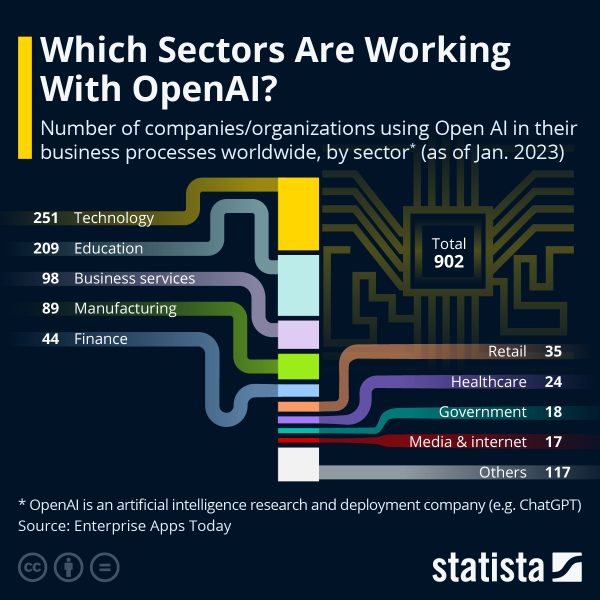
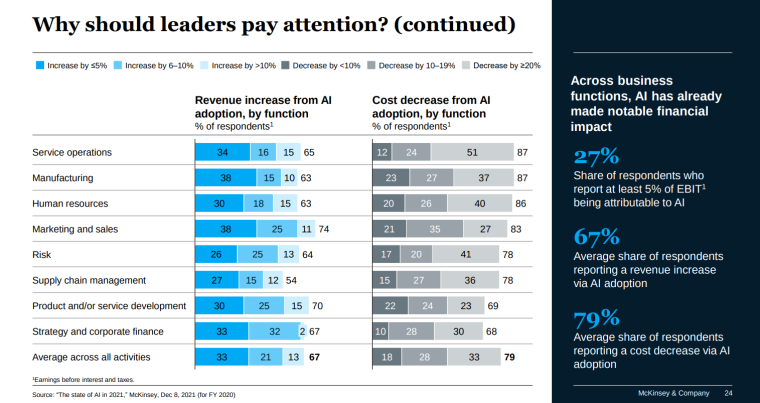
Artificial intelligence can assist businesses in many ways, from cutting costs to improving efficiency. However, with the fast pace of AI development and its increasing applications, it can be hard to keep track, much less figure out where to begin. That’s why we’ve put together 16 important benefits of AI to help you stay on top, regardless of your industry.
Keep reading to discover the benefits of artificial intelligence, including real-life examples, key business use cases, and how businesses of all sizes are using AI to their advantage in 2025.
How Are Businesses Using Artificial Intelligence?
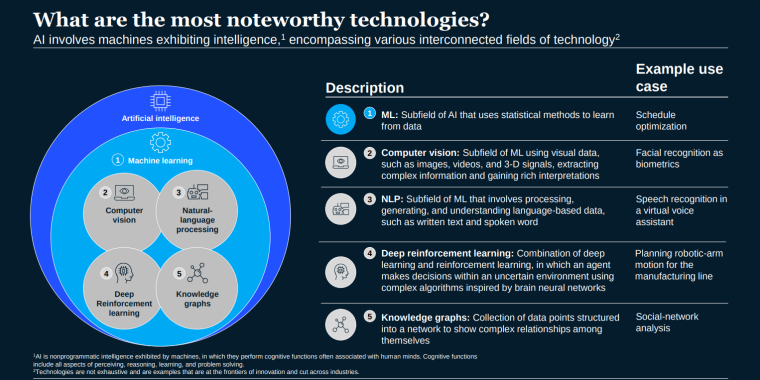
AI or artificial intelligence encompasses several technologies that perform tasks such as:
- Machine learning (ML): This AI field uses pre-trained models rather than programmed rules to make predictions.
- Computer vision: This AI field works with visual data, such as images, videos, and 3D signals.
- Natural-language processing (NLP): This AI field analyzes and generates language-based data, such as text and speech.
- Deep reinforcement learning: This AI field uses artificial neural networks and training through trial and error to make predictions.
With AI technologies like machine learning, computer vision, and natural language processing, businesses across various industries can harness the power of data and extract insights to:
- Automate processes.
- Add or augment capabilities.
- Improve decision-making.
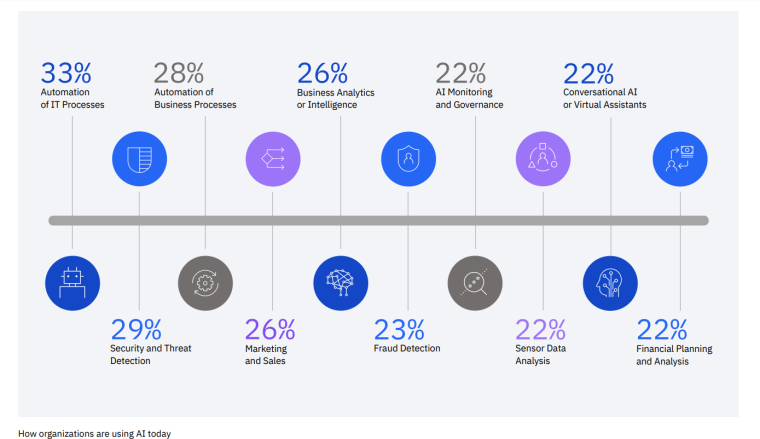
As per Stanford’s 2023 AI Index Report, businesses are using AI in diverse ways such as:
- Robotic process automation (RPA): 39% of businesses are using RPA to automate repetitive tasks.
