The history of Comcast, a global media and technology megacorp, has evolved from its origins as a single-system cable operator into the largest American multinational telecommunications and media company. Over the years, Comcast has strategically expanded its footprint and influence in the industry, transforming into a powerhouse that transcends traditional cable services (even though it’s notoriously hated).
Our experts at Business2Community have curated a compilation that highlights Comcast’s key milestones and significant dates, offering a narrative that unveils the story of Comcast’s ascent to becoming the most successful media company in the contemporary landscape.
A History of Comcast – Key Dates
- Comcast was originally named American Cable Systems when launched in 1963.
- Comcast Corporation had its IPO on June 29, 1972.
- In 1997, Microsoft invested $1 billion in Comcast.
- Comcast acquired NBC Universal in 2009.
- In 2023 Disney paid Comcast Corp’s NBC Universal $8.61 billion for full ownership of streaming service Hulu.
Who Owns Comcast?
Comcast Corporation is a public company owned by institutional and individual investors. The majority of ownership lies with institutional investors, with The Vanguard Group Inc. holding 9.09% of shares and Blackrock Inc. owning 4.81%. The principal individual shareholder is Brian Roberts, who serves as the chairman and CEO of Comcast.
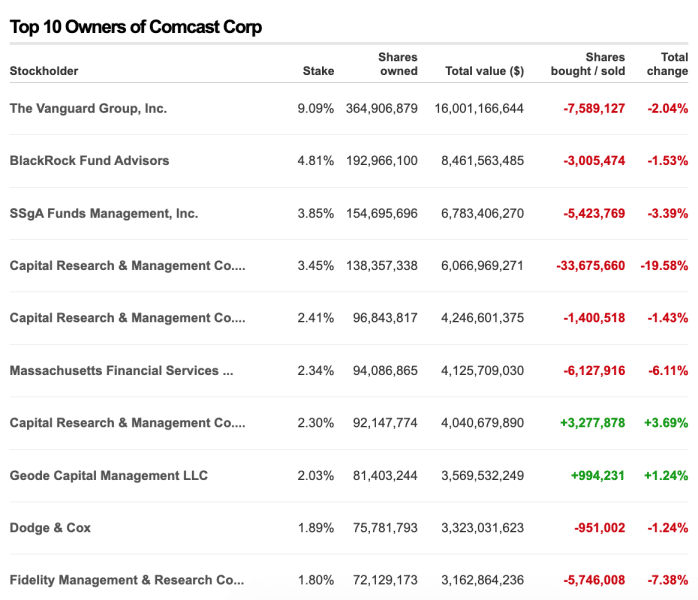
Comcast’s stock structure includes Class A (CMCSA) and Class B (CMCSK) stocks. As of January 2024, Brian Roberts held 26,332,391 shares of Comcast Corporation Class A stock.
Additionally, Brian Roberts owns Class B common stock, which is not publicly traded. The Class B stock is held by Brian Robert’s limited liability company and two estate planning trusts.
Brian Roberts’ ownership of Class B common stock grants him an undilutable 33⅓% of the total voting power across all classes of the company’s common stock.
Who is the Comcast CEO?
Brian Roberts is Chairman and CEO of Comcast Corporation. In 1990 he assumed the role of president at Comcast.
Ralph Roberts, his father and the founder of Comcast, served as the CEO of the company until Brian succeeded him in 2002 at the age of 31.

Brian Roberts joined Comcast in 1974 as an intern, contributing to the company’s initiatives in supermarket promotions. Then in 1975, he obtained hands-on experience by completing his first training as a cable installer in the company’s Westmoreland cable system.
As of January 2024, Brian Roberts has a net worth of $ 2 billion. He has ranked on widely recognized CEO lists, including his recent inclusion in The World’s Most Influential CEOs and Business Executives of 2024.
Throughout the history of Comcast, the role of CEO has been passed within the family, held exclusively by Ralph Roberts and Brian Roberts.
Comcast Headquarters
Comcast Corporation’s headquarters is located in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, USA. Since its incorporation in 1969, the company has maintained its headquarters in Philadelphia.
Additionally, Comcast has offices in Manchester, New Hampshire; Atlanta, Georgia; and Denver, Colorado.

