Qualitative data analysis observes and defines contextual information that can’t be quantified. It extracts crucial information, providing rich data for companies to work on and formulate profitable strategies.
Our experts at Business2Community put together this detailed article where we go over everything you need to know about qualitative data analysis, including a step-by-step guide and several examples to demonstrate its real-life applications.
Qualitative Data Analysis – Key Takeaways
- Qualitative data analysis examines non-quantifiable information to inspect the strengths and weaknesses of a company.
- Companies need to interpret the qualitative data objectively to avoid contaminating the results with personal bias.
- Due to its limitations, you should incorporate qualitative analysis methods with other tools to generate the most comprehensive results cost-effectively.
What is Qualitative Data Analysis?
Qualitative data analysis refers to the process of gathering and analyzing non-numerical data to identify themes, trends, strengths, and weaknesses to improve service quality and build more profitable business strategies.
Textual data reveals your business’s structure in a way that quantitative data cannot. It looks at factors that are not easily quantifiable, using logical reasoning and other tools to rank their priorities and interpret their meanings.
Common data collection methods for qualitative data analysis include:
- Customer surveys
- Interview transcripts
- Employee & user feedback
- Conceptual information on documents
For example, you can gather customer feedback on a new beauty product to try to refine the shopping experience for them. The survey responses can be valuable qualitative data that helps expose the shortcomings of the product like a lack of after-sale support or imperfect packaging.
Since qualitative research doesn’t usually offer clear benchmarks to follow as quantitative analysis does, interpreting qualitative data can be tricky. Your company will need experts to fully understand your qualitative research findings and make the best use of them.
There are five types of qualitative data analysis methods, namely content analysis, discourse analysis, thematic analysis, narrative analysis, and grounded theory analysis.
We’ll look into these research methods later in this article so you can fully grasp the usage and benefits of this tool.

Who Needs to do a Qualitative Data Analysis?
A qualitative analysis benefits essentially everyone in the business field. It can extract vital business information without complicated calculations, making it an ideal tool for small businesses or a startup without a huge budget.
Qualitative data can help foresee upcoming trends and the influence of external forces like political changes. It is crucial for companies to conduct qualitative research regularly to be aware of any non-numerical updates in the operations.
Qualitative research also benefits individuals like entrepreneurs, stock traders, and business students. You can utilize qualitative data to better understand your competitiveness and areas to work on to stay ahead of the game.
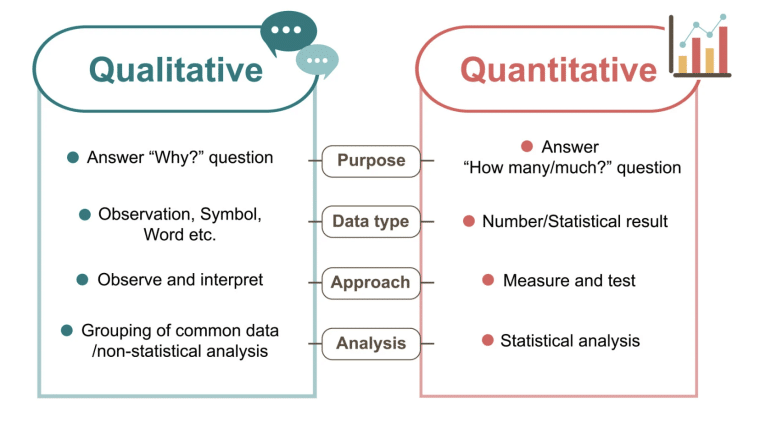
Quantitative vs Qualitative Data Analysis
In essence, quantitative data analysis deals with quantifiable data that is measurable and countable, whereas qualitative data analysis works with descriptive, and interpretation-based information.
Quantitative data often has a clear benchmark/target for companies to measure the outcomes. Some examples of quantitative data would include client satisfaction rates, return on investments, and turnover rates. The information is factual and not biased.
Quantitative data analysis studies these numbers, telling you the number and frequency of things. Since quantitative data does not involve personal judgment, it standardizes the analysis results and can be shared across the board more easily.
Qualitative data analysis looks at descriptive data that explains a situation, focusing on the written or spoken language that can’t be measured by numbers. Due to its descriptive nature, the results can be interpreted differently. Therefore, you need a team of reliable experts to analyze the logically collected data.
How to Conduct Qualitative Data Analysis
Qualitative analysis comes in handy when you want to evaluate the current state of your company and predict the effects of certain strategies you want to implement. As a business owner or decision-maker, you need to familiarize yourself with the procedures of qualitative data analysis so you can read and understand the results.
To perform a qualitative analysis, follow these five steps.
Step 1: Collect Qualitative Data
Choose your qualitative research objectives to focus on and collect raw data with reliable qualitative analysis methods like surveys or interviews. If you have several unrelated research objectives that target different areas of your business, it is better to conduct several qualitative data analyses to avoid generating misleading results.
Make sure the data collection process is unbiased. Gathering qualitative data randomly from your target pool is an excellent way to prevent your results from skewing to one side.
Step 2: Organize and Arrange Data
After the data collection step, you need to organize all the data in a meaningful way. You can sort the data points by connecting them to the research questions so the presentation is clear and easily readable.
You need to systematically group your data because unorganized data can complicate the analysis process, providing obstacles to analyzing data effectively.
Step 3: Assign a Code to the Qualitative Data
The coding process will condense a large set of data into manageable groups and will let you present the findings based on their characteristics. You can use qualitative data analysis software or do manual coding like labeling folders in a storage drive.
Managing data is a vital part of the data analysis process. If you have to adjust your qualitative research questions or the focus groups later, a methodically coded storage drive allows you to access actual data related to your project quickly.
Step 4: Analyze the Qualitative Data
Qualitative data is unstructured data that provides a deep understanding of the business environment. You need to look at the qualitative research data objectively to decipher its meanings and implications.
Connect the data back to the original research questions to identify patterns in the findings and how user behavior impacts your business.
Step 5: Draw Conclusions and Share the Results
The last step of a qualitative data analysis process is to conclude your research findings and share the results with your team of qualitative researchers or other stakeholders.
The report should be in readable format and clearly state the qualitative data analysis method used, findings, and limitations. Based on the results, discuss with your team about possible solutions to eliminate risks.
Five Qualitative Data Analysis Methods
There are five qualitative research methods that are highly useful in a business context.
Depending on your research objectives, choosing the right analysis method can provide valuable insights into your business operations and identify the next money-making strategy.
Content Analysis
Content analysis is one of the most popular qualitative methods widely adopted by companies to analyze their content quality. It analyzes content like videos, audio, texts, and graphics to find out how well the content is achieving its intended goals.
For example, you can use content analysis to break down the elements on your company website to see how well the color theme aligns with the brand and if the content is precise and concise.
The whole research process doesn’t require interactions with research participants, making content analysis simple and affordable to carry out. It is important to note that content analysis can be both quantitative and qualitative.-
Discourse Analysis
Discourse analysis dissects the power dynamics between factors, highlighting possible reasons for your audience to feel a certain way. This way, researchers can build a deep understanding of user behavior and formulate strategies to accommodate their needs accordingly.
Companies typically use the discourse analysis method to answer the research question about brand recognition to learn about why users perceive the brand this way.
Thematic Analysis
Thematic analysis collects crucial information from all the data available to identify patterns. User experience (UX) designers often rely on thematic analysis to break down customer feedback. This analysis method can expose patterns like poor website loading speed and responsiveness for engineers to work on.

Narrative Analysis
Narrative analysis analyzes users’ feelings towards the brand based on research participants’ stories like product reviews, testimonials, and other qualitative feedback.
Through narrative analysis, you can learn about your users’ motivations and expectations for your brand. With narrative analysis results, you can personalize the shopping experience to enhance customers’ willingness to return.
Grounded Theory Analysis
Grounded theory analysis produces theories about the current state by analyzing the textual data. Researchers can collect data from surveys or reports and build theories based on the findings.
Businesses that adopt grounded theory analysis to try to explain certain situations like high turnover rates. This type of qualitative research highlights possible reasons contributing to these situations and why something happens.
Examples of Qualitative Data Analysis
Qualitative data analysis methods should penetrate every business sector and production step so that every flaw or inefficiency can be optimized. Utilizing qualitative data in your research process can significantly enhance performance and lead to more sales.
Here are three real-life examples of using qualitative analysis for your firm.
Example 1: Use Qualitative Research to Improve a Company’s Image
Let’s say you are the head of the marketing team working on a research project about improving the company’s image. To achieve this goal, you can conduct a narrative analysis to understand why your audiences perceive your company in a certain way.
Set an appropriate qualitative data collection method. You can gather qualitative feedback from customer social media stories and investigate the content your audiences interact with the most on social media and other channels. The narrative analysis results may reveal the audience’s preferences for young brands. Then, you can construct your marketing models accordingly to refine the company’s image.
Example 2: Use Discourse Analysis to Identify Trends
You’re a fashion designer and have noticed a growing “boho” trend among 30-something women. Discourse analysis allows you to dive deep into your clients’ preferences, knowing how this style speaks to them and how you can design similar products to their liking.
With discourse analysis, you can identify themes and seize the opportunities to develop products before everyone else.
Example 3: Use Content Analysis to Align Company Vision
Content analysis is a magnificent tool that puts your current content under the microscope. For example, if you run a meditation studio, you’re likely looking to establish a brand that emphasizes inner peace and harmony.
Therefore, you can analyze qualitative data like fonts, graphics, and colors that you use. In this case, they should be neutral and easy on the eye to appeal to your audience. A content analysis points out the weaknesses in the current settings so you can make adjustments based on the results.
How to Adjust Qualitative Data Analysis
In this fast-paced business world, making adjustments to a qualitative analysis is common. Companies update their qualitative analysis process regularly so it reflects the business reality and minimizes the risks of making human mistakes.
If you want to update your research questions or change the qualitative data analysis method, you’ll need to collect data again so the results are time-sensitive.
Check to see if you have to update the qualitative data collection process as well and find new channels and sources. If not, you can distribute the same customer feedback survey or use any appropriate data type for this study.
Check the data collected and construct a new qualitative data analysis using your chosen analysis method.
When you adjust one part of the qualitative data analysis, it will most likely affect the subsequent steps as well. Updating your research project can be complicated but given its benefits, it is vital to refresh the analysis when necessary.
Limitations of Qualitative Data Analysis
Qualitative data analysis methods are beneficial in constructing your business model. However, there are a few major drawbacks to this technique that you should take into consideration when reading the results.
The Results Will Often be Subjective
Unlike quantitative data analysis with set standards, qualitative data is contextual information that can be interpreted differently by individuals. A firm may struggle to explain the findings to potential investors if their values do not align.
It takes professional qualitative researchers to objectively analyze the data collected, generating the most unbiased reports for the business. If a firm lacks capable hands that can read and interpret qualitative data, the misleading results could be catastrophic to operations.
It Can be Time-Consuming
Collecting non-numerical data is time-consuming. From designing a suitable research question and choosing the right analysis method to distributing customer surveys and analyzing the data collected, the entire process can take weeks or even months.
The long process is not suitable for companies looking for quick solutions to address an immediate issue.
It Needs to be Updated Regularly
Since qualitative data analysis deals with the current shortcomings in the product and possible threats for the future, it needs to be updated frequently to produce relevant results. Constantly conducting entire analyses is not only time-consuming but also expensive. It can be challenging for firms without sufficient funding or resources to fully utilize this technique.
The Value of Qualitative Data Analysis
Qualitative data analysis builds the foundation for business development and paves the way for further analyses. With the results, qualitative researchers and decision-makers can evaluate and compare different strategies to best prepare the business for future endeavors. It is a vital tool that should be incorporated into the decision-making process.
A strong analysis could also be used to optimize marketing and branding strategies to help you connect with your loyal customers, prospective customers, and stakeholders. By gathering opinions, you not only gain valuable information that you can implement feedback into your business, but you can also improve your customer relations by letting your community know their input and opinions are valued and heard.
When conducting a qualitative data analysis, you need to be mindful of its limitations. The best way is to adopt other analytical tools like quantitative research techniques to cover aspects overlooked by the qualitative methods.