In the fast-paced world of online commerce, small businesses and marketers are constantly seeking innovative ways to stay competitive and enhance the shopping experience for their customers. In 2025, the integration of AI in ecommerce is offering tools and solutions that not only level the playing field for small businesses but also provide invaluable insights and tools for marketers.
With the vast amount of information scattered across numerous reports and websites, it can be challenging to discern the key insights and trends in AI’s role in ecommerce. At Business2Community, we have meticulously curated a comprehensive list of information, so we can delve into how it is revolutionizing online shopping in 2025.
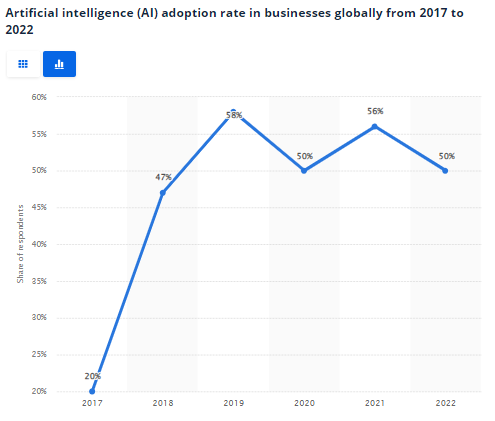
In the realm of ecommerce, artificial intelligence (AI) takes on various forms and plays a role in enhancing the online shopping world and experience. The State of AI in 2022, as reported by the McKinsey Global Survey on AI, showed several key trends and insights: Goldman Sachs strategists believe that AI has the potential to increase net profit margins by nearly 400 basis points over a ten-year period. This potential profit margin expansion from AI contrasts with other near-term challenges, including the possibility of a recession, interest rate changes, high inventory levels, and inflation. OpenAI’s ChatGPT launch in 2022 sparked interest, with companies rushing to develop AI-related tools and investors showing increased interest in AI-related investments. After experiencing remarkable growth in adoption rates between 2017 and 2018, AI adoption has slowed down since 2019. 2022 witnessed nearly 2.5 times the adoption rate of AI compared to 2017. Machine learning in ecommerce refers to the use of AI algorithms to analyze customer data. This enables personalized product recommendations, fraud detection, and customer behavior analysis. Businesses employing machine learning are able to manage over 95% of their customer service representatives’ interactions through AI and digital channels. AI-enabled customer service enables institutions to provide personalized and proactive experiences for customer engagement. Two-thirds of millennials expect real-time customer service, and three-quarters of customers expect consistent cross-channel service. With that, 84% of ecommerce businesses are working on how to adopt AI and/or machine learning into their business. Generative AI, often used for content creation, helps ecommerce platforms and businesses generate unique and appealing content, ensuring that products stand out in a crowded market. Product descriptions can be automatically written, and AI-generated product visuals are used to enhance the shopping experience. As per findings updated in 2023 in the “Cracking the Consumer Code” report by Salsify, 88% of shoppers emphasize the importance of product content when making purchasing decisions. Generative AI, with its ability to generate accurate and appealing product descriptions and images, can help address the issue of mismatched product descriptions, which is the reason for 50% of consumers having to make a return. 43% of consumers want organizations to implement generative AI, and these are their expectations for its adoption: Big data analysis uses AI to process customer data. This resource helps ecommerce businesses make data-driven decisions, optimize pricing strategies, and anticipate market trends. In 2020, the global market for big data analytics in retail reached a valuation of $4.85 billion. It is anticipated to reach $25.56 billion by 2028, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 23.1% from 2021 to 2028. This growth is attributed to several factors, including greater investments in big data analytics tools, a growing demand for personalized customer experiences to boost sales, and the expanding ecommerce sector. Natural language processing is simply the combination of computer science and linguistics that gives computers the power to understand and modify speech. NLP enables chatbots and virtual assistants to understand and respond to customer inquiries. It enhances customer support by streamlining communication. It is anticipated that by 2025, the NLP market will expand nearly 14-fold compared to its size in 2017, up from approximately $3 billion in 2017 to over $43 billion in 2025. Natural language processing can help ecommerce businesses understand customer needs and improve recommendations. In fact, Amazon has reported that when it introduced recommendations on the site, revenue grew by 35%. Computer vision enhances visual search capabilities, allowing customers to find products by uploading images or using their device’s camera. Computer vision is also used for applications such as inventory management, store layout optimization, self-checkout, barcode scanning smartphone apps, and virtual mirrors & recommendation engines. A 2018 survey of Gen Z and Millennial shoppers found that 62% of them expected visual search features when shopping online. Pinterest introduced visual search features in 2018 and Amazon followed suit a year later. AI-driven customer segmentation analyzes customer data to identify distinct groups with similar preferences. This empowers ecommerce businesses to target their marketing efforts with precision. Hubspot notes that companies that use segmentation see an increase in ROI of 20% and email campaigns see 14% higher open rates with segmented audiences. Armed with AI-driven customer segmentation, ecommerce platforms can tailor their marketing strategies to cater to specific customer segments. Alibaba is a multinational technology company based in China, specializing in ecommerce, technology, and various other sectors. As of 2021, it has over 251,000 employees and is valued at $570 