considering artificial intelligence, various elements impact the expenses associated with AI software:
- AI type (chatbots, virtual assistants, analysis systems)
- Project type
- AI features
The Future of AI in Manufacturing
The manufacturing sector’s reliance on heavy machinery positions it as a prime candidate for implementing AI technologies.
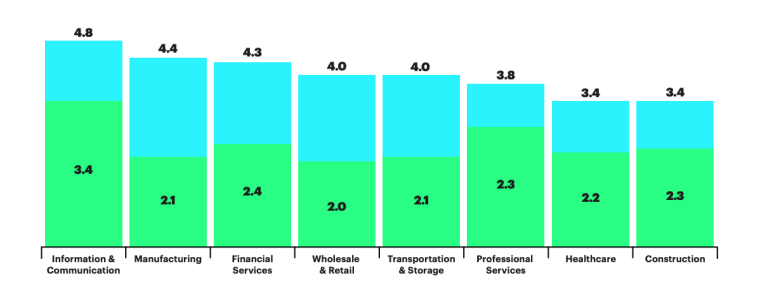
Studies indicate that in an AI-driven scenario, the sectors of information and communication, manufacturing, and financial services are poised to experience the most substantial annual growth rates in gross value added (GVA) by 2035. The growth numbers numbers break down as:
- Information and communication: 4.8%
- Manufacturing: 4.4%
- Financial services: 4.3%
Research indicates that by 2035, AI could contribute an extra $3.8 trillion in GVA to the manufacturing sector, marking an impressive 45% growth compared to regular operations.
AI’s future in manufacturing can reshape the industry’s landscape, driving innovation, optimizing processes, and enhancing the bottom line and the customer experience. It will happen by:
- AI-driven automation streamlining manufacturing by reducing errors and labor intensity.
- Predictive analytics foreseeing maintenance needs, minimizing downtime.
- Intelligent supply chains optimizing inventory and logistics, cutting waste.
- AI enabling personalized products through data insights, enhancing customer satisfaction.
- Safety improving with AI sensors identifying hazards, ensuring a safer workplace and higher productivity.
Final Thoughts
The integration of AI in manufacturing heralds a transformative era marked by efficiency, innovation, and strategic advancement.
As the industry embraces AI-driven automation, predictive maintenance, and human-robot collaboration, businesses stand to gain from enhanced productivity and reduced operational costs.
The journey forward for manufacturing with AI promises not only to reshape production landscapes but also to drive significant economic growth, positioning AI as a cornerstone of future manufacturing strategies.
FAQs
How is AI used in the manufacturing industry?
How is AI changing the manufacturing industry?
What is the future of AI in manufacturing?
What are the challenges of AI in manufacturing?
Sources
- Plant Engineering
- Francesc Bonada
- MIT
- Nanyang Technological University
- Statista
- Statista
- Mohsen Soori
- DAAAM
- University of Maribor
- Peerless Research Group
- Tesla
- Wall Street Journal
- Pharmaceutical Technology
- GlobalData
- FDA
- Grandview Research
- IMMAGO
- AATTC
- Mordor Intelligence
- GN Corporations Inc.
- University of Tehran
- IBM
- Mitsubishi Electric
- APQC
- WebFX