Growth and Development of Comcast
Comcast Corporation was the second-leading global telecommunications company in 2023 with a market capitalization of $182.5 billion. It also claimed the position of the second-leading global media brand by revenue in 2022.
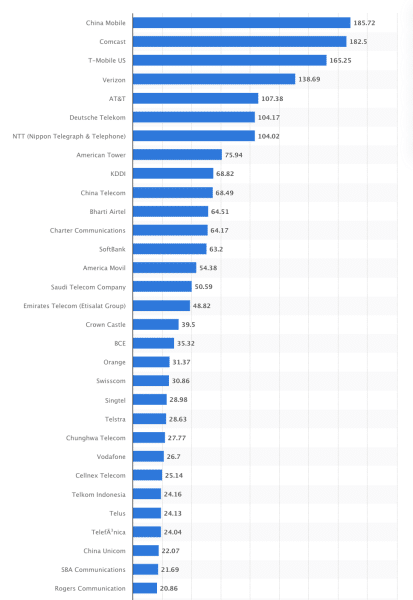
So how did Comcast’s cable business unfold? Let’s take a look at the history of Comcast and key moments that have shaped Comcast’s growth and development on the global stage.
1960s: Early Years of Comcast
Comcast Corporation was initially known as American Cable Systems when it was founded by Ralph Roberts in Tupelo, Mississippi, in 1963. It operated with a 1,200-subscriber cable system.

Ralph Roberts purchased American Cable Systems for $500,000. Daniel Aaron and Julian A. Brodsky became Ralph Roberts’ earliest business partners, joining him as cofounders of Comcast Corporation.
During the 1960s, American Cable Systems made two notable acquisitions. Firstly, in 1965, American Cable Systems purchased Storecast Corporation of America, a marketing firm dedicated to aiding food companies in tracking and optimizing the placement of their products in supermarkets. Subsequently, in 1968, Comcast made its first Muzak franchise purchase in Orlando, FL. Muzak provided background music and audio content for various businesses and public spaces.
In 1969, Ralph Roberts rebranded the company name from American Cable Systems to Comcast Corporation. The original name sounded too generic for the expanding nature of his company. The new name Comcast was derived from the combination of “communications” and “broadcast.”
1970s: Comcast Goes Public
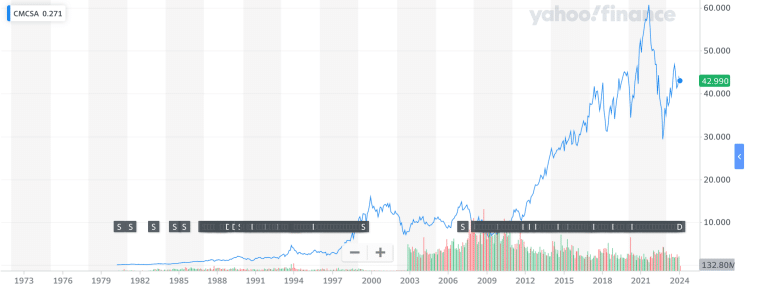
Comcast Corporation went public with its initial public offering (IPO) on June 29, 1972. During this IPO, 430,000 shares of CMCSA were issued at $7 per share.
As of January 2024, Comcast Corporation’s shares were valued at $42.90.
Comcast expanded its cable television services in 1977 with the introduction of HBO, or Home Box Office.
The company attracted new customers in Western Pennsylvania by offering a five-night free preview to 20,000 individuals. Following the preview period, over 3,000 customers opted to subscribe to the service.
1980s: Evolution of Comcast Under Brian Roberts
Brian Roberts dedicated himself to the development and expansion of Comcast in the 1980s. Upon graduating from The Wharton School at the University of Pennsylvania in 1981, Brian Roberts immersed himself in Comcast’s growth, starting as a trainee for the Trenton system.
He then moved to Flint, Michigan a year later, taking charge of marketing, customer service, and apartment building expansion. Ascending to the position of General Manager for the Trenton system in 1983, Brian Roberts assumed responsibility for day-to-day operations.
By 1984, Brian Roberts became the Vice President of Comcast Corporation for the cable division. Under his direct involvement, Comcast’s cable customer base grew to 1.2 million by acquiring a 26 % interest in Group W Cable, Inc. in 1986.