- Computer vision: 34% of businesses are using computer vision to analyze visual data.
- Natural language text understanding: 33% of businesses are using natural language text understanding to analyze text data.
- Virtual agents: 33% of businesses are using virtual agents to interact with customers.
According to 2023 research by Accenture:
- 97% of executives state that generative AI will be transformative to their company and industry.
- 67% of businesses are prioritizing investments in AI.
- 56% of executives cite data readiness as the top challenge to adopting AI.
- 93% of executives support some level of government regulation around AI.
- 95% of businesses are increasing their AI investment as a percentage of revenue.
- 70% of businesses have specific training programs planned for 2023 to ensure workers are prepared to use generative AI tools.
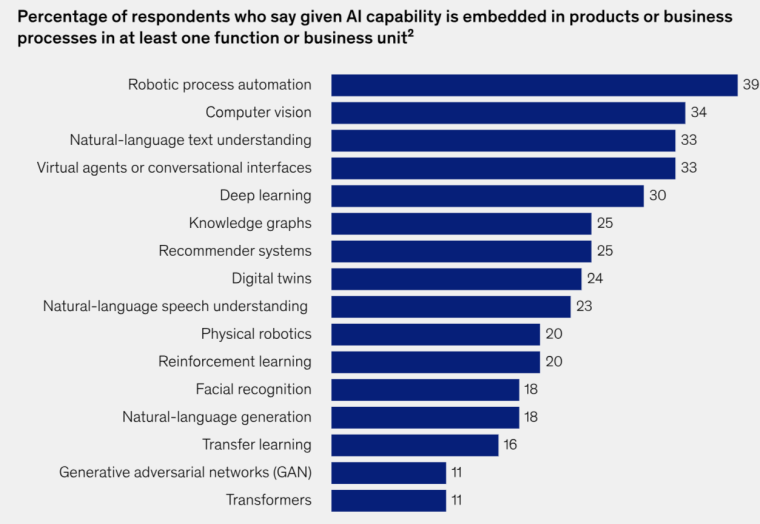
According to McKinsey, the average number of AI capabilities used in business, such as natural-language generation and computer vision, doubled from 1.9 in 2018 to 3.8 in 2022.
Among these capabilities, robotic process automation and computer vision have remained the most commonly deployed each year, while natural-language text understanding has moved up from the middle of the pack in 2018 to the top of the list — just under computer vision.
Additionally, throughout 2022, Stanford’s 2023 AI Index reported that the most common use cases for AI in business were:
- Service operations optimization – 24%
- Creating new AI-based products – 20%
- Customer segmentation – 19%
- Customer service analytics – 19%
- AI-based enhancement of products – 19%
The report further revealed that the AI focus areas that saw the largest investment in 2022 were:
- Medical and healthcare ($6.1 billion)
- Data management, processing, and cloud ($5.9 billion)
- Fintech ($5.5 billion)
Generative AI in Business
Interest in generative AI has increased 3x from 2021 to 2022.
Generative AI has high potential and applicability across most industries. Together with other foundational models, generative AI takes assistive technology to a new level. Unlike previous generations of AI which could only perform one task, generative AI enables the creation of new, unstructured content. This includes text, images, audio, video, code, and even consumer journeys — all based on information derived from similar formats of unstructured data.
Foundational models, which lie at the core of this technology, can be adapted to a wide range of tasks like summarization, classification, and drafting. As a result, they reduce application development time and bring powerful capabilities to nontechnical users.
Generative AI is projected to generate over $4.4 trillion in economic value from a range of specific use cases and more general uses such as drafting emails.
Generative AI is set to unlock new use cases and improve existing ones. For example, it can enhance product development, improve customer experience, and open up new revenue streams. However, its most notable impact is likely to be in improving employee productivity and experience.
Case in point: While GPT-3 performed in the bottom 10% of bar exam takers, GPT-4 performed in the top 10% Moreover, GPT-4 can now use both images and text as inputs, process up to 25,000 words (versus 4,000 with GPT-3), and is 40% more likely to generate accurate responses.
80% of current AI research is focused on generative AI.
Venture capital investments in the field have increased by 425% since 2020. Notable deals include Microsoft’s $10 billion investment into OpenAI, the creators of ChatGPT. Given the potential of generative AI technologies to disrupt entire industries, it’s no surprise that businesses in a variety of industries are exploring their use cases.
