With a legacy spanning nearly two centuries, John Deere (Deere & Company) is a world leader in agriculture and construction manufacturing.
As of November 2024, John Deere’s net worth is $110.16 billion, reflecting its market leadership and global impact.
Our experts at Business2Community scoured an array of sources to craft a comprehensive overview of John Deere’s net worth and journey from its humble beginnings as a plow manufacturer. Read on to discover the company’s key milestones, controversies, and more.
John Deere Key Company Data
John Deere Net Worth: $110.16 billion
Date Founded: 1837
Founded By: John Deere
Current CEO: John C. May
Industries: Agriculture, machinery manufacturing, financial services
John Deere Stock Ticker: NYSE: DE
Dividend Yield: 1.46%
John Deere HQ: Moline, Illinois
What Is John Deere’s Net Worth?
As of November 2024, John Deere has a net worth, also known as market market cap, of $110.16 billion. This is based on a share price of $402.65 and 279 million shares outstanding.
John Deere’s fiscal year ends on October 31 and the company typically releases its annual financial results in late November or December of the same year. In addition, John Deere’s financial results are also released quarterly, in February (Q1), May (Q2), August (Q3), and November (Q4).
Since December 1998, John’s Deere’s net worth has increased by 1,231% from $8.2 billion to over $112 billion, reflecting the company’s continued expansion and leadership in agriculture and heavy machinery. This strong growth trajectory began early, with John Deere surpassing the $1 billion revenue mark in 1967.
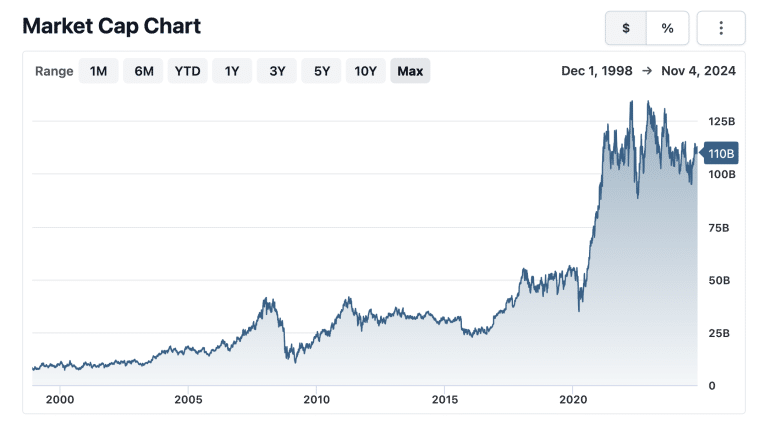
John Deere’s shares have also appreciated significantly. From a share price of around $29 in November 1997, the stock is now valued at $402 as of November 2024 — an impressive 1,317% return over 26 years.
In 2020, John Deere’s share price hit record levels, with shareholders realizing a total return of over 30%, compared to a 10% return for the broader market.
John Deere stock’s all-time high is $438.28, achieved in July 2023. Between January 2021 and August 2024, the company’s shares increased by 50% from $255 to around $380, in line with gains seen in the S&P 500 over the same period.
John Deere Revenue
Financial data related to John Deere’s first 118 years isn’t publicly available. However, in 1955, when the company joined the Fortune 500 list, John Deere reported revenues of $295.6 million.
Over the next decade, operations accelerated, with John Deere generating $1 billion in net sales in 1967. By 1978, revenue had more than tripled to $3.6 billion, reflecting the strong demand for its products.
After recovering from the 1980s farm crisis, the company achieved revenues of $7.2 billion with $380 million in net income in 1990, before reaching record earnings of $960 million in 1997.
