ICICI Bank is a leading private sector Indian multinational bank and financial institution that has long shaped the country’s economy. The ICICI Bank history begins with a government-led collaboration to boost Indian industry post-independence, and now the bank offers a wide range of banking and investment services to both business and individual customers.
At Business2Community, we’ve analyzed a range of reliable sources to give you a comprehensive account of ICICI’s journey from a long-term project financer to becoming a diversified financial services group. Read on to learn about the key developments and milestones that have helped shape ICICI’s offer and cement its place in the global banking industry.
A History of ICICI Bank – Key Dates
- ICICI was founded in 1955 as a collaboration between the World Bank, the Indian Government, and Indian banking industry to provide funding for homegrown industrial projects.
- The ICICI Banking Corporation Limited was launched in 1994 as a wholly-owned subsidiary of ICICI, changing to simpl ICICI Bank in 1998.
- ICICI went public and joined the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) in 1999 – the first Indian company to be listed on the NYSE.
- In 2001, the boards of ICICI Limited and ICICI Bank approved a plan to merge ICICI Limited and two of its subsidiaries into ICICI Bank.
- In 2018, the managing director and CEO of ICICI Bank, Chanda Kochhar, resigned following allegations of corruption.
Who Owns ICICI Bank?
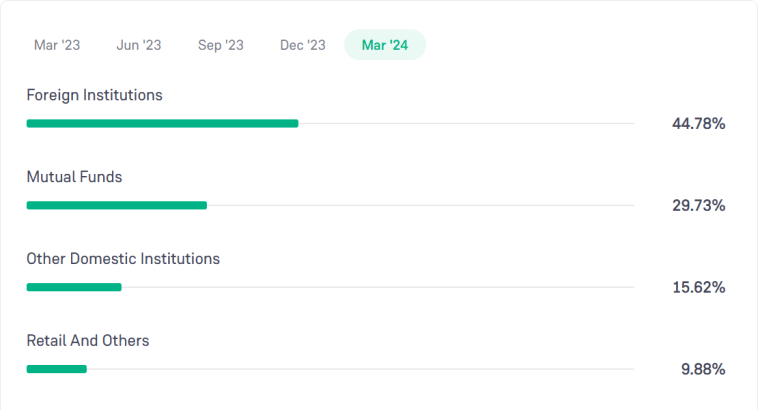
Around 45% of ICICI Bank’s equity shares are owned by domestic institutional investors and mutual funds, such as SBI Funds Management Ltd and the Life Insurance Corporation of India. International institutions also own around 45% of shares in ICICI Bank. The remaining 10% is owned by public and individual investors.
ICICI Bank Ltd.’s equity shares are listed on the Bombay Stock Exchange and the National Stock Exchange of India Limited. Its American Depositary Receipts (ADRs) are listed on the NYSE.
ICICI Bank, headquartered in Mumbai, provides a range of corporate banking and personal financial services across 16 countries. The corporation also has several subsidiaries offering services across asset management, venture capital, insurance, and investment banking.
The bank was founded by the Industrial Credit and Investment Corporation of India (ICICI) as a fully-owned subsidiary in 1994. ICICI was a government organization founded in 1955 through a collaboration between the World Bank, the Indian Government, and Indian insurance and banking institutions. Their goal was to establish a financial institution that could support Indian businesses through long-term project financing.
In 1999, the ICICI group went public and joined the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE). In doing so, it became the first Indian company and the first non-Japanese bank or financial institution from Asia to be listed on the NYSE.
Directors of ICICI and ICICI Bank Ltd. approved a merger in 2001 that brought all the group’s financing and banking operations together into a single entity. The merger was completed in 2002 and the new entity has since been known as ICICI Bank Limited.
Who is the ICICI Bank CEO?
Sandeep Bakhshi has been the managing director and CEO of ICICI Bank since 2018. He has held various roles across the group since he joined the organization in 1986. Bakhshi was previously Managing Director and CEO of ICICI Prudential Life Insurance from 2010 to 2018.
Bakhshi succeeded Chanda Kochhar, who resigned following controversy surrounding her conduct. Kochhar had been managing director and CEO of ICICI Bank since 2009. She is facing ongoing allegations and charges related to financial misconduct and money laundering.
Following the 2002 merger, former managing director and CEO of ICICI, KV Kamath, took charge of ICICI Bank Limited.
| CEO | Tenure |
| KV Kamath | 2002-2009 |
| Chanda Kochhar | 2009-2018 |
| Sandeep Bakhshi | 2018-present |
Growth and Development of ICICI Bank
ICICI Bank began as a collaborative effort to kickstart the Indian economy following independence from British rule. Here, we run through the key moments in ICICI history that have shaped the leading financial institution we see today.
1955-1994: ICICI Supports Economic Growth Across India
ICICI was formed in 1955 as a collaboration between the World Bank, the Indian government, and banking and insurance industry representatives.
Having gained independence from British rule in 1947, India found itself with a low GDP, lack of foreign investment, and heavy reliance on imports. The goal was to establish a development-focused financial institution, offering project financing to home-grown industrial projects that would enable the country to realize its aspiration of achieving economic independence.
Throughout the remainder of the 1950s and early 1960s, ICICI funded hundreds of projects across the country in a wide range of industries with support totaling ₹100 million (approx. $21 million) between 1955 and 1964. This included paper, cement, fertilizer, and steel production. Many of the companies supported in these early years have gone on to become household names, including Tata Motors, Air India, and Johnson & Johnson.
As the national economy evolved, the organization found new ways to support its people and the economy. In 1977, for example, faced with a shortage of affordable housing finance, ICICI launched the Housing Development Finance Corporation. ICICI continued to play a role in setting up new institutions throughout the 1980s, including the Shipping Credit and Investment Company of India (SCICI), the Credit Rating Information Services of India Limited (CRISIL), and the Stock Holding Corporation of India Limited (SHCIL).