Elected to the Comcast Corporation Board of Directors in 1988, Brian Roberts influenced strategic decision-making. Comcast acquired 50% of Storer Communications, Inc., surpassing 2 million subscribers and affirming its status as one of the country’s largest cable companies.
Furthermore, Brian Roberts directed Comcast into the cellular telephone field with the acquisition of American Cellular Network Corporation for $230 million, leading to the formation of the Comcast Cellular Communications division.
After a decade of steering Comcast’s growth, Brian Roberts was elected as President of Comcast Corporation in 1990, marking his influential role in the company’s leadership.
1990s: Comcast’s Strategic Investments and Acquisitions
By the 90s, Comcast had established 65 cable television systems across 19 states. The largest cable television company continued to further develop its services through strategic acquisitions.
In 1992, Comcast acquired a controlling interest in Metro Media Company for $650 million in cash and $450 million in zero coupon notes. The deal expanded the company’s reputation beyond cable system services, granting Comcast cellular service in Philadelphia with 7.4 million subscribers.
In 1994, Comcast acquired Maclean Hunter’s US cable operations, solidifying its position as the third-largest cable operator in the United States with 3.3 million subscribers. Comcast then purchased E.W. Scripps Cable Systems in 1995 through an exchange involving $1.5 billion worth of the company’s common stock. This strategic acquisition led to a total Comcast customer base of 4.3 million subscribers.
1996 saw Comcast officially begin its cable high-speed internet service. Comcast@Home introduced its first high-speed cable modem services in Baltimore, Maryland, and Sarasota, Florida. Furthermore, Comcast Cable began the broadcast of promotional commercials for Comcast Home Theater, featuring their pay-per-view movies, available for $3.95.
Ed Snider partnered with Comcast to form Comcast-Spectacor in 1996, a sports and entertainment television company.
The collaboration led to Comcast officially owning the NHL’s Philadelphia Flyers and the NBA’s Philadelphia 76ers under the Comcast-Spectacor umbrella. By 2016, Comcast Corporation acquired Snider’s 24% stake, securing full ownership of the NHL’s Philadelphia Flyers, Wells Fargo Center, and Spectra businesses.
Comcast also showcased its commitment to sports media by launching its regional sports channel Comcast SportsNet in 1996.
In 1997, Microsoft invested $1 billion in Comcast Corporation. The cash investment helped Comcast improve high-speed data and video services through its cable delivery network.
In collaboration with the Walt Disney Company, Comcast purchased a 50% controlling interest in E! Entertainment Television. By 2004 Comcast had a total interest of 60.5% of E! Entertainment.
Additionally, Comcast launched a separate digital TV service. By 1999, the digital TV service had over 170 channels and 100,000 subscribers.
Between 1998 and 1999, Comcast continued to broaden its scope in cable television and telephone services. Key highlights include:
- Jones Intercable, Inc., is purchased by Comcast, adding 1 million customers to Comcast Cable.
- Comcast secured an additional 430,000 subscribers with its investment in Prime Communications.
- AT&T and Comcast swapped cable systems, securing 1.5 million subscribers.
- Julian Brodsky formed Comcast Interactive Capital Group for tech and internet-related investments.
2000s: Comcast Expands Cable Systems and Internet Service
After its investment in Lenfest Communications, Inc. in 2000, Comcast Cable expanded its subscriber base by 1.3 million. Comcast officially launched the G4 cable network in 2002, which established its position within the video game and interactive entertainment sector.
Moreover, Comcast purchased AT&T Broadband for $47.5 billion, making it the largest cable company in the United States.
The Comcast business consequently gained 22 million video customers, 6.3 million digital video customers, and 3.3 million high-speed data customers. To complement this major acquisition, Comcast launched high-speed internet, a service that would lead the company into the future as cable dies off.
The company also introduced its HDTV service, following the introduction of Video On Demand and Comcast Digital Video Recorder in 2003.
Furthermore, Comcast sold its QVC stake for $7.9 billion to Liberty Media Corporation. It had initially invested $380 million in the American free-to-air television network in 1988, followed by an additional $1.4 billion in 1995.