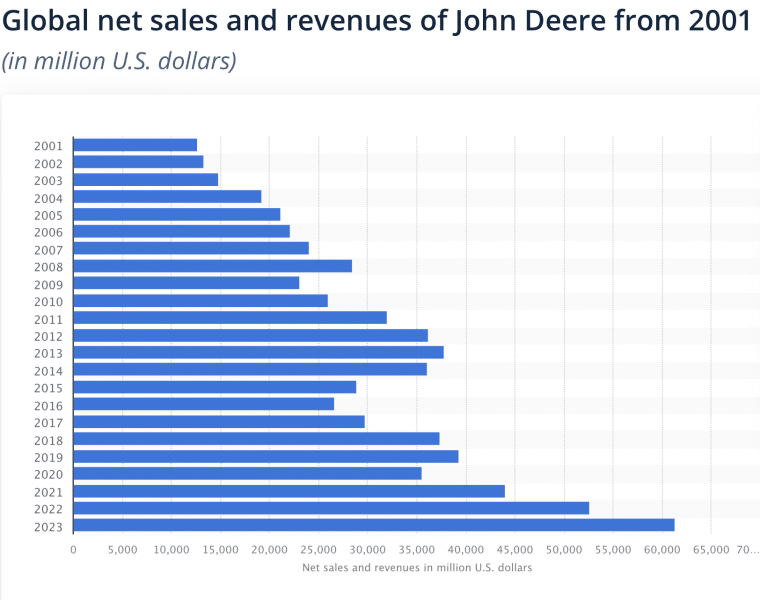
John Deere entered the new millennium with revenues of $11.7 billion and profits of $239 million before its net sales nearly doubled to $21 billion by 2005.
While revenues in 2009 dipped to 2007 levels during the global financial crisis, they rebounded strongly to $32 billion by 2011. By 2019, John Deere’s revenue had grown to $39 billion, representing a 22% increase over 8 years.
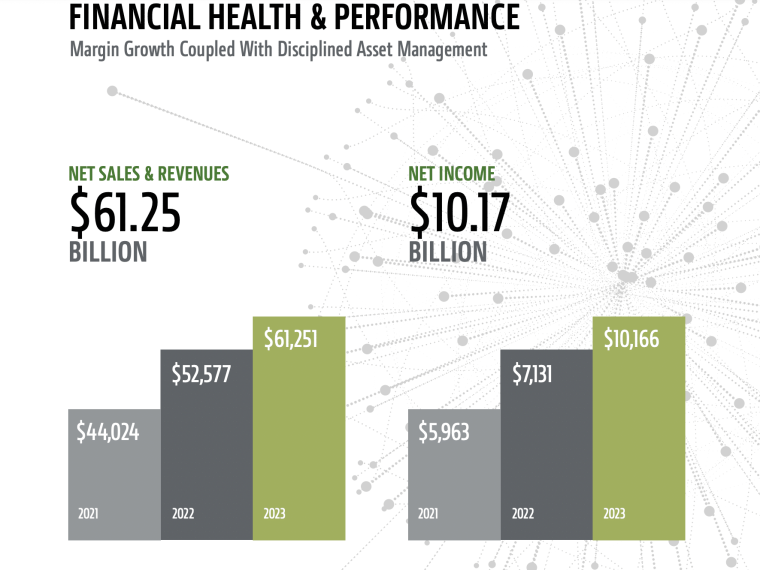
Though revenues briefly fell to $35 billion in 2020 due to pandemic-related disruptions, the company achieved notable post post-pandemic growth, with revenues of $44 billion in 2021, $52.6 billion in 2022, and $61.3 billion in 2023.
For the first nine months of 2024, net income attributable to Deere & Company was $5.85 billion, or $21.04 per share, compared with $7.79 billion, or $26.35 per share, for the same period last year.
| Year | Revenue ($ billions) | Net Income ($ billions) |
|---|---|---|
| 2013 | 37.8 | 3.54 |
| 2014 | 36.1 | 3.16 |
| 2015 | 28.9 | 1.94 |
| 2016 | 26.6 | 1.52 |
| 2017 | 29.7 | 2.16 |
| 2018 | 37.4 | 2.37 |
| 2019 | 39.3 | 3.25 |
| 2020 | 35.5 | 2.75 |
| 2021 | 44.0 | 5.96 |
| 2022 | 52.6 | 7.13 |
| 2023 | 61.3 | 10.17 |
John Deere Dividend History
John Deere has a long history of paying dividends, and over the past two decades alone, has spent more than $43 billion on stock buybacks and dividends.
As of November 2024, John Deere had a trailing twelve-month (TTM) dividend payout of $5.88 along with a dividend yield of 1.46%.
The company has had a total of 8 stock splits, with the last one being in November 2007.
| Date | Stock Price ($) | Dividend ($) | Yield (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 11/06/2019 | 163.30 | 2.83 | 1.73 |
| 03/30/2020 | 133.13 | 2.84 | 2.14 |
| 06/29/2020 | 145.61 | 2.86 | 1.96 |
| 09/29/2020 | 209.30 | 2.87 | 1.37 |
| 12/30/2020 | 253.72 | 2.88 | 1.14 |
| 03/30/2021 | 357.32 | 3.03 | 0.85 |
| 06/29/2021 | 334.30 | 3.17 | 0.95 |
| 09/29/2021 | 337.16 | 3.46 | 1.02 |
| 12/30/2021 | 329.68 | 3.74 | 1.14 |
| 03/30/2022 | 401.55 | 3.90 | 0.97 |
| 06/29/2022 | 291.62 | 4.13 | 1.42 |
| 09/29/2022 | 331.85 | 4.22 | 1.27 |
| 12/29/2022 | 418.31 | 4.38 | 1.05 |
| 03/30/2023 | 395.19 | 4.59 | 1.16 |
| 06/29/2023 | 394.38 | 4.72 | 1.20 |
| 09/28/2023 | 379.11 | 4.95 | 1.31 |
| 12/18/2023 | 394.88 | 5.24 | 1.33 |
| 03/27/2024 | 406.11 | 5.47 | 1.35 |
| 06/28/2024 | 372.32 | 5.71 | 1.53 |
| 09/30/2024 | 417.33 | 5.85 | 1.40 |
| 11/05/2024 | 400.37 | 5.85 | 1.46 |
Who Owns John Deere?
As a publicly traded company, John Deere is owned by various shareholders. The largest shareholder as of June 30, 2024, was the Vanguard Group with an ownership stake of 7.94%. This was followed by BlackRock Inc. (5.98%) and JP Morgan Chase & Company (4.13%).
John Deere’s origins date back to 1837 when John Deere invented the self-scouring steel plow. Following key partnerships, the company grew and was incorporated as the Deere Company in 1868. During the early 1900s, John Deere ventured into harvesting equipment, tractors, and engines.
The company’s preferred stock debuted on the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) under the ticker symbol DE in 1912. In 1958, Deere & Company was incorporated as John Deere–Delaware Company and officially assumed the name John Deere.
Who is the John Deere CEO?
John May is the Chairman and chief executive officer (CEO) of John Deere. Appointed in 2019, May has focused on executing the company’s Smart Industrial Strategy and preserving John Deere’s legacy of manufacturing excellence.
Under his leadership, John Deere’s net worth has more than doubled, crossing the $100 billion mark for the first time.

In 2023, May had a total yearly compensation of $26.72 million, comprising 6% salary, 94% bonuses, and company stock and options. The CEO also directly owned 0.039% of the company’s shares, worth $42.44 million.
Over its 187-year history, John Deere’s leadership has held strong through ten successive leaders, including five generations of the Deere family.
These visionaries have focused on upholding the core values of integrity, quality, humanity, commitment, and innovation.
They have also contributed to John Deere’s consistent growth and allowed the company to successfully adapt to changing agricultural and industrial markets.
| Year | CEO |
|---|---|
| 1837-1886 | John Deere |
| 1886-1907 | Charles Deere |
| 1907-1928 | William Butterworth |
| 1928-1955 | Charles Deere Wiman |
| 1955-1982 | William Hewitt |
| 1982-1990 | Robert Hanson |
| 1990-2000 | Hans Becherer |
| 2000-2009 | Robert Lane |
| 2010-2020 | Samuel R. Allen |
| 2019-Present | John May |
Who Is the John Deere CTO?
In June 2024, John Deere appointed its first-ever Chief Tractor Officer or CTO, Rex Curtiss, to create content for its social media channels, including a brand new TikTok channel. His title is a bit confusing, especially because John Deere already had a CTO or Chief Technology Officer, but they are totally unrelated roles.

As a recent Environmental Studies graduate, Curtiss brings a deep passion and knowledge of the industry that aligns with John Deere’s mission. The new CTO also comes from a family of fourth-generation farmers and has worked closely with local food systems in his community.
In his first few months in office, Curtiss has focused on showcasing the people, systems, and industries that power the Deere brand.
The John Deere TikTok account had over 500,000 followers and 5.9 million likes. One post, in particular, features the largest John Deere tractor ever built and has since amassed over 42 million views.
@johndeere it’s a Farm Progress Show iykyk
John Deere’s Company History
John Deere (Deere & Company) is a global leader in the production of agricultural, construction, and forestry equipment and solutions. The company’s operations are managed through the following four business segments:
- Production and precision agriculture (PPA): Develops global equipment and technology solutions for production-scale growers of large grains, small grains, cotton, and sugar.
- Small agriculture and turf (SAT): Produces global equipment technology solutions to unlock value for dairy and livestock producers, high-value crop producers, and turf and utility customers.
- Construction and forestry (CF): Provides machines and service parts used in construction, earthmoving, road building, material handling, and timber harvesting.
- Financial services (John Deere Financial or FS): Finances sales and leases by John Deere dealers of new and used heavy equipment, turf equipment, construction equipment, and forestry equipment.
Where Is John Deere Based?
John Deere’s headquarters is in Moline, Illinois, USA. This location serves as the center of the company’s operations, overseeing corporate and manufacturing strategy.
Globally, John Deere has over 82,000 employees. In the US alone, the company employs approximately 30,000 people in more than 60 US-based facilities across 16 states.
More than 75% of all John Deere products are assembled at US-based manufacturing facilities. Key locations include:
- Waterloo, Iowa
- Horicon, Wisconsin
- Dubuque, Iowa
- Augusta, Georgia
The company also manufactures tractors, agriculture equipment, and other John Deere products in various locations around the world including:
- Mannheim, Germany
- Pune, India
- Montenegro, Brazil
- Rosario, Argentina
Below, we run through John Deere’s journey to becoming a manufacturing giant and leading agriculture company.
1837-1907: John Deere Breaks Ground
In 1837, John Deere invented the self-scouring steel plow from a broken steel saw blade. Deere built two more plows the next year, followed by 10 more in 1839. In 1843, Deere officially entered the plow business through a partnership with local businessman Leonard Andrus.

Five years later, in 1848 Deere formed a partnership with Robert Tate and John Gould. The trio moved and took their operation from Grand Detour to Moline (which are both in Illinois). By 1850, their state-of-the-art factory was in operation, doubling the production rate to over 2,000 plows.
In 1852, Deere, Tate, and Gould dissolved their partnership, leaving Deere to work as a sole proprietor for the first time in nearly a decade. In 1868, Deere incorporated the business as Deere & Company.
Following John Deere’s death in 1886, his son Charles Deere took over. Charles Deere established the Deere company’s modern-day marketing centers and ventured into producing steel plows, cultivators, corn and cotton planters, and more.
1908-1955: John Deere Launches a Full-Lineup
From 1908, the company underwent a reorganization to create a more modern and diversified Deere & Company. 1910 saw the company consolidate branches and manufacturing operations. It also began a series of acquisitions to mark its entry into harvesting and produce a full line of agricultural products.

In 1912, the company expanded into the tractor business and found immediate success in the harvester market. By the end of the year, Deere & Company had 15 manufacturing facilities, 24 sales branches, and a Moline-based export department.
Deere & Company acquired the Waterloo Gasoline Engine Company for $2.25 million in 1918, solidifying its leadership in the tractor business. Under the leadership of John Deere’s great-grandson, Deere & Company persevered, successfully launching the Model A and B tractors during the Great Depression (1929-1941).
1956 -1989: John Deere Expands Globally
In 1956, John Deere took the company’s operations overseas. This initially included a manufacturing plant in Mexico and the acquisition of Heinrich Lanz, a German tractor and combine manufacturer. A factory was also constructed in northern Rosario, Argentina in 1958. By 1959, John Deere had created its Industrial Equipment division, along with dealerships and a full line of construction equipment.
In 1960, the company revealed four new models of four- and six-cylinder tractors to John Deere dealers from around the world on Deere Day in Dallas, Texas. Three years later, John Deere launched its Consumer Equipment division offering lawn and garden tractors and attachments like mowers and snow blowers.
1964 saw John Deere unveil its corporate headquarters in Moline. The company also generated $639 million in revenue, overtaking competitors like Caterpillar to become the global sales leader in agriculture and industrial equipment.
Throughout the 1970s, John Deere’s revenues soared, hitting $4.9 billion in 1979. However, the 1980s proved challenging due to the crippling farm crisis. Then Chairman and CEO Robert Hanson successfully led the company through inflation, low employee morale, and declining sales.
Hanson also championed the company’s diversification efforts, forming John Deere Health Care in 1985. In 1986, John Deere reported a $229.3 million loss, prompting company-wide restructuring. As the company focused on its core competencies, sales picked up, reaching $5.4 billion by the end of 1989.
1990-2009: John Deere’s Revenue Soars
1991 marked the formation of a Worldwide Commercial & Consumer Equipment Division. By 1997, John Deere had launched notable products including the Gator, 7760 Cotton Harvesters, and 8000 series tractors. That year, it reported net sales of $11.3 billion and record profits of over $960 million.

In 1999, John Deere acquired Timberjack Group, the world’s largest producer of forest harvesting equipment for $600 million. Between 2000 and 2008, the company’s revenues more than doubled from $11.7 billion to $28.4 billion.
After 2008, John Deere made several acquisitions and adopted standardized processes. It also made major investments in other markets such as Brazil, Russia, China, and India. These strategic moves paid off, helping the company remain profitable through the global recession.
2010-2019: John Deere Prioritizes Global Growth and Technology
In 2011, the company reported revenues of $32 billion, up 23% year-over-year. Over the next few years, John Deere focused on acquisitions to grow its key segments.
In 2013, John Deere acquired the Planter manufacturer, Bauer Built Manufacturing for $84 million. It then acquired Brazilian onboard technology company, Auteq Telematica in 2014. This was followed by the Precision Planter in 2015.

2017 saw the company make some of its largest acquisitions ever. John Deere acquired German construction equipment company Wirtgen Group for $5.2 billion, doubling the size of its construction and forestry workforce. It also acquired AG computer-vision and machine-learning tech startup Blue River Technology for $305 million.
By 2019, the company had expanded its global footprint, increased its customer base, and upgraded its product lines by focusing on innovation. That year, Deere & Company reported net sales and revenues of over $39.3 billion, marking an impressive five-year high.
2020- Present: John Deere Launches Smart Industrial Strategy
Despite ongoing challenges associated with the pandemic, John Deere delivered strong financial results in 2020. Notably, profitability measured by operating return on sales reached its highest level since 2014.

In 2021, John Deere intensified its commitment to technology, speed, and efficiency with the launch of its Smart Industrial Operating Model. This operating plan aimed to create intelligent, connected machines that enhance profitability and sustainability across industries.
That same year, to support its new strategy, John Deere introduced the fully autonomous 8R tractor. The company acquired Bear Flag Robotics for $250 million as well as Guss Automation and AgriSync for $124 million.
By the end of 2023, John had made other acquisitions related to its tech-forward strategy. This included Kreisel Electric Inc., a leading pioneer in the development of immersion-cooled battery technology along with Smart Apply, Inc., a precision spraying equipment company. Highlighting the success of its strategy, the company reported net income of $10.2 billion and record revenues of $61.3 billion for 2023, up 73% from $35.5 billion in 2020.
John Deere Controversies
Below, we run through John Deere’s most recent controversies.
John Deere Bribery Scandal
In September 2024, the SEC fined John Deere $10 million over a bribery scheme involving its subsidiary, Wirtgen Thailand. Investigations revealed that after being acquired by John Deere in 2017, Wirtgen bribed officials at the Royal Thai Air Force and the country’s transportation agency through cash payments, massage parlor visits, and international travel.
These actions, which violated the Foreign Corrupt Practices Act, continued through 2020 and resulted in over $4.3 million in profit.

In an official statement, John Deere officials said the matter was a clear violation of the company’s policies and ethical standards.
The allegations are in direct conflict with our core values — particularly our commitment to — and we strongly condemn such practices. The individuals involved in this matter are no longer with the company.
John Deere Layoffs
Between October 2023 and September 2024, John Deere laid off over 3,000 employees, sparking outrage and accusations of corporate greed. Workers and unions criticized the company’s actions, pointing to high profits, generous payouts to investors, and steep CEO compensation as signs that the layoffs were unjustified and actually aimed at shifting production to Mexico.
In September 2024, former President Donald Trump announced that, if re-elected, he would impose a 200% tariff on John Deere’s imports should the company follow through with its plan to move its production to Mexico. Now that Trump won the election, Deere is likely reconsidering the move already.
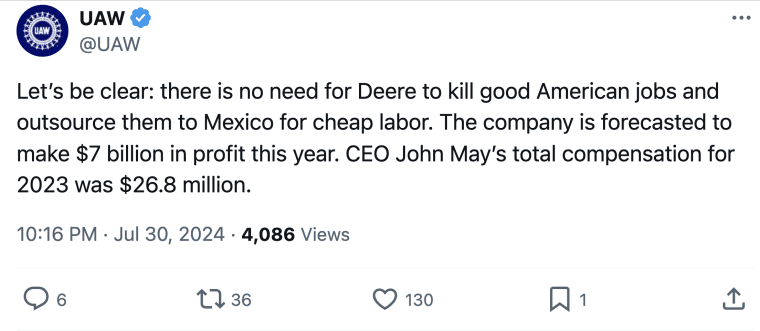
The following month, John Deere announced more layoffs, further raising workers’ frustrations. However, the company maintained that these layoffs were not due to production being moved to Mexico but rather reduced demand and a 20% decline in sales.
What Can We Learn From John Deere?
John Deere’s success highlights the power of identifying a need, creating a solution, and continuously improving it to create more value. By revolutionizing farming efficiency, John Deere has established a legacy of innovation and emerged as a global leader in machinery and equipment manufacturing.
The company’s market leadership demonstrates how a strong brand and a global market presence can be a key source of competitive advantage. Through strategic acquisitions and innovation, John Deere has consistently outpaced competitors while expanding its reach.
John Deere’s resilience and long-term value creation highlight the power of a diversified product portfolio. By catering to various industries, the company has reduced its reliance on a single industry and remained profitable through market fluctuations.
While John Deere has historically upheld strong values, ethics, and corporate governance, recent controversies involving bribery and corporate greed have tarnished the company’s reputation. This underscores the importance of maintaining ethical business practices and corporate integrity.