billion. In 2023, Alibaba introduced its extensive language model, Tongyi Qianwen, which is an artificial intelligence model that undergoes training on massive datasets. This model serves as the foundation for generative AI applications, like ChatGPT, capable of producing human-like responses in reaction to user queries. Alibaba also uses AI for personalized recommendations, chatbots for customer service, and AI-driven logistics. ASOS is a British online fashion and cosmetic retailer. The company has around 4,000 employees and is valued at $5 billion. ASOS also leverages AI through its Profile Builder, an innovative solution that empowers customers to share detailed insights about their style preferences. This valuable information serves as the foundation for crafting personalized experiences and delivering recommendations that are relevant to each individual customer. When Profile Builder launched in 2019 ASOS saw a 7% increase in gross profits. Etsy is an American ecommerce platform focused on handmade and vintage items and craft supplies. The company, valued at $23 billion and having around 1,400 employees, uses AI to offer personalized shopping experiences to its customers. To enhance the relevance of its search results, Etsy has incorporated various search engine technologies, encompassing relational aspects (such as interactions between buyers, listings, and shops) and semantic elements (the ability to comprehend user search intent even when expressed vaguely). These enhancements extend to analyzing the actual text within search queries. Using machine learning, the company was able to remove 29% more listings that violated its “handmade” rule in the first half of 2023, compared to the previous period. AI can help ecommerce companies stay ahead of the competition by providing a range of capabilities that increase efficiency and improve customer experiences. While manufacturing and risk were key areas of value from AI in 2018, in 2022 the biggest reported revenue effects are in marketing and sales, product and service development, and strategy and corporate finance. Companies that integrate AI into their operations have reported cost reductions. In a 2021 study, over 50% of respondents in 2021 reported reduced costs in supply chain management, with the majority of these reductions being under 10%. In product and service development, 30% achieved cost reductions of 10% or more, and 6% achieved reductions exceeding 20%. By using chatbots and AI-driven recommendation engines, companies can provide personalized shopping experiences. According to a survey conducted by Epsilon and GBH Insights, 80% of respondents expressed a strong desire for personalization when interacting with retailers. 90% of the surveyed individuals found the concept of personalization appealing, emphasizing that shoppers increasingly seek customized recommendations, content, and offers that align with their preferences and needs. Further insights from the report underscore the potential for personalization within specific sectors: According to the report, 90% of respondents express a higher likelihood of engaging with grocery/drug store websites and apps that offer personalized experiences. However, only 71% believe that these platforms currently provide such experiences effectively. The most motivating personalized features for grocery/drug stores are: In the travel and leisure sector, 87% of respondents express an increased inclination to do business with websites/apps offering personalized experiences. Nevertheless, only 64% believe that the current offerings in this industry are delivering personalization effectively. The most motivating features for travel and leisure brands include: For the automotive sector, the report reveals that 86% of respondents are more inclined to engage with websites/apps that provide personalized experiences. However, only 55% believe that these platforms are currently delivering personalization effectively. The most motivating features for auto brands include: The majority of retail business leaders, about 95% according to a 2020 Periscope by McKinsey survey, place emphasis on customer experience personalization in their strategic planning. Despite this, 23% of customers feel their personalization efforts are adequate. This divide is mainly due to the fact that most retailers are still in the infancy of implementing personalization strategies. The data reveals only 15% of retailers have fully rolled out these strategies, while over 80% are either still outlining a strategy or are in the trial stage. The following organizations have implemented ecommerce business strategies using AI: Amazon: Amazon uses sophisticated analytics to personalize customer experiences. It recommends products frequently purchased together, bundled items, and more. Sephora: Sephora offers omnichannel personalized experiences, allowing customers to book in-store makeovers and consultations through their mobile app. Sales associates can access customer profiles in-store, offering tailored recommendations Nike: Nike allows customers to configure their own clothes and shoes, offering real-time customization. It offers personalized experiences in physical locations for NikePlus members. According to McKinsey, early adopters who have integrated AI-powered supply-chain management have achieved a 15% reduction in logistics costs. AI can aid in streamlining inventory management, alleviating the issues of overstocking or understocking for ecommerce companies. These enhancements also include a 35% decrease in inventory levels, and a 65% increase in service levels, in contrast to competitors with a slower adoption rate. AI excels in identifying patterns, making it an effective tool for detecting and preventing fraudulent transactions. In 2023, Visa