In a fiercely competitive landscape, understanding and exploiting unique organizational strengths is a critical business success factor. This is where the VRIO analysis comes in — as a strategic planning tool, it can help you identify and leverage the internal resources and capabilities that give your business a sustainable, competitive advantage.
At Business2Community, we’ve done the hard work to consolidate all you need to know about this valuable tool, including how to complete it and relevant examples. Keep reading to discover how to leverage the VRIO framework to maximize your business’s potential and ensure its long-term success.
VRIO Analysis – Key Takeaways
- A VRIO analysis is a strategic management framework used to identify an organization’s unique resources and capabilities.
- This qualitative method evaluates internal resources based on their value, rarity, imitability, and organization, so they can be conserved and optimized to achieve sustainable competitive advantage.
- As a strategic planning method, the VRIO analysis is best combined with other frameworks like SWOT and PESTEL. For additional quantitative insights, it can be integrated with tools such as ratio analysis.
What is a VRIO Analysis?
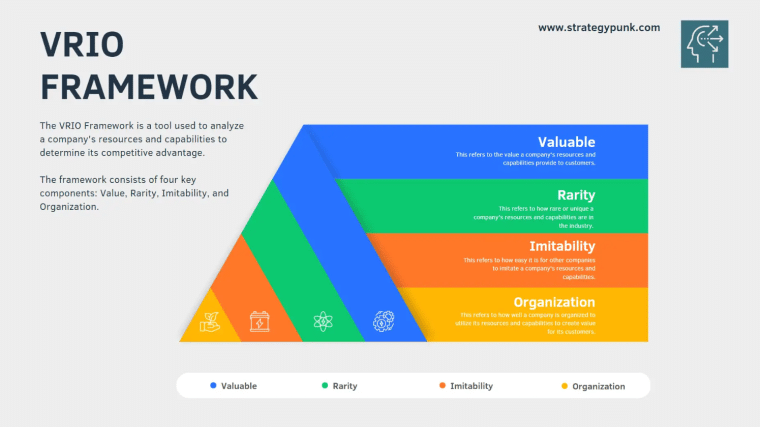
A VRIO analysis is a four-question strategic management framework developed by Jay Barney, a professor at the University of Utah, in 1991 to identify the unique resources and capabilities that give a business a competitive advantage. By evaluating internal resources based on their value, rarity, imitability, and organization, they can be protected and optimized to achieve a sustained competitive advantage.
When Does a Company Need to Do a VRIO Analysis?
A company would need to do a VRIO analysis to identify the internal resources and core competencies that are crucial for creating a long-term competitive advantage. Armed with this knowledge, informed decisions about resources can be made, existing capabilities can be optimized, and a business can achieve a sustained competitive advantage.
Key VRIO use cases include:
Strategic Decision-Making
As part of its strategic planning, a company might use a VRIO analysis to assess its core competencies. For example, global tech giant Apple might leverage the framework to evaluate its innovation capabilities, brand reputation, and customer loyalty to determine if these factors will continue to give it an edge over competitors like Samsung.
Entering New Markets
Before entering a new market, a company like Netflix could conduct a VRIO analysis to determine if its content, technology, and data analytics capabilities can provide a sustainable competitive advantage.
Mergers and Acquisitions
A VRIO analysis can be used to evaluate whether a target company has valuable and rare resources that are costly to imitate and properly organize. This will determine whether the company has a competitive advantage that can be leveraged post-acquisition.
Responding to Competition
In competitive markets, businesses may regularly use a VRIO analysis to understand whether their marketing strategies, brand assets, and global distribution networks provide a competitive edge over rivals.
Product Development
Before developing a new product, a company might use a VRIO analysis to assess whether it has the necessary R&D capabilities, patents, and organizational structure to successfully bring the product to market and gain a competitive advantage.
Digital Transformation
A company looking to invest in AI and other emerging technologies like cloud computing and IoT might use a VRIO analysis to determine if this would provide a sustainable competitive advantage, and whether the company is prepared to implement the technologies effectively.
Resource Allocation
A company might use a VRIO analysis to determine which assets and capabilities need to be preserved, optimized, or divested. By identifying the parts of its operations that are essential, more informed decisions about resource allocation can be made.