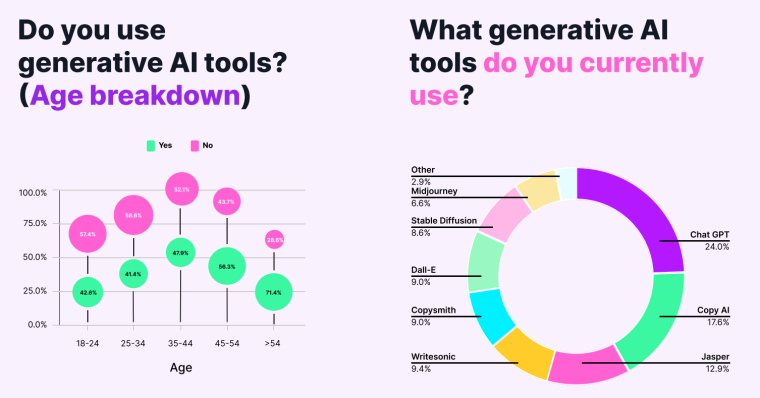
In January 2023, Jasper and Omniscient Digital surveyed 500 professionals across a wide spectrum of role levels, professional backgrounds, and company sizes, and uncovered the following insights regarding generative AI.
- With an average adoption rate of 58%, Millennials and Gen Z used generative AI tools the most in their day-to-day work.
- Companies with 201-500 employees had the greatest adoption rate, at 67.6%, while companies with between 11-1000 employees had an average adoption rate of 61.5%.
- Just under 33% used generative AI in their work daily while 46.1% used it a few times a week.
- Budget was the primary barrier to adopting generative AI for most businesses with the majority of respondents spending between $200-500 per month on generative AI tools.
Natural Language Processing (NLP) in Business
According to IBM, NLP combines computational linguistics, statistical modeling, machine learning, and deep learning to enable computers to process human language and understand its full meaning, including the speaker or writer’s intent and sentiment. NLP has a wide range of applications in business including:
- Customer service – automating customer service tasks, such as answering FAQs, resolving issues, and providing support.
- Sales and marketing – analyzing customer data, identifying potential leads, and generating personalized marketing messages.
- Product development – compiling feedback from customers, identifying new product opportunities, and generating product descriptions.
- Chatbots – powering chatbots that can converse with humans in a natural way.
- Sentiment analysis – analyzing sentiment and determining whether it is positive, negative, or neutral.
IBM’s 2022 Global AI Index revealed that businesses used NLP in the top five following ways in 2022:
- Customer care – 38%
- Security – 36%
- Business development – 32%
- Sales – 30%
- Marketing – 29%
Machine Learning in Business
Machine learning allows AI models to learn, adapt, and become more accurate in predicting outcomes without human intervention. These models sift through vast amounts of data to detect patterns and more. Some of the most common machine learning applications include:
- Image recognition
- Natural language processing
- Speech recognition
- Recommendation engines
- Fraud detection
- Risk assessment
- Customer segmentation
- Supply chain optimization
- Predictive maintenance
Industrializing machine learning (ML), ML operations, or MLOps, refers to the practices needed to scale and sustain ML applications in an enterprise. McKinsey’s 2023 Tech trends report found that:
- Organizations that industrialize ML successfully can shorten the production time frame for ML applications by about eight to ten times and reduce development resources by up to 40%.
- 60% of enterprises will have implemented MLOps by 2024.
- A total of $3.4 billion was invested in companies involved in ML industrialization during 2021 and 2022.
Deep Learning in Business
Deep learning is a type of machine learning that uses artificial neural networks to learn from data. Neural networks are inspired by the human brain and can identify complex patterns in data. This makes deep learning well-suited for tasks that require nonlinear reasoning, such as fraud detection and self-driving cars.
Fintech companies and banks use deep learning to identify connections between criminal conduct and account activity. This increases the effectiveness of their fraud detection efforts and prevents major financial losses for all parties involved.
Self-driving cars, such as those made by Tesla, need to be able to navigate the world without human input. This is a complex task that requires them to perceive and respond to a wide range of factors, such as the location of other vehicles, the speed of traffic, and more. That’s where deep learning comes in: it helps self-driving cars make sense of their surroundings by analyzing data from various sensors.
AI for Business Industries
Deloitte studied thousands of businesses across various industries and found that the top use cases of AI include:
- Cloud pricing optimization – 44%
- Voice assistants, chatbots, and conversational AI – 41%
- Predictive maintenance – 41%
- Uptime or reliability optimization – 41%
Businesses in the automotive and financial services industries are far more likely to use AI compared to other industries.
Below, we discuss a few examples of how AI is being used in key industries such as agriculture, finance, retail, and healthcare.
AI in Agriculture
Agriculture businesses are using AI to improve agricultural productivity in three major ways. Namely agricultural robotics, soil, and crop monitoring, and predictive analytics. Companies such as John Deere have pioneered the use of fully autonomous tractors.
Through the use of high-quality AI and machine learning training data, autonomous tractors can perform tasks such as cultivating, fertilizing, harvesting, and planting with little human intervention. Additionally, using predictive analytics combined with real-time sensor data and visual analytics data from drones, AI can provide farmers with insights to improve crop yields and detect pests or diseases.
AI in Retailing and Logistics
Retailers such as Amazon and Walmart use predictive logistics to analyze customer data, monitor inventory, and manage shipping. Additionally, businesses in the industry use AI and geolocation data to improve transparency in their supply chains and to meet their sustainability targets.
AI is also used in customer service, with many businesses using AI-powered chatbots to address customer concerns, take orders or assist in shopping.
According to research by PwC, the three areas in retailing with the greatest AI potential are:
- Personalized design and production.
- Anticipating customer demand.
- Inventory and delivery management.
In terms of transport and logistics, the three areas with the most AI potential are:
- Autonomous trucking and delivery.