launched a deep-learning-driven fraud detection model to monitor instant settlement payments. In 2021, the company also rolled out VisaNet +AI, which is a suite of tools to help banks, merchants, and consumers reduce fraud throughout the payment process. Lastly, AI can help ecommerce companies devise more effective marketing strategies by analyzing customer behavior and trends. According to McKinsey, the most successful companies are implementing AI to facilitate hyper-personalization in their marketing approaches. In these organizations, the following characteristics are observed: Concerns about privacy and data misuse often obstruct the widespread acceptance of AI. In 2022, Western countries displayed the highest level of hesitancy when it came to placing trust in and embracing AI systems within private and personal domains. Conversely, among those who exhibited a greater inclination to trust and welcome AI, the BRICS nations (Brazil, India, China, and South Africa) were the most inclined to have confidence in algorithms. In a January 2023 survey conducted in the US, 45% of surveyed consumers admitted to having limited comprehension of the workings of AI and machine learning technologies. Nevertheless, 73 % of participants expressed their belief in the potential of AI and machine learning to influence customer experience. Additionally, 48% of those surveyed indicated their willingness to engage with AI on a more regular basis if it enhanced their interactions with a brand by making them smoother, uniform, and more convenient. AI systems are dependent on the data they are fed. Inaccurate or incomplete data can lead to incorrect predictions, impacting customer experience and business operations. In a McKinsey survey, around 67% of the participants confessed they lacked the necessary tools to deploy personalization at a large scale. Additionally, 41% found choosing the right solution partner challenging. In the same survey, the acquisition, assimilation, and analysis of customer data was noted as a major hurdle for 67% of respondents. Almost half the retailers, about 48%, said they found it challenging to obtain and sustain in-house analytics and data science expertise. While AI can reduce operational costs in the long run, the initial setup and implementation of AI technology can be expensive. This can be a deterrent for smaller businesses with limited resources. In IBM’s Global AI Adoption Index 2022, the high cost of implementation was listed as the second biggest obstacle to AI adoption. However, this survey was conducted in early 2022, approximately 10 months prior to OpenAI’s ChatGPT launch, which reduced the cost of AI and simplified integration. As AI systems handle a substantial amount of personal data, ecommerce companies need to ensure they comply with consumer data and protection regulations. In a McKinsey survey, siloed processes within many retail companies impede a quick and efficient sales process. Meanwhile, the sharing of customer data and promotion strategies was a concern for 43% of the surveyed group. About 25% found these siloed structures made it tough to secure vendor funding or support for personalized products. Over-reliance on AI systems can potentially make companies vulnerable to technical glitches and cyber-attacks. Approximately 34% of consumers expressed a level of concern regarding the possibility of phishing attacks in a Capgemini report. This AI in ecommerce statistic underscores the importance of addressing cybersecurity awareness and implementing appropriate safeguards in the realm of AI technology. Predictive personalization leverages machine learning algorithms to analyze past behavior and predict future actions, enabling ecommerce companies to tailor offerings and recommendations to individual customers. According to a report by McKinsey, 35% of Amazon’s sales are generated by their recommendation algorithm, an example of predictive personalization. Visual search allows shoppers to search for products using images instead of text. Visual search is an emerging technology that has been used in innovations like Google Lens, Snapchat’s Scan, and Apple’s Visual Look Up. Its potential in ecommerce business has profound implications for social commerce. For example, if you spot a product you love on Instagram but don’t know where to buy it, you can now simply take a screenshot, add it to your cart, and make a purchase. Voice shopping, powered by AI assistants, will become increasingly common. From searching for products to finalizing purchases, all can be done through voice commands, offering a hands-free shopping experience. In 2022, 123.5 million adults used voice assistants at least once per month. The adoption of voice assistants is expected to continue growing among both consumers and companies. Younger Millennials (ages 25-34) are the most likely age group to use voice assistants, with nearly two-thirds of them being monthly users. Consumers primarily use smartphones (42.7%) and smart speakers (32.2%) to access voice assistants. Amazon is the leader in the US smart speaker market, with nearly 64 million monthly users of Amazon Echo in the previous year. AI algorithms will continue to enhance security by predicting and detecting fraudulent behavior before it happens. These advanced systems will help to safeguard customer information. In the realm of financial services, the majority (58%) within the sector report fraud detection as being the most important use case for AI. One of the key domains where AI-driven fraud detection has had an impact is in the field of ecommerce, such as by safeguarding online transactions, protecting customers from fraudulent activities, and upholding the integrity of digital payment systems.AI in Ecommerce Statistics Highlights
How Is AI Used in Ecommerce?