ICICI also sought to support technology and research-based start-ups, which were struggling to secure opportunities for funding and investment at the time. It began offering venture capital and loans to these enterprises and, in 1988, it launched the Technology Development and Information Company of India (TDICI). TDICI would later become ICICI Venture.
Throughout the 1990s, the Indian economy changed significantly with the government passing several policy changes aimed at opening up the country’s economy to the world. The government sought to increase private and foreign investment to drive economic growth and development.
Having previously only offered project finance, during the 1990s ICICI transformed its business model to become a much more diversified financial services provider. ICICI began to offer a wider range of products and services through new delivery channels and launched new business segments such as the ICICI Securities and Finance Company Limited – an investment banking subsidiary – and the ICICI Asset Management Company Limited.
1994-2002: The Commercial Entity ICICI Bank is Born
In a bid to capitalize on this opportunity to provide a much broader selection of financial products and services to a wider range of clients, the commercial bank ICICI Banking Corporation Limited was launched in 1994. The ICICI Banking Corporation was a wholly-owned subsidiary of ICICI. Its first branch was opened in Chennai. In 1998, it became known more simply as ICICI Bank.

ICICI Bank led the way in adopting digital technology such as ATMs and internet banking. It became the first Indian bank to offer online services in 1997. The organization also drove the consumer finance revolution in India, making things like car loans, home loans, and credit cards more accessible to India’s growing middle class.
It went public on the NYSE in 1999.
In its drive to stay at the forefront of the industry, ICICI established the ICICI Prudential Life Insurance Company in 2000 in collaboration with Prudential Corporation plc, the world’s biggest life insurance company. ICICI Prudential was one of the first life insurance companies in India. The following year, ICICI entered the insurance industry with the launch of the ICICI Lombard General Insurance Company.
2002-2024: Realizing ICICI’s Universal Banking Strategy
As the Indian banking sector became increasingly competitive, ICICI directors began to consider various corporate structure alternatives. Ultimately, they concluded that a merger of ICICI with ICICI Bank would be the best strategic move, creating the ideal for ICICI group’s universal banking strategy.
In 2001, the Boards of ICICI Limited and ICICI Bank approved a plan to merge ICICI Limited and its subsidiaries ICICI Personal Financial Services Limited and ICICI Capital Services Limited, into ICICI Bank. ICICI Bank became the second-largest Indian bank.
By becoming a bank, ICICI could offer a wider range of products and services, such as low-cost demand deposits. It also presented several opportunities to earn non-fund-based income, such as fees and commissions. The merger brought added benefits for ICICI shareholders through better availability of low-cost deposits, and the ability to provide transaction banking services. For ICICI Bank shareholders, the merger offered a large capital base, access to ICICI’s corporate relationships, and entry into new business segments.

The merger also enabled an international expansion for ICICI Bank. In 2003, it established subsidiaries in both the UK and Canada, ICICI Bank UK and ICICI Bank Canada respectively. ICICI Bank UK operates across seven locations in the UK and has around 250,000 customers.
ICICI Bank itself has branches in:
- Bahrain
- China
- Dubai
- Hong Kong
- Singapore
- South Africa
- The USA
In 2007, the Reserve Bank of India approved the acquisition of Sangli Bank by ICICI Bank, which enabled it to expand its reach into rural parts of India.
In 2007, ICICI Bank was involved in several high-profile legal cases surrounding its loan recovery tactics after a former customer died by suicide. Most of the allegations were that the bank’s recovery agents behaved inappropriately and aggressively.
During the 2008 global financial crisis, many customers flocked to ICICI ATMs and branches to withdraw their savings amid fears of a crash. In response, ICICI launched a widespread communication campaign to reassure customers and dispel rumors. When this was unsuccessful, the Reserve Bank of India had to step in and confirm that ICICI had enough cash and that it would make more money available to the bank should it be needed.
In 2010, ICICI Bank acquired the Bank of Rajasthan Ltd. The move was said to be in part driven by regulatory pressure and accusations leveled at the Tayal family who held around 55% of the Bank of Rajasthan Ltd.’s shares.
In 2013, ICICI Bank was one of several leading Indian financial institutions to be accused of money laundering. In what became an infamous investigation by the website CobraPost, officials were allegedly recorded offering to help a corrupt politician launder his money through bank accounts and insurance products. A government inquiry was ordered to officially investigate the claims.

In further controversy, in 2018, the managing director and CEO of ICICI Bank, Chanda Kochhar (above), resigned following allegations of corruption. In 2019, the ICICI Bank’s Board terminated her employment after it found her guilty of violating internal policies and professional misconduct. It also demanded she pay back most of her bonuses and benefits, estimated to be worth millions of dollars.
In relation to the ICICI Bank case, in 2020 the Indian authorities seized in excess of ₹780 million ($10.92 million at the time) worth of assets belonging to Kochhar. Kochhar and her husband Deepak were also arrested and charged with corruption. However, in 2024, the Bombay High Court ruled that the arrest was illegal.
In 2024, ICICI shareholders approved a merger of ICICI Securities Limited with the parent company. The merger is intended to deliver business synergies in areas such as customer service, acquisition, technology, and banking solutions.
History of the ICICI Bank Logo
The ICICI Bank logo has remained the same since it was established in 1994. It shows the full name of ICICI Bank. Unlike many other bank logos, ICICI’s doesn’t include any obvious shapes. Instead, it uses four simple colors that represent ICICI Bank’s different divisions.
Each of ICICI’s group companies uses the same basic logo style and color scheme but replaces the word ‘bank’. For example, ICICI Venture adds ‘venture’ and an underscoring line.

The Future of ICICI Bank
The ICICI group has weathered its fair share of controversy over recent years, but what does the future hold for this titan of the Indian banking industry?
In part, ICICI sees further technological transformation as its goal for the future. It already employs state-of-the-art digital tools and infrastructure to offer its customers specially tailored products and services, self-service apps, and branches and bank managers who are supported by deep insights from data and analytics.
ICICI also makes use of AI and chat bots which work alongside its staff to serve customers 24 hours a day. This has all paid off with ICICI being named as the Bank of the Year in the BT-KPMG Best Banks and Fintechs Survey 2021-22 for the third year in a row.
Under Sandeep Bakhshi’s leadership, ICICI has embarked on a culture shift under the mantra “One Bank, One Team”. The new system is based upon the concept that every employee joins the bank to do their best, express themselves, and reach their full potential. Bakhshi has been widely credited with returning the bank to its former glory and, under his eye, it seems that ICICI has a bright future ahead.
FAQs
Who are the owners of ICICI Bank?
Who is the largest shareholder of ICICI Bank?
Where is ICICI Bank based?