Additionally, Comcast gained 99.9% ownership in The Golf Channel. The cable systems company made its initial Golf Channel investment alongside five other major cable companies in 1994.
In 2004, Comcast collaborated with Gemstar-TV Guide and Microsoft to create an interactive program guide, aiming to enhance service features and improve the user interface.
Comcast then announced the launch of Comcast Digital Voice in 2005. The service included advanced digital phone features delivered over the internet, providing users with benefits like voicemail, call waiting, and unlimited nationwide calling.
In the mid to late 2000s, Comcast introduced a series of innovative developments and company foundations:
- Comcast Interactive Media (CIM) for digital ventures
- The expansion of Comcast SportsNet
- Fancast.com launch
- Universal Caller ID for TVs and computers
- Comcast Entertainment Group
- TV Everywhere by Comcast and Time Warner Cable

Comcast also entered strategic partnerships with renowned entities:
- A merger with PBS introduced PBS KIDS Sprout
- Comcast and Time Warner acquired Adelphia Communications
- Acquired a 20% interest in Metro-Goldwyn-Mayer Inc.
- Takes a 50% interest in Insight Communications
Additionally, numerous acquisitions further enriched Comcast’s portfolio, including:
- Susquehanna Communications’ cable systems for $775 million
- The Walt Disney Company’s 39.5% ownership stake in E! Networks
- The Platform (a leading online video management and publishing company)
- Patriot Media for $483 million and 81,000 video subscribers
In 2009, the history of Comcast changed significantly with a crucial agreement. Comcast gained 51% ownership and control over NBC Universal businesses through a joint venture with General Electric.
2010s: Comcast’s Brand Development and Global Expansion
In the 2010s, Comcast broadened its portfolio making notable strides in sports partnerships with the Olympic Committee and NASCAR midway through the decade.

In 2012, Comcast enhanced its wireless service offerings through a strategic partnership. Verizon Wireless and Comcast revealed plans to exchange services in Atlanta and introduce a range of promotions and incentives for both new and existing customers. Comcast’s powerful network of WiFi hotspots combined with the mobile virtual network operator (MVNO) agreement with Verizon Wireless, allowed Comcast to deliver an exceptional wireless experience to its customers.
In 2014, Comcast announced plans to merge with Time Warner Cable to form a world-class technology and media company under the umbrella of Comcast Corporation. However, the $45.2 billion deal was abandoned in 2015 due to substantial concerns that the merger would establish Comcast as an unavoidable gatekeeper for internet-based services reliant on a broadband connection to reach consumers.
Demonstrating a commitment to technological advancements, Comcast entered the Internet of Things industry in 2017 when it launched machineQ.

Additionally, Comcast expanded globally in the 2010s starting with the acquisition of UK satellite TV provider Sky from 21st Century Fox in 2018. Comcast gained 75% of Sky’s issued ordinary share capital.
During the same period, Comcast Business broadened its global footprint by entering the Canadian broadband market in 2019. Amidst this global expansion, the 2010s marked a robust decade for Comcast’s Xfinity brand and its relationship with NBC Universal.
Throughout the 2010s, Comcast Corporation strengthened its partnership with NBC Universal, exemplified in 2011 when Comcast and General Electric concluded their transaction to form NBCUniversal, LLC.
Also in 2011, NBCUniversal acquired The Blackstone Group’s 50% stake in Universal Orlando. This strategic move granted NBC Universal and Comcast full ownership of Universal Orlando Resort.
Additionally, NBC Universal and Comcast bought full ownership of Universal Studios Japan in 2017.

Comcast secured GE’s 49% ownership interest in NBC Universal for $16.7 billion in 2013. The acquisition helped position Comcast as a leading media and technology company.
In 2015, the enduring partnership between NBC Universal and Comcast was exemplified when 30 Rockefeller Plaza, in New York City housing NBC offices and studios, was renamed The Comcast Building.

Furthermore, in 2016 Comcast NBC Universal acquired DreamWorks Animation for $3.8 billion.
2020s: Comcast Adapts to a New Era
Understanding the economic strain caused by the COVID-19 pandemic, Comcast committed more than $500 million to support its employees where operations were paused or impacted.
Additionally, the introduction of the Comcast RISE aided small businesses affected by COVID-19. As of January 2024, the program had supported a total of 13,500 small businesses with over $125 million in grants.

Comcast enhanced its streaming and entertainment offerings by launching a new streaming platform, Peacock, in the United States in 2020. In 2021, Peacock solidified its content dominance as Universal Filmed Entertainment Group announced an exclusive licensing agreement, making all Universal film content available solely on Peacock.
Moreover, Comcast launched XClass TV in 2021, bringing its entertainment and voice platform to smart TVs across the US, without requiring an Xfinity subscription.
In 2022, XClass TV and Apple TV joined the Xfinity Stream app, offering customers additional ways to access their TV subscriptions at home. In November 2023, The Walt Disney Company announced the acquisition of the 33% stake in Hulu, LLC previously held by Comcast Corp’s NBC Universal Disney paid NBCU approximately $8.61 billion for the transaction.
History of Comcast Xfinity
In 2010, Comcast Corporation introduced its new brand, Xfinity, signaling a shift in technology platforms and product offerings. The plan may have had a secondary motive to distance its controversial “Comcast” brand from its new offerings. Operating under the Xfinity brand, Comcast Cable Communications delivers consumer cable television, internet, telephone, and wireless services.
The largest cable company announced the launch of xfinityTV.com and introduced the Xfinity TV app, granting millions of customers 150,000 video choices online. In 2011 Comcast formed partnerships with Samsung and Apple to bring the Xfinity TV app to smart TVs, tablets, and iPads.
The Xfinity TV app offered premium content from HBO, Showtime, Cinemax, Starz, and Encore. Additionally, Comcast announced a collaboration with Microsoft to launch Xfinity On Demand on the Xbox 360.
Comcast partnered with tech leaders for the next-generation Xfinity TV experience. By 2012, the X1 platform had launched nationwide, offering an interactive, personalized interface.
In the 2010s Comcast continued to introduce a series of Xfinity innovations:
- The X1 Remote Control app
- A Wireless Gateway for the fastest in-home WiFi
- Home Control – the first security-free smart home solution
- The Xfinity TV Go app with access to 35 channels on Apple and Android mobile devices
- Xfinity On Campus for college students to watch live TV and On Demand content on their devices
Additionally, Comcast strategically integrated popular video platforms like Netflix, YouTube, and Amazon Prime into X1, enhancing the user experience by providing a one-stop entertainment solution with access to diverse content.
In 2017, Comcast expanded the Xfinity brand by launching Xfinity Mobile. The wireless service utilized the largest 4G LTE network and 18 million WiFi hotspots to provide reliable mobile internet for users. Xfinity Mobile’s introduction of “Bring Your Own Device” at Xfinity stores nationwide in 2018 positioned Xfinity Mobile as a more customer-centric and competitive mobile service provider.
In 2020, Comcast’s Xfinity broadband experienced record growth, gaining an additional 2 million customers. The introduction of xFi Advanced Gateway in the same year brought multi-gigabit speeds with WiFi 6 technology.
This success continued in 2021, with Xfinity broadband adding 1.3 million customers, enabling connections for nearly one billion devices over WiFi.
By 2022, Comcast further enhanced its broadband offerings with the release of the xFi Advanced Gateway, incorporating WiFi 6E for faster speeds and increased device capacity. The same year, Xfinity Mobile had more than 5 million customers and was named the fastest mobile service in Comcast service areas.
Operational Structure and Growth
In Q3 2023, Comcast reported a total revenue of $30.12 billion. Notably, Comcast’s revenue for 2022 amounted to $121.43 billion, marking a $5 billion increase compared to the previous year.