- Traffic control and reduced congestion.
- Security and ease of transportation.
AI in Energy
AI in the energy sector is primarily concerned with grid management and efficiency. For example, in the US, the Department of Energy uses AI as part of its smart grid strategy. In the UK, the National Grid has teamed up with IBM to develop cloud-based analytics. These efforts enable real-time monitoring of power grids, demand forecasting, and efficient responses to surges in output or demand.
Research by PwC identified the following three areas in energy as having the most AI potential:
- Smart metering and real-time information on energy usage.
- Efficient grid operation and storage.
- Predictive infrastructure maintenance.
AI in Finance
Businesses in the finance industry rely on AI for fraud detection. Visa, Mastercard, and PayPal for example, use machine-learning algorithms to analyze data on customer behavior. This helps detect unusual account behavior and flag fraudulent activity.
Investment firms have deployed AI for automated investing and robo-advisors, which can automate tasks such as portfolio rebalancing, tax-loss harvesting, and more. Popular US robo-advisors include Vanguard’s Digital Advisor and SoFi’s Automated Investing bot.
According to PwC, the three areas in finance with the most AI potential include:
- Personalized financial planning.
- Fraud detection and anti-money laundering.
- Process automation in both back-office and customer-facing operations.
AI in Healthcare
Healthcare businesses use AI in several ways including drug discovery, diagnostics, and resource allocation. Pfizer, Genentech, and Sanofi are among the companies using AI and machine learning to optimize their research and development efforts.
By combing through historic research papers and clinical trial data, AI can spot new patterns. It can also analyze genetic data from both patients and diseases to generate new insights.
GE Healthcare, for example, leverages AI to enhance its operations. Its centralized command centers, based at Johns Hopkins Hospital (US) and Bradford Royal Infirmary (UK), make use of predictive AI analytics to aid physician decision-making, manage patients, and collaborate on research.
The four areas in health with the most AI potential as per PwC’s research include:
- Supporting diagnosis.
- Early identification of potential pandemics.
- Tracking incidence rates.
- Imaging diagnostics (radiology, pathology).
AI in Automotive
AI continues to drive innovation in the automotive sector, with a wide range of applications such as design, production, vehicle maintenance, and autonomous driving. For example, AI algorithms, combined with inputs from sensors (including LiDAR) and cameras, can direct self-driving vehicles within prescribed, self-contained areas.
The Tesla Model S and GM’s Cadillac Escalade can now assist with steering, braking, accelerating, and adaptive cruise control. Other companies such as Waymo (owned by Alphabet) and Pony.ai (based in China) are experimenting with level 4 driverless Robotaxis in cities.
AI is also used for vehicle design, workflow solutions, and robotics at production lines. Through machine-vision systems, AI drives automatic inspection and helps detect defective products. AI also powers in-vehicle infotainment, navigation, and security through biometric recognition, and driving monitoring for insurers.
The three areas in the automotive industry with the most AI potential include:
- Autonomous fleets for ride-sharing.
- Semi-autonomous features such as driver assist.
- Engine monitoring and predictive, autonomous maintenance.
Ways to Use AI in Business – 16 Key Benefits of Artificial Intelligence
In this section, we explore 16 key benefits of artificial intelligence and provide real-life examples of how businesses in different industries are successfully harnessing its power.
1. Improved Customer Service
The ability of AI to speed up and personalize customer service is among the top benefits businesses can reap from AI. Around 40% of larger companies are using AI to:
- Improve customer service agent productivity.
- Create more personalized experiences.
- Streamline how customers and employees find information.
- Survey or feedback analysis.
- Resolve frequently asked questions.
- Decrease call wait times.
AI powers smarter chatbots that enable businesses to streamline their customer service processes. Through a combination of natural language processing, machine learning, and AI, chatbots can process customer requests or help route customers to real-life representatives who are better able to address their concerns. This takes the pressure off strained customer support teams and gives customers access to round-the-clock assistance.
Real-world Example
E.ON, the largest energy and renewable electricity supplier in the UK, has 50 conversational AI solutions serving customers and employees and covering about 30% of demand. This has enabled the company to offer a better customer service experience and significantly reduce operational costs.
2. Faster Product Development
Through AI sentiment analysis, businesses can explore how customers feel about a product or service, allowing them to identify opportunities and potential issues. Armed with better insights, businesses can make profitable product decisions. AI also facilitates shorter development cycles and shortens the time between design and commercialization for a quicker return on investment (ROI).
Real-world Example
- Exscientia is leveraging generative AI across all stages of its research and development process, claiming an average time from biological target to drug candidate of approximately 11 months, compared with a 54-month industry average and at a cost that is 80% lower.
- Insilico Medicine developed a generative AI model to predict clinical-trial success rates with a reported accuracy of 80%.
3. Better Quality Control
AI can help businesses improve quality and reduce human error. AI excels at automating repetitive tasks, identifying and correcting errors, and ensuring that processes are followed consistently.
When AI is combined with robotic process automation (RPA), the results are even more impressive. RPA automates tasks that are repetitive, allowing employees to focus on more strategic and creative work. Not only does this result in a significant reduction in errors, but a more efficient and streamlined workflow.
Additionally, AI can be used to train RPA bots so they become more efficient and accurate over time. This can be a valuable asset for businesses looking to improve quality and maximize their resources.