How to Complete a VRIO Analysis
To complete a VRIO analysis:
- List your firm’s resources or capabilities.
- Categorize the resources according to the VRIO framework.
- Review and optimize your VRIO resources.
- Prioritize continuous improvement.
Let’s explore these steps in greater detail below.
Step 1: Identify Your Resources and Capabilities
Before diving into the VRIO framework, identify your resources and capabilities. Resources are the various materials, assets, and inputs that your business needs to operate successfully.
They can be categorized as either tangible or intangible.
- Tangible resources or material resources: Consider your physical and financial resources such as capital, machinery, and buildings. As these are easy to acquire, they generally aren’t considered a source of competitive advantage.
- Intangible resources or non-material resources: These are assets such as cost advantages, intellectual property, company culture, brand reputation, informational resources, or network relationships. As these are harder to acquire and replicate, they may form part of your business’s competitive advantages.
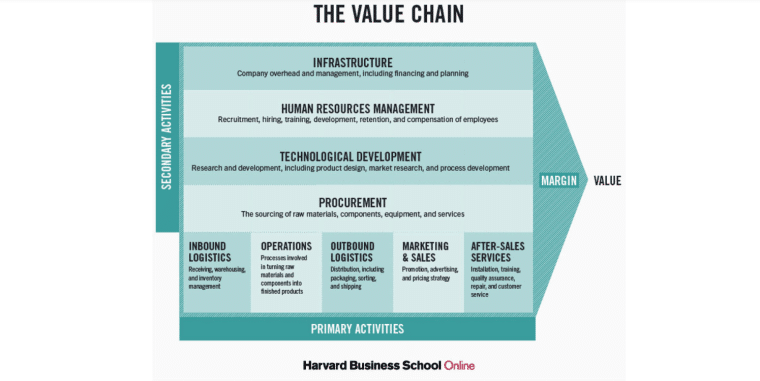
Capabilities, on the other hand, refer to your business’s ability to use resources efficiently and include elements such as human resources and proprietary systems.
For additional help identifying your most valuable resources and capabilities, conduct a value chain analysis. Breaking down the series of activities and resources involved in producing your final product allows you to pinpoint those that are essential for overall business efficiency, strategic planning, and competitive positioning.
Step 2: Conduct a VRIO Analysis
In this crucial next step, categorize the resources and capabilities you identified above using the four-question VRIO framework. Let’s explore each question below.
Value: Is it Valuable?
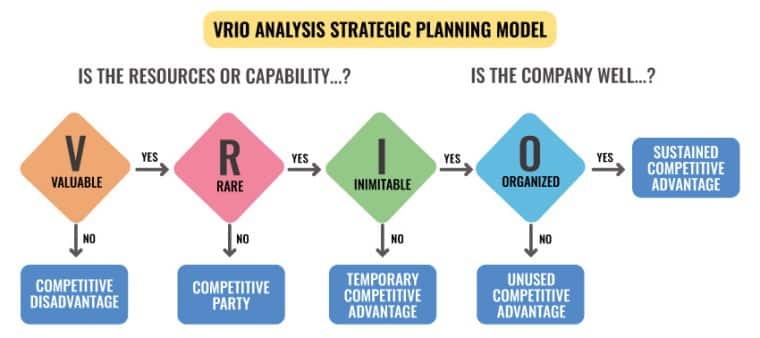
Evaluate whether the resources and capabilities you identified provide value to the company. Valuable resources are those that help you take advantage of opportunities or overcome threats in the market. They also benefit customers, add to the bottom line, and align with your key strategic goals to boost your competitive positioning. Resources not deemed valuable place your business at a competitive disadvantage and should be addressed.
Rarity: Is it Rare?
Next, consider if the valuable resources you identified are rare. Rare resources are ones which are scarce and give you an edge in your industry. If competitors can acquire and exploit a valuable resource, it isn’t considered rare, and you’ll be in a state of competitive parity. Competitive parity isn’t a desired state, so your valuable resources should still be protected and optimized.
Imitability: Is it Imitable?
If you have any company resources that are valuable and rare, assess whether they are inimitable. Inimitable resources are those that are difficult and costly to imitate. When a resource is valuable, rare, and there is a significant cost disadvantage to competitors obtaining, developing, or replicating it, a temporary competitive advantage is achieved.
Organization: Is it Organized?
The next question should be: is your firm organized to leverage the value, rarity, and inimitability of the resource or capability? This includes having the right organizational structure and management systems to leverage your inimitable, valuable, and rare resources. When a resource or capability meets all the VRIO requirements, it is considered a source of sustained competitive advantage for a company.
A poor organizational structure can negatively impact a company with valuable, rare, and costly-to-imitate resources, placing it at a competitive disadvantage. Similarly, if a company isn’t sufficiently organized to exploit rare and valuable resources, this represents an unused competitive advantage.
Step 3: Review and Optimize Resources
Once you’ve categorized your resources and capabilities, the next step is to consider the competitive implications of your findings. As you develop a strategic plan, allow the following questions to guide you:
- What can be done to preserve the value, rarity, or inimitability of each resource?
- Is your company organized or structured to leverage these resources?
- Can any of these resources be optimized and shifted from their current category into a higher one? For example, could resources in the unused competitive advantage category be turned into long-term competitive advantages?
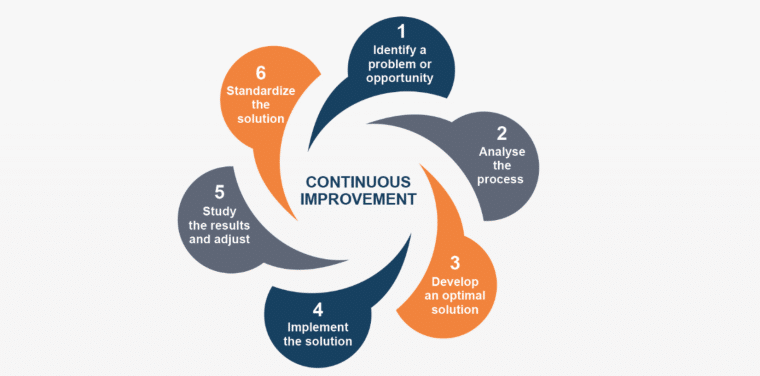
Step 4: Prioritize Continuous Improvement
Today’s business landscape is extremely competitive, undergoing constant and disruptive change that can quickly render a company obsolete. The decline of Blockbuster in the 2000s is a prime example of a company failing to maintain a sustainable competitive advantage in the face of changing industry dynamics.
Blockbuster, once a giant in the video rental industry, struggled to adapt to the rapid shift toward digital streaming and online content delivery. To ensure your company maintains its sustainable competitive advantages, continuous analysis and optimization of key resources and capabilities is crucial.
Examples of VRIO Analysis
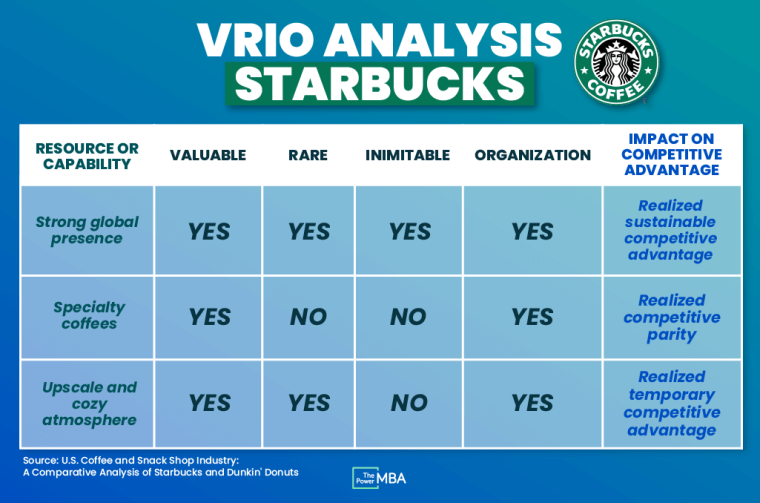
Based on the VRIO analysis shown in the image below, Starbucks has a realized competitive parity related to its specialty coffees and a realized temporary competitive advantage related to the upscale and cozy atmosphere of its stores.
Key strategic implications of this VRIO analysis might include:
- Developing a secret blend of coffee that is both rare and inimitable to create a sustainable competitive advantage.
- Continually investing in the look, feel, and experience of all its stores so that its temporary competitive advantage becomes a sustainable competitive advantage.
Early Stage Planning
Suppose a small tech startup develops a unique algorithm for data analysis. A VRIO analysis could help assess if this algorithm is a valuable tool, if it is rare, how difficult it is for competitors to imitate it, and whether the startup is organized to exploit it. The insights gleaned from the analysis would then help the startup with early-stage planning, allowing it to organize its operations for a sustained competitive advantage.
Optimizing Performance
Let’s consider a company that’s known for exceptional customer service. A VRIO analysis can be used to determine if this capability provides a competitive advantage, how rare it is in the industry, whether this level of service can be easily imitated by competitors, and if the company’s culture or organization supports maintaining this high standard. Based on the findings, the company could make critical decisions to preserve and optimize its capability for a long-term competitive advantage.
Managing Resources
A company conducts a VRIO analysis and discovers that its main source of competitive advantage is its highly-skilled team. To sustain this competitive advantage, the company needs to prioritize employee satisfaction and ensure the right conditions to foster creativity, innovation, and a high level of engagement among its workforce.
How to Adjust a VRIO Point
Below we discuss how to adjust each VRIO point for greater business success.
Value
To positively influence value, focus on optimizing unique company resources and capabilities that provide a competitive edge.
- Assess how valuable resources and capabilities contribute to customer satisfaction and implement strategies that continuously enhance their uniqueness, quality, and efficiency.
- Leverage customer feedback and market trends to continually adapt and innovate.
- Prioritize resources that directly increase value for customers, ensuring your offerings stand out in the marketplace.
Rarity
To improve rarity, identify and nurture resources or capabilities that are unique to your company. This includes:
- Identifying and capitalizing on elements that competitors lack, such as specialized skills, proprietary technology, or exclusive partnerships.
- Continuously enhancing rare attributes through strategic investments and focused development.
- Protecting rare resources through patents or unique business models.
- Emphasizing rarity to ensure your business offerings stand out in the marketplace.
Imitability
To enhance inimitability, focus on developing and maintaining resources and capabilities that are challenging for your competitors to replicate. This includes:
- Fostering unique company culture, brand reputation, deep customer relationships, or advanced technological expertise.
- Encouraging continuous innovation and protecting intellectual property through patents or trade secrets.
- Building complex systems or processes that are unique to your organization.
Organization
Enhancing your organization involves ensuring that your resources are organized to maximize potential. To achieve this, consider the following measures:
- Integrate efficient management systems with the company’s resources and establish robust management control systems.
- Optimize management structures to effectively leverage unique capabilities and follow a structured approach to meet strategic goals.
- Implement data-based employee management to maximize the potential of human resources.
- Keep up with key trends through authoritative industry resources like the Strategic Management Journal.
Limitations of VRIO Analysis
While the VRIO framework is an invaluable tool for assessing your competitive position and providing strategic insights, it has certain limitations.
As VRIO is an internal analysis tool, it doesn’t take into account external factors that can significantly affect a company’s strategy. This could include environmental shifts, changes in market dynamics, emerging digital trends, changes in customer preferences, industry regulations, and more.
So, combine it with other analysis methods and frameworks such as the SWOT analysis or PESTEL analysis for a more comprehensive overview of your business.
A key advantage of the VRIO analysis is that it is simple to conduct, however, its qualitative focus does not provide a complete picture of a business’s performance or its resource utilization.
Supplement it with other analytical and quantitative techniques such as ratio analysis to understand how financial resources are being used and variance analysis to pinpoint any performance gaps.
The Value of VRIO Analysis
VRIO analysis is an often extremely valuable tool that allows companies to identify the resources and capabilities that are crucial for maintaining a competitive edge.
Use its four-question framework to:
- Discover what your business excels at.
- Assess if your internal strengths are unique.
- Evaluate how easily your resources and capabilities can be replicated or acquired by competitors.
- Measure how efficiently your business is organized to exploit these resources.
Ultimately, no matter what line of business you’re in, the VRIO analysis can help you achieve a sustained competitive advantage, driving your business toward lasting success. For a comprehensive strategic planning process, integrate it with quantitative, or forward-looking analysis methods.
FAQs
What are the 4 questions of a VRIO analysis?
What’s the difference between SWOT and VRIO analysis?
What is the VRIO framework process?