| Year | Revenue |
| 2022 | $121.43 billion |
| 2021 | $116.39 billion |
| 2020 | $103.56 billion |
| 2019 | $108.94 billion |
| 2018 | $94.51 billion |
| 2017 | $85.03 billion |
| 2016 | $80.74 billion |
| 2015 | $74.51 billion |
| 2014 | $68.78 billion |
| 2013 | $64.66 billion |
| 2012 | $62.57 billion |
| 2011 | $55.84 billion |
| 2010 | $37.94 billion |
| 2009 | $35.76 billion |
| 2008 | $34.42 billion |
| 2007 | $31.06 billion |
| 2006 | $24.97 billion |
| 2005 | $21.08 billion |
| 2004 | $19.22 billion |
| 2003 | $18.35 billion |
| 2002 | $8.10 billion |
| 2001 | $5.94 billion |
| 2000 | $8.36 billion |
Comcast Corporation operates within three primary business segments:
- Comcast Cable Communications
- NBCUniversal
- Sky
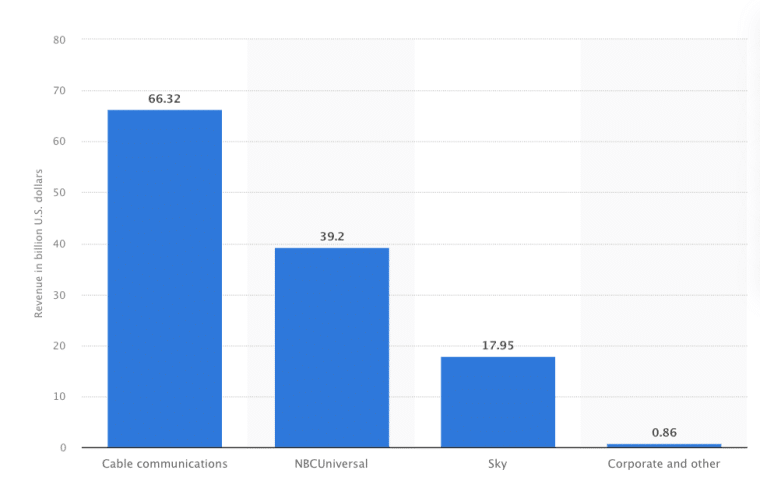
In 2022, the Comcast Cable Communications segment was the top revenue generator, contributing $66.3 billion.
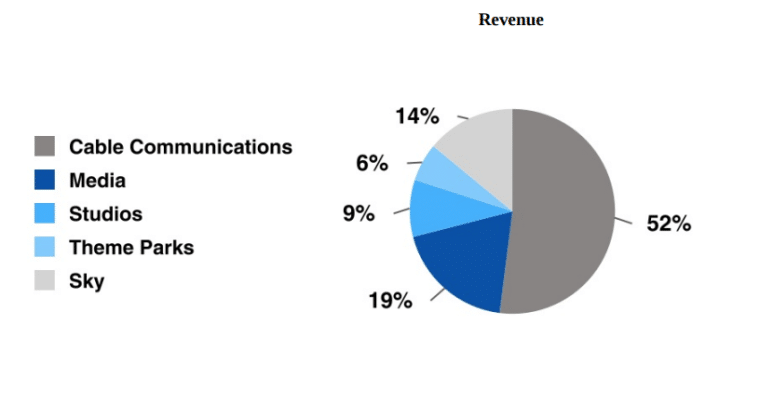
Within the NBCUniversal business, revenue is further categorized into three distinct segments:
- Media
- Studios
- Theme parks
The NBC Media segment contributed 19% to Comcast’s total revenue, following Comcast Cable Communications maintaining a substantial lead at 52%.
As of 2022, Comcast Cable Communications had 34.3 million customer relationships, with 31.8 million in the residential customer sector and 2.5 million in business services.
In Q3 2023, Comcast reported a total of 52.3 million connectivity and platform customer relationships. Comcast’s Peacock paid subscribers count increased to 28 million customers in Q3 2023, marking an 80% increase compared to the prior year period.
What Does Comcast Own?
Comcast has acquired over 50 businesses since its inception as a cable company in 1963.
Here is a list of some of the companies Comcast owns as of January 2024:
| Company | Date |
| Comcast Spectacor | 1997 |
| Home Team Sports | 2000 |
| AT&T Broadband | 2001 |
| NBC Universal | 2009 |
| Xfinity | 2010 |
| Sky Group | 2018 |
| Xumo | 2020 |
| Blueface | 2020 |
| Masergy | 2021 |
Comcast’s most extensive entertainment portfolio is under the banner of the NBC Universal segment. Among its assets are NBