In today’s interconnected world, individuals have increasingly relied on technology for activities ranging from communication and information access to entertainment, productivity, and everyday essentials like banking. Meanwhile, businesses increasingly rely on technology to drive their operations and facilitate communication.
While this digital revolution has brought numerous benefits, it has also exposed individuals and organizations to the ever-looming threat of cybercrime. Cyberattacks have emerged as a pressing concern, capable of widespread chaos in businesses of all sizes and industries. To truly comprehend the gravity of this issue, it is essential to explore the world of cyberattack statistics. By understanding how frequently these attacks occur, we can gain valuable insights into the magnitude of the challenge and why it demands our utmost attention.
Cyberattacks Key Stats
How Many Cyberattacks Happen Per Day?
Studies conducted by the University of Maryland’s A. James Clark School of Engineering have revealed that over 2,200 cyberattacks happen daily.
Furthermore, the study disclosed that someone becomes a victim of a data breach, phishing attack, or other cybercrime attack approximately every 39 seconds.
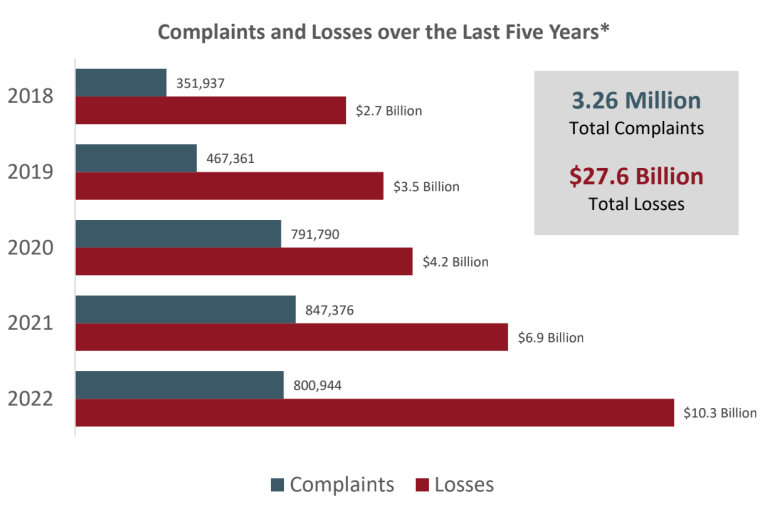
According to the FBI’s Annual Internet Crime Report (FBI IC3), the public collectively filed 800,944 cyberattack complaints in 2022.
Given the annual amount of complaints filed, the average number of cyberattacks equated to 2,450 every day.
Since 2018, the IC3 has consistently received an average of approximately 1,787 cybercrime complaints per day.
These incidents, amounting to a total of 652,000 complaints annually, encompass a wide range of internet scams that affect victims worldwide.
The potential total loss due to cyberattacks has experienced a notable surge since 2018, averaging approximately $27.9 million daily.
This dollar figure significantly increased from $6.9 billion in 2021 to $10.2 billion in 2022.
On average, there have been over 1,297 cybercrime attacks daily from 2018 to 2022, with a cumulative count reaching 3.26 million.
Consequently, this has led to a substantial total loss of approximately $20.5 million daily, amounting to $27.6 billion annually.
Cyberattack Statistics by Attack Type
The daily average of reported complaints for phishing attacks stood at approximately 822 incidents in 2022.
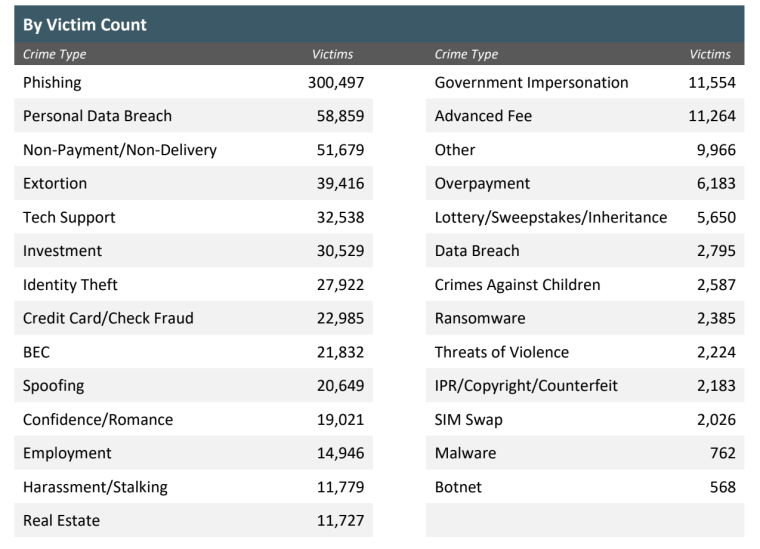
According to the FBI’s IC3 report, phishing attacks were the most widespread crime type, with 300,497 reported complaints.
Phishing attacks continue to prevail as the top form of cyber attack, with approximately 3.4 billion spam emails sent daily.
Based on Norton’s statistics, spear phishing attacks are encountered by approximately 88% of organizations within a year, implying that businesses face targeted cyberattacks nearly daily.
Investment fraud in cybercrime saw an astounding 127% rise, with losses skyrocketing from $1.45 billion in 2021 to $3.31 billion in 2022.
This equates to a daily average increase of approximately $4.5 million in reported losses.
Additionally, the daily average for cryptocurrency investment fraud significantly surged, reaching approximately $4.4 million.
The total sum soared from $907 million in 2021 to $2.57 billion in 2022, representing a remarkable increase of 183%.
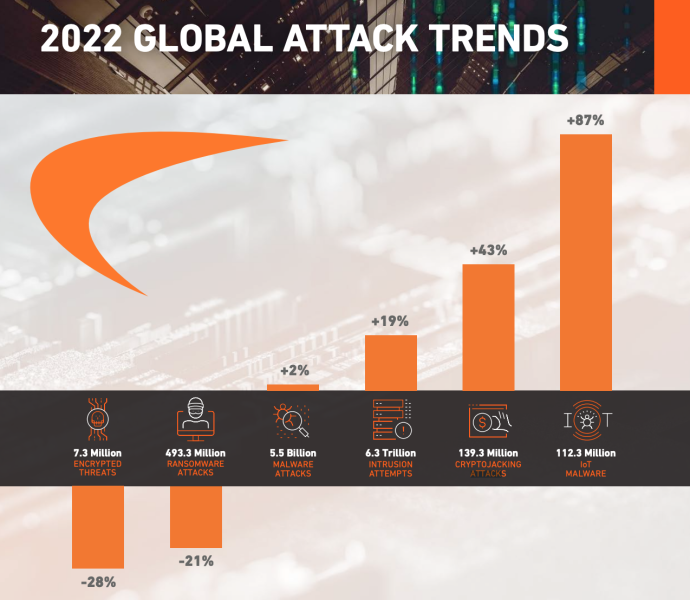
According to SonicWall’s report data, in 2022, intrusion attempts amassed a total of 6.3 trillion attacks globally, averaging around 17.26 billion daily attacks.
Simultaneously, malware attacks accounted for a significant total of 5.5 billion attacks, with an average daily malware attack frequency of approximately 15.07 million.
As the number of connected devices continues to rise, there has been a significant surge in IoT malware instances.
IoT malware demonstrated a remarkable year-on-year increase, with a daily average surge of 238.36%.
The total number of ransomware attempts in 2022 reached 493.3 million, averaging around 1.35 million daily attempts.
This reflects a significant decline of 21% compared to 2021. In contrast, there was a 62% increase in 2020, followed by an additional surge of 105% in 2021.
Where Do Cyberattacks Happen?
Cyberattacks can originate from various locations across the globe, showcasing the borderless nature of this digital threat. Attackers may launch their malicious activities from countries known for harboring cybercriminals or utilize anonymous networks to hide their true origins.
The ever-expanding reach of the internet enables cybercriminals to launch attacks from virtually anywhere, emphasizing the need for robust cybersecurity measures, regardless of geographical boundaries.
In 2022, the US reported that 479,181 individuals were affected by cybercrime attacks, claiming the leading position globally, according to the FBI IC3 report.
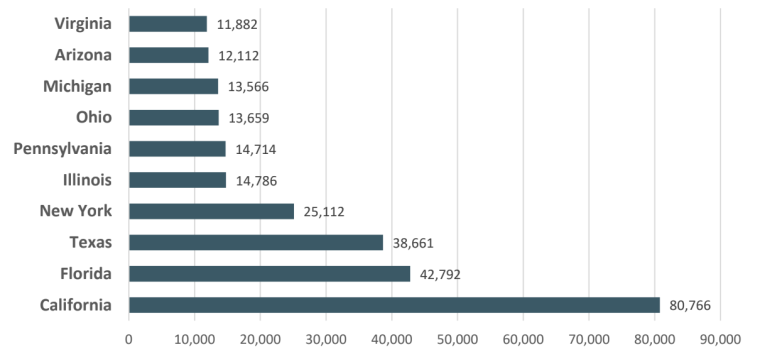
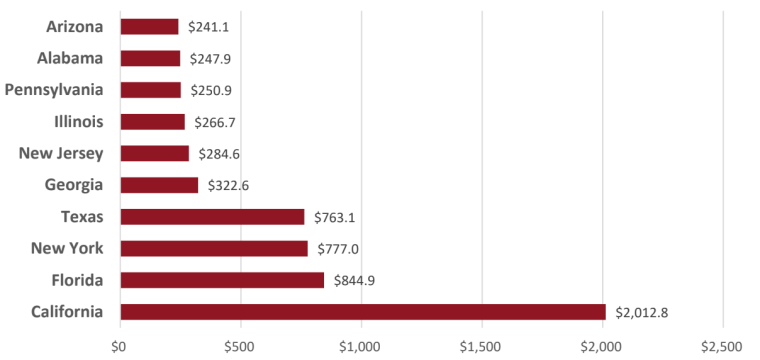
With a total of 80,766 individuals affected, California emerged as the state with the highest number of cybercrime victims, resulting in substantial financial losses amounting to $201 billion.
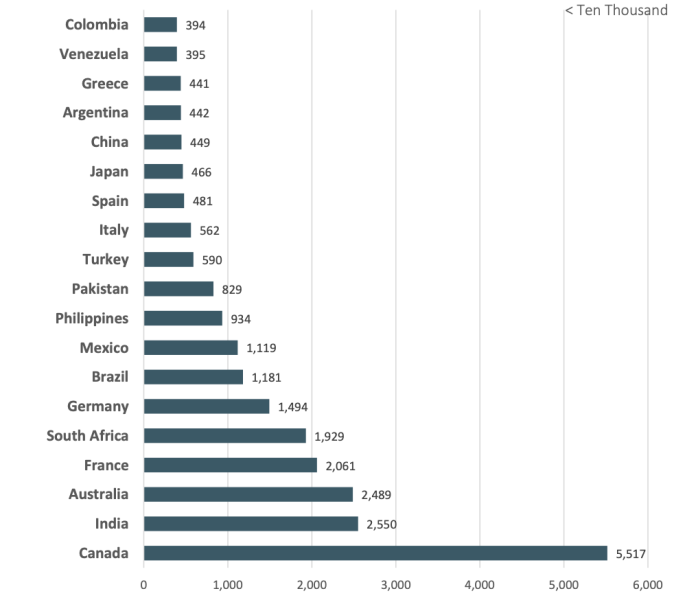
Following the US, the UK ranked as the second top country in terms of cyberattack victims, with a substantial total of 284,291 people affected by cybercrime incidents.
The chart below compares the US and the UK with the top 20 countries based on the total number of victims.
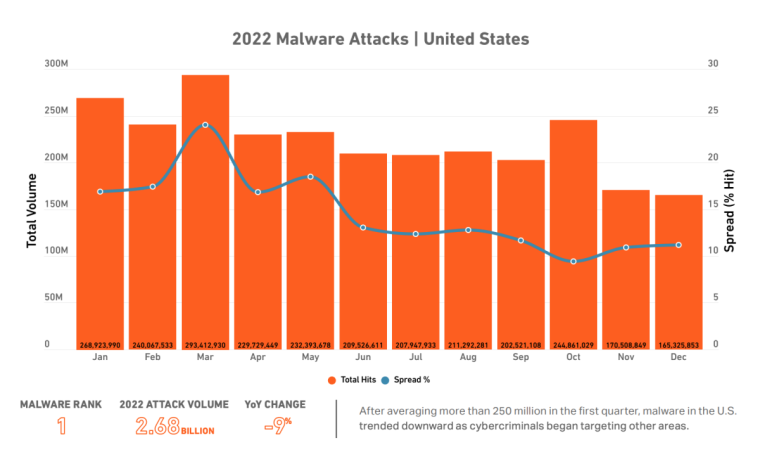
The US also claimed the top position on SonicWall’s cyberthreat list, reporting the highest volume of malware attacks, reaching a total of 2.68 billion.
However, there has been a year-over-year decrease of 9% in malware instances, suggesting a shift in cybercriminals’ focus toward targeting countries other than the US.
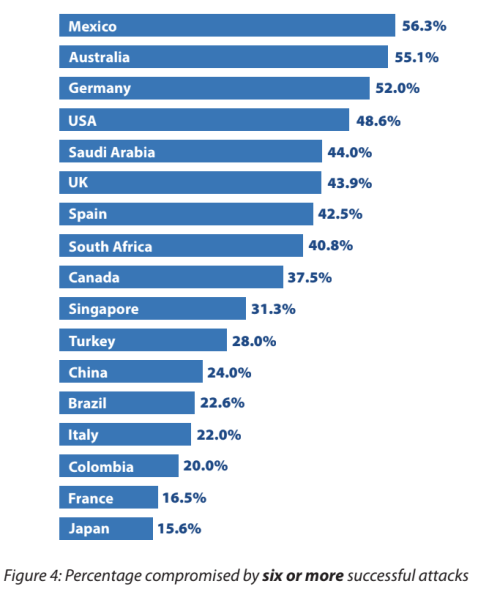
A cyber threat defence report (CDR) uncovered three countries where over half of the organizations reported six or more successful cyberattacks in 2022.
Mexico topped the list with 56.3%, followed by Australia at 55.1%, and Germany at 52%. Meanwhile, in the US, the percentage was just below half, with 48.6% of organizations experiencing six or more successful cyberattacks.
The Origin of Cyberattacks
According to an article released by the BBC, 74% of all profits generated from ransomware attacks in 2021 were acquired by hackers linked to Russia.
Furthermore, researchers discovered that over $400 million in cryptocurrency payments were made to groups that are highly likely to be associated with Russia.
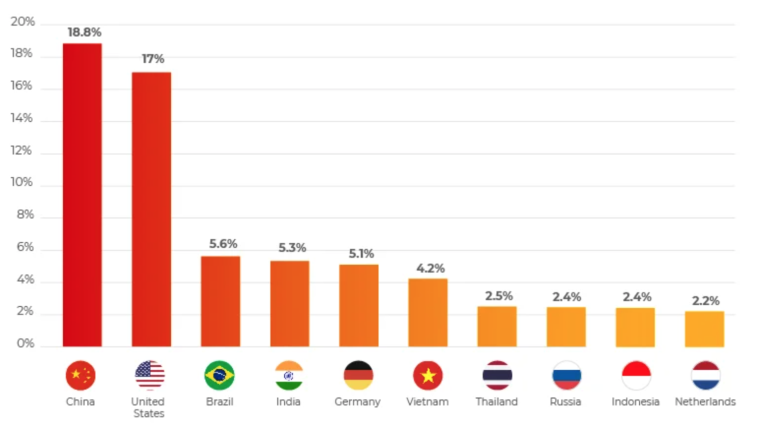
After analyzing IP addresses and geolocation data from feeds in 2021, CyberProof researchers devised a method to assess countries’ involvement in cybercrime.
The findings revealed that China accounted for 18.8% of the observed cyberattacks, with the US following closely at 17%, and Brazil securing the third position with 5.6%.
According to an alternative source, China and Russia have emerged as dominant players in the cybersecurity landscape, collectively accounting for nearly 35% of global attacks.
A total of 79 confirmed attacks on national governments were traced back to China, while 75 attacks were attributed to Russia.
Following them are North Korea and Iran, jointly responsible for 16% of worldwide attacks, with the US trailing behind, accounting for 3% of global attacks.
North Korean hackers had a remarkable year in 2021, reportedly absconding with $400 million in cryptocurrency.
Who Are the Victims of Cyberattacks?
Cybercriminals target many victims, including individuals, government institutions, financial institutions, healthcare providers, and even critical infrastructure sectors, seeking to exploit vulnerabilities for financial gain, data theft, or disruptive purposes.
The impact of cybercrime extends across various ages.
However, the 60+ age group has the highest number of victims and financial losses, as evidenced by 88,262 individuals affected and losses totaling $3.1 billion.
Age
Victim Complaints
Financial Losses
Under 20
15,782
$210.5 million
20-29
57,978
$383.1 million
30-39
94,506
$1.3 billion
40-49
87,526
$1.6 billion
50-59
64,551
$1.8 billion
60+
88,262
$3.1 billion
Cyberattacks Against Industry
Overall, critical infrastructure organizations encountered an average data breach cost of $4.82 million, surpassing the average cost across other industries by $1 million.
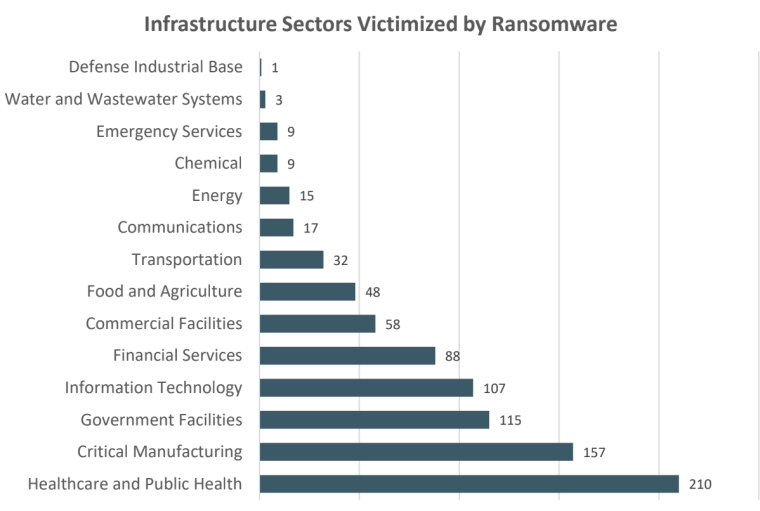
As per the FBI’S IC3 report, the healthcare and public health sector took the hardest hit of ransomware attacks in the US, experiencing 210 incidents.
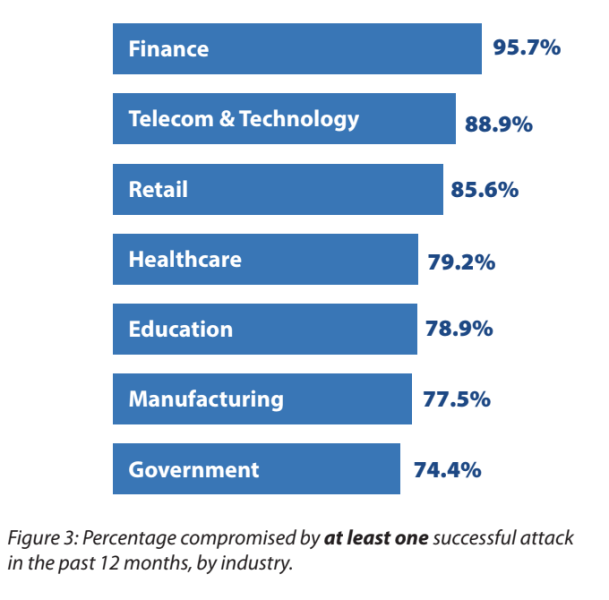
An alternative source suggests that the finance sector emerged as the most victimized among the seven major industries surveyed in 2023.
95.7% of organizations within the finance industry reported experiencing a successful cyberattack within the past 12 months.
On a positive note, the education sector displayed significant improvement, with a notable decline from 90.5% in the 2022 survey to 78.9% in the latest assessment.
The IC3 recorded a total of 2,385 complaints in 2022 specifically attributed to ransomware attacks on organizations, resulting in adjusted losses exceeding $34.3 million.
870 complaints received by the IC3 pointed to ransomware attacks targeting organizations in critical infrastructure sectors.
Cyberattacks Against Business
During 2022, the IC3 received 21,832 complaints related to business email compromise (BEC), which resulted in adjusted losses exceeding $2.7 billion.
BEC cyberattacks progressed beyond the initial stages of hacking or spoofing business and personal email accounts, now encompassing more advanced techniques. For example, fraudulent requests to transfer funds to illegitimate bank accounts.
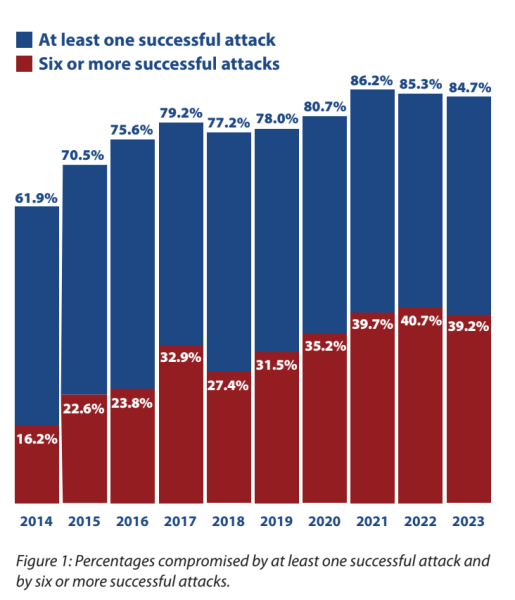
According to CyberEdge, the percentage of organizations experiencing at least one successful cyberattack has slightly declined since 2021.
It decreased from 86.2% in 2021 to 85.3% in 2022 and further down to 84.7% in 2023.
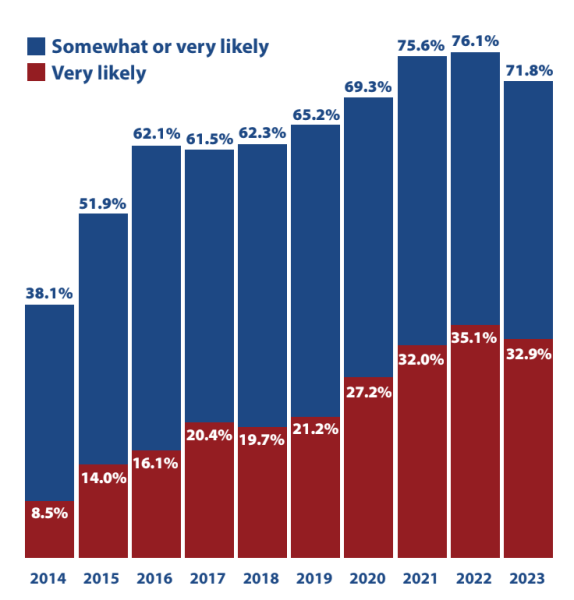
The figures for the likelihood of a cyberattack decreased as well, with 71.9% of organizations acknowledging that their network had experienced a successful cyber attack to some extent in 2023.
There was a year-on-year decrease of approximately 3.25% in the likelihood of a cyberattack, as it decreased from 75.6% in 2021 to 76.1% in 2022, and further down to 71.85% in 2023.
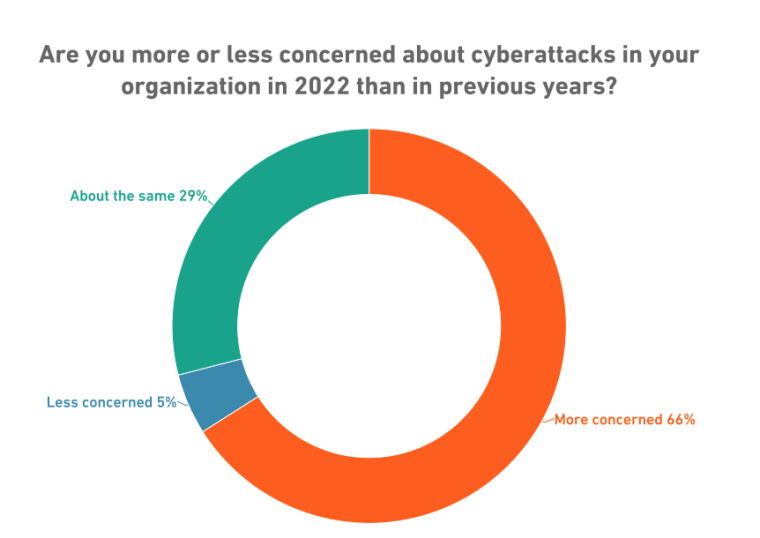
Sonic Wall’s 2022 cyber threat survey revealed that 66% of respondents expressed heightened concern about cyberattacks compared to the previous year.
Additionally, 29% reported having a similar level of concern about attacks as they did in 2021. Only 5% of respondents reported being less concerned.
High-Value Company Cyberattacks in 2023
In June 2023, the mass breach of the file transfer tool MOVEit affected 378 organizations and potentially impacted up to 19 million individuals.
Several federal agencies and many schools throughout the US have fallen victim to cyberattacks.
T-Mobile uncovered a security breach in January 2023 that occurred in November of the previous year.
The breach resulted in the theft of personal information, including names, emails, and birthdays, of over 37 million customers.
Yum! Brands, the parent company of well-known fast food chains KFC, Taco Bell, and Pizza Hut, disclosed a cyber attack that took place in January 2023.
As a result of the cyberattack, Yum! took their systems offline to mitigate the incident and temporarily shut down approximately 300 restaurants in the UK for a day.