Machine Learning
Generative AI
Big Data Analysis
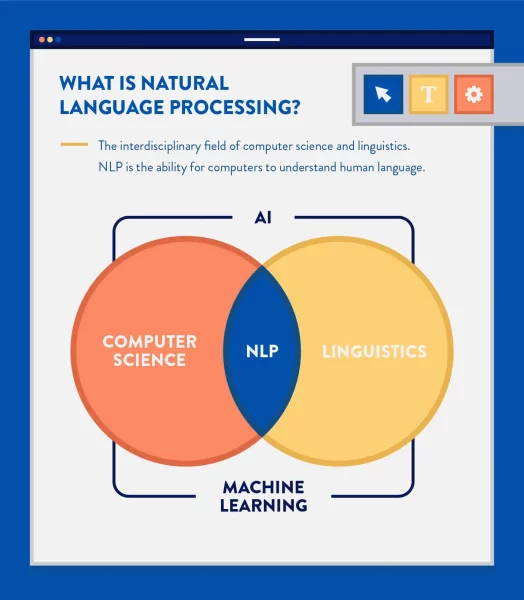
Natural Language Processing (NLP)
Computer Vision
Customer Segmentation
Who Is Using AI in Ecommerce?
Alibaba
ASOS
Etsy
Benefits of AI in Ecommerce
Reduction in Operational Costs
Enhanced Customer Experience
Grocery and Drug Store Websites
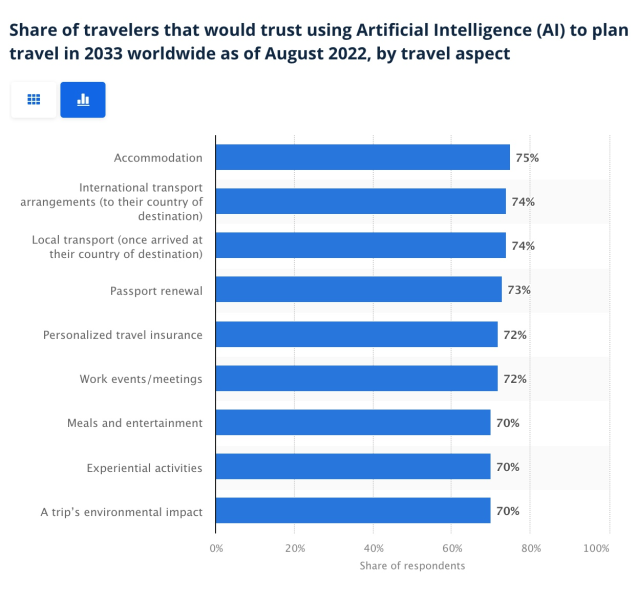
Travel & Leisure Websites
Automotive Industry Websites
Improved Inventory Management
Fraud Detection and Prevention
Data-Driven Marketing Strategies
Challenges of AI in Ecommerce
Public Perception and Trust
Technical Deficiencies
High Implementation Costs
Regulatory Challenges
Dependence on AI
The Future of AI in Ecommerce
Predictive Personalization
Visual Search Capabilities
Voice Shopping and Assistant
Advanced Fraud Detection
FAQ
How is AI used in ecommerce?
How is AI improving ecommerce?
How will AI disrupt ecommerce?