Real-world Example
Freeport-McMoRan deployed a custom-built AI model loaded with three years’ worth of operating data to optimize production processes and total output at a copper mill. In doing so, it increased production by 10% while reducing capital expenditures on a planned expansion.
4. Improved Monitoring
AI gives businesses the power to take in and process massive amounts of data in real-time. By relying on AI’s near-instantaneous monitoring, businesses are able to detect issues and take swift action. Some AI systems can be trained to recommend fixes and implement them, if necessary.
In addition, AI has excellent device and equipment management capabilities. It can identify problems and predict needed maintenance, preventing costly breakdowns. AI’s monitoring capabilities can also be used in other areas, such as enterprise cybersecurity operations, where large amounts of data need to be analyzed.
Real-world Example
Baxter, a medical-device manufacturer, has avoided hundreds of hours of unplanned machine downtime by adopting a proactive maintenance strategy powered by an AI-based end-to-end solution hosted on edge computing devices.
5. Increased Efficiency and Productivity
AI allows businesses to improve their efficiency and productivity. It does this by handling tasks at a scale and velocity that isn’t possible for humans. This gives employees the opportunity to focus on more strategic and creative work.
Additionally, AI can automate many of the mundane and repetitive tasks that are often a drain on employee productivity. In turn, this enables businesses to minimize costs and maximize the talents of their human capital.
Real-world Example
Developers using AI-enabled tools such as GitHub’s Copilot enhanced their productivity by automating routine tasks and suggesting solutions to problems. Developers reported time savings of 35 to 45% in code generation and 20 to 30% in code refactoring.
They also report an improvement in happiness, flow, and fulfillment while using AI-enabled tools, which suggests that adopting these tools could help companies retain talent in a competitive talent market.
6. Improved Talent Management
AI can be used to improve several key aspects of talent management, such as hiring, training, communication, and retention. AI can streamline sourcing, screening, and hiring, saving businesses time and valuable resources. Additionally, AI tools can be used to:
- Gauge employee sentiment.
- Identify high performers.
- Retain employees.
- Determine equitable pay.
- Deliver personalized and engaging workplace experiences.
Despite clear benefits, even Fortune 500 companies are falling behind when it comes to their use of AI in attracting, engaging, and converting talent. In fact, 91% scored poorly in this area according to Phenom’s 2022 State of Candidate Experience Report.
Real-world Example
Brother International Corporation, a premier provider of home office and business products, wanted a better way to market its brand and attract talent. The company decided to use AI to promote its brand and attract quality candidates. After just three weeks of launching its new AI recruiting tools, Brother achieved:
- 140% increase in completed applications.
- 45% increase in total page views.
- 40% increase in job seekers.
- 15% increase in returning job seekers.
- 25% decrease in time to fill.
7. Higher Profitability
As businesses incorporate AI into more areas of their operations, they are likely to realize benefits such as improved productivity, reduced costs, higher efficiency, and potential growth opportunities.
In addition to these benefits, AI can also help businesses improve their competitive advantage. By using AI, businesses can improve their productivity, efficiency, and customer service. This can set them apart from their competitors and attract loyal customers, ultimately leading to higher profitability and long-term growth.
Real-world Example
Emirates Team New Zealand dramatically accelerated hydrofoil design and testing by using AI to train a “digital twin” or a digital replica of a sailor, to test designs in a simulated environment. By using the AI “sailor” to remove the bottleneck of human sailors performing the tests, the team reduced costs by 95% and was able to test ten times as many designs.
8. Increased Innovation
AI drives innovation by unlocking new insights and capabilities. It also aids businesses in conducting research, testing new ideas, and developing new products and services.
Additionally, as employees become more confident working with AI, they are likely to experiment with various tools, further promoting creativity and innovation. As a result, through the use of AI, businesses are not only able to develop new products and services but improve their operations.
Real-world Example
Using a neural network trained on widely available weather forecasts and historical turbine data, DeepMind and Google applied machine learning algorithms to 700 megawatts of wind power capacity and configured the DeepMind system to predict wind power output 36 hours ahead of actual generation.
9. Better Product Recommendations
Businesses can use AI to recommend products that align with customers’ interests to drive engagement and boost conversions. The ability to track customer behavior and present relevant product recommendations is especially useful for e-commerce businesses.
Streaming services such as Netflix and Disney Plus also rely on AI to make personalized recommendations. By analyzing customer habits and preferences, they are able to increase and manage viewership rates more effectively.
Real-world Example
Wimbledon uses a suite of AI-powered digital tools for its Wimbledon App and wimbledon.com. These include:
- IBM Power Index Leaderboard
- IBM Match Insights
- Personalized Highlights Reels and Recommendations
Using over 100,000 data points from every shot played across the tournament, Wimbledon makes it easier for fans to understand which players to follow, how they compare to their opponents, and who’s likely to win. Fans are kept updated and engaged throughout the tournament with fresh insights tailored to the players they’re following.
10. Improved Audience Segmentation
Being able to reach the right audiences is essential in today’s competitive landscape. Just as AI can be used to recommend products, it can also be used to segment audiences and create targeted advertising campaigns. Using AI, businesses can gather accurate data to not only inform their marketing decisions but to also allocate their resources optimally.
Real-world Example
Telkomsel in Indonesia built a new data analytics platform supplemented by AI-driven tools to better understand customers across thousands of microsegments. Using 9,000 data points per customer across more than 50 models, the company drives personalization by identifying the right way to interact with customers and offering the most relevant products and services.
11. Higher Customer Satisfaction
Sentiment analysis is conducted by businesses to understand customer brand perception. Using AI and machine learning, businesses can analyze data from a multitude of sources, such as social media posts, reviews, and ratings. With the vast amounts of data collected, businesses can identify opportunities for improvement and better serve their customers.
Real-world Example
Moosejaw, a Canadian retailer of outdoor recreation clothing and equipment, turned to AI for a solution to its costly reverse supply chain. With the help of AI, Moosejaw identified that almost 15% of online purchases returned by its customers were due to size sampling. Using a data-driven personalization platform called True Fit, Moosejaw reduced the rate of size sampling by 24% in one year.
12. Enhanced Fraud Detection
AI can be used to help businesses identify and respond to fraud threats. Machine learning algorithms are able to identify suspicious transactions, stop suspicious transactions from going through, and alert the relevant parties. Overall, the use of AI can help businesses protect themselves from financial loss, make better investment decisions and maintain their reputation.
Real-world Example
- OTP Bank generated a Hungarian large-language model to enable more than 30 banking use cases across the organization, with an initial focus on spoken and text customer interactions, fraud detection, and cybersecurity.
- NatWest, which serves 19 million customers across 12 banking and financial services brands uses a combination of conversational AI, behavioral data, and voice-biometric technology to detect and stop fraud across its network.
- With 2.5 billion payment cards used in more than 200 countries and territories across the globe, Mastercard faces a massive fraud risk and manages it by combining fraud-detection technologies with AI. Using the data it collects over its network, Mastercard seeks to strike a balance between denying and approving transactions.
13. Optimized Supply Chain Operations
AI-driven solutions help businesses optimize their supply chains. Through the use of AI, businesses can:
- Predict the price of materials and shipping.
- Estimate how fast products can move through the supply chain.
- Analyze historical data to predict future demand.
- Identify potential bottlenecks in the supply chain.
- Optimize transportation routes.
- Manage inventory levels.
- Forecast consumer demand.
Real-world Example
Zipline, a next-generation logistics platform enabled by a fleet of autonomous, electric drones, estimates it can complete deliveries seven times faster than traditional automobiles and with 97 percent fewer emissions. A study published by Lancet found that hospitals using Zipline services were able to reduce their total annual blood supply waste rate by 67%.
14. Smarter Cyber Assistants
Skilled AI systems, also known as cyber assistants, are able to identify abnormal behaviors, assess vulnerabilities dynamically, and flag suspicious activity that could indicate new threats. AI also has the ability to improve its knowledge over time by consuming billions of data artifacts, which will help it better understand cybersecurity threats and cyber risks.
Real-world Example
- Using artificial intelligence and machine learning technology, Malwarebytes protects customers against zero-day malware or malware that has not yet been researched and classified.
- In March 2023, Microsoft launched a cybersecurity assistant called Security Copilot to help cybersecurity professionals identify breaches and threat signals while better analyzing data, using OpenAI’s latest GPT-4 generative AI model. The assistant will use Microsoft’s security-specific model which is fed more than 65 trillion signals every day.
15. Synthetic Data Generation
Real-world data can be expensive, biased, and subject to privacy, ethics, and copyright laws. Synthetic data, which is computer-generated, can be used to augment or replace real data and:
- Speed up the training of AI models.
- Protect sensitive data.
- Improve accuracy.
- Find and mitigate bias.
- Address security weaknesses.
By 2024, 60% of the data used for the development of AI and analytics projects will be synthetically generated.
Real-world Example
In 2013, researchers at MIT started developing the Synthetic Data Vault, an open-source software tool for creating and using synthetic data sets. Today, the Synthetic Data Vault is freely available on GitHub, and the latest of its 40 releases was issued in December 2022.
The software which is now part of DataCebo, has been downloaded more than a million times, and is used by financial institutions and insurance companies, among others.
16. Lower Environmental Impact
Businesses can use AI to mitigate environmental risks and achieve carbon neutrality. Through AI, businesses can establish more transparent, traceable, and decarbonized supply chains. Additionally, AI can help businesses collect data, identify risks, validate documentation, and provide audit trails. Ultimately, this allows businesses to efficiently manage their:
- Carbon footprint
- Waste
- Energy use
- Eater consumption
- Material usage
Real-world Example
Vistra partnered with McKinsey to develop more than 400 AI models and used MLOps to standardize their deployment and maintenance. This helped the company optimize thermal efficiency across 26 of its plants, generate more than $20 million in energy savings, and reduce carbon emissions by 1.6 million tons per year.
The Case for AI in Business
AI in Business Adoption
Estimates suggest that the number of businesses adopting AI in 2022 has more than doubled since 2017.
Driven by greater financial investment and easier access, AI adoption in business has steadily increased. AI technologies continue to break new frontiers, increasing the number of use cases. According to McKinsey, AI adoption by business organizations across all geographies more than doubled to 50% in 2022 from 20% in 2017. This is driven by major market developments such as:
- A 94.4% improvement in training speed for AI models since 2018, enabling easier and more affordable AI implementation.
- Rapidly evolving innovation as shown by a compound annual growth rate of 77% in the relative number of AI patents filed in 2021 compared to 2015.
- Greater investment in AI-related companies. In 2022, private investment in AI was 18 times higher compared to 2013.
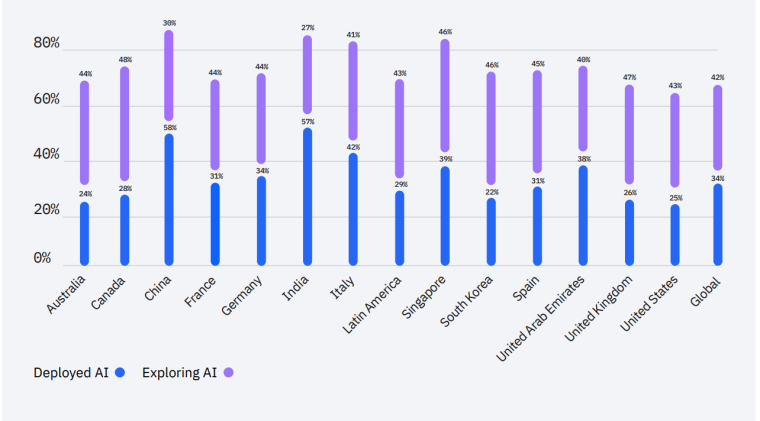
For its 2022 Global AI Adoption Index, IBM analyzed the deployment of AI across 7,502 businesses around the world and found that:
- 35% reported using AI in their business, and an additional 42% reported exploring AI.
- 30% used AI to address labor and skills shortages and automate repetitive tasks.
- 50% experienced significant benefits from using AI to automate IT, business, or network processes.
- 54% experienced cost savings and efficiencies.
- 53% saw improvements in IT or network performance.
- 48% were able to create better experiences for customers.
While AI adoption differs across companies, geographies, and industries, the gap in AI adoption between larger and smaller businesses grew significantly in 2022.
Larger companies were 100% more likely than smaller companies to have deployed AI in 2022, compared to only 69% in 2021. In addition, Chinese and Indian companies led the way, with nearly 60% of IT professionals in those countries stating that their organizations actively used AI.
The top 4 reasons businesses adopted AI in 2022 included:
- Advancements and greater accessibility – 43%
- Needing to reduce costs and automate key processes – 42%
- Increasing the amount of AI embedded into standard, off-the-shelf business applications – 37%
- Competitive pressure – 31%
AI in Business Value
About 87% of businesses believe that AI plays a crucial role in achieving business goals.
These goals include growing revenue, increasing operational efficiency, and boosting customer experience.
Businesses using AI report experiencing significant cost decreases and revenue increases.
Using AI can yield notable financial benefits. In fact, 25% of respondents in a 2023 McKinsey survey credited 5% or more of their earnings to AI.
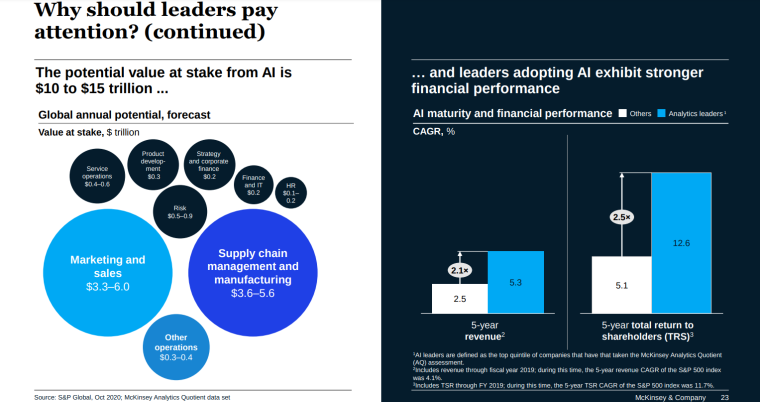
The potential economic value at stake from AI stands at between $17 – $26 trillion.
The industries set to experience the highest value gains include:
- Marketing and sales
- Supply chain management
- Manufacturing
AI in Business Projections
The AI market is expected to exceed $500 billion by 2024.
According to forecasts, global spending on AI in business is expected to exceed $89 billion in 2025. This is up from just $3.2 billion in 2016.
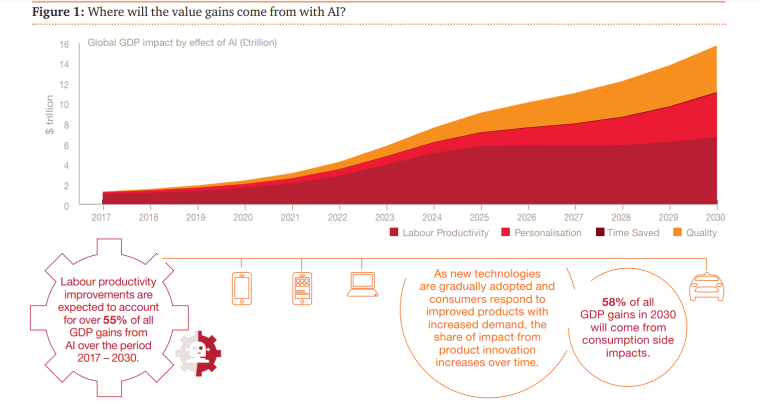
According to PwC, AI could contribute up to $15.7 trillion to the global economy in 2030.
$6.6 trillion is likely to come from increased productivity and $9.1 trillion is likely to come from consumption-side effects, which makes AI the biggest commercial opportunity in today’s fast-changing economy
The largest sector gains will be in retail, financial services, and healthcare.
AI is set to increase productivity, product quality, and consumption in these industries.
AI in Business Sustainability
Two-thirds of companies either executed or planned to apply AI to address their sustainability goals in 2022.
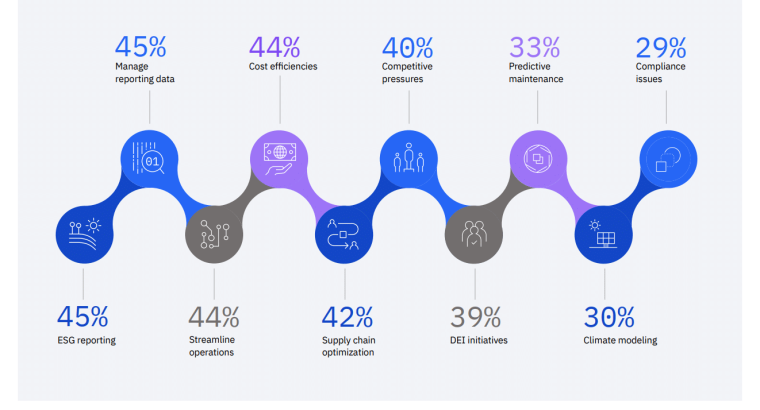
According to IBM’s AI Index, the sustainability challenges businesses believed AI could address were:
- Driving more efficient business processes and daily operations – 37%
- Providing more accurate and verifiable data on environmental performance factors for reporting purposes – 33%
- Automating the collection and reporting of data across complex operations and endpoints – 29%
- Analyzing and deriving insights from vast amounts of data related to desired sustainability outcomes – 29%
- Meeting regulatory and compliance requirements – 28%
60% of businesses planned to apply AI to address their sustainability goals in 2023.
Meanwhile, just under 40% actually invested in sustainability-related AI in 2022.
In 2022, over 33% of businesses used AI to drive more efficient business processes and operations.
Businesses used AI for supply chain optimization, predictive maintenance, and climate modeling. In the coming years, AI is poised to solve sustainability challenges related to business process efficiency and data accuracy. In addition, businesses across industries will continue to look to AI to reduce costs and consumption, manage reporting, and streamline their operations.
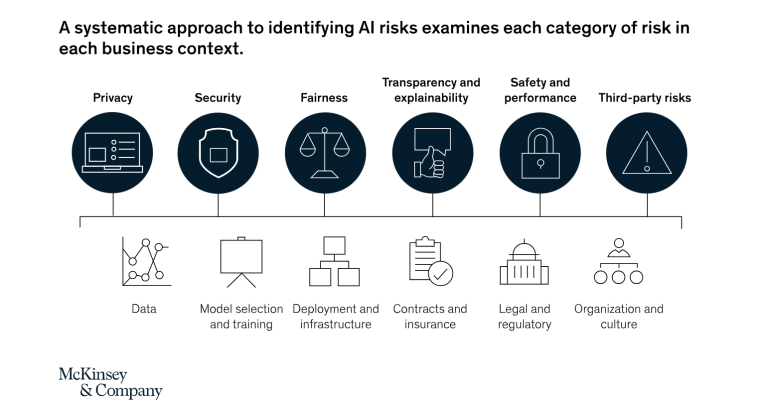
Key AI Considerations for Business
While AI can add immense value to businesses, there are still organizational, technical, ethical, and regulatory issues that must be ironed out before its full potential can be realized.
Key issues affecting AI in business in 2023 include:
- Cybersecurity
- Privacy concerns
- Ethical considerations
- Regulation and compliance
- Copyright ownership and protection
- Limited resources, talent, and funding
Echoing the findings above, IBM’s 2022 AI Index reported the following barriers to AI adoption:
- Limited AI skills, expertise, or knowledge – 34%
- Very high costs – 29%
- Lack of tools or platforms to develop models – 25%
- Complex projects too difficult to integrate and scale – 24%
- Too much data complexity – 24%
To reap the benefits of AI, findings by McKinsey suggest that businesses need to consider:
- The applications that will benefit them and their stakeholders the most.
- The features that make AI technologies trustworthy and ethical and how they can be integrated into various applications.
- The checks that should be put in place to safeguard against AI-related risks associated with data privacy and security, equity, fairness, and compliance.
- How the different types of AI can be used synergistically.
FAQs
What is an example of business AI?
What are the four types of AI?
How can AI solve business problems?
References
- McKinsey Technology Trends 2022
- Stanford AI Index 2023
- Accenture
- McKinsey
- McKinsey Technology Trends 2023
- Jasper AI Report 2023
- IBM
- IBM Global AI Index 2022
- Deloitte 2022 State of AI Report
- Economist Intelligence
- Raconteur AI for Business 2022 Report
- Baxter
- OReilly
- Phenom
- DeepMind
- IBM
- Technology Review
- CNBC
- Malwarebytes
- Reuters
- Gartner
- MIT Sloan
- Global News Wire
- IDC
- PwC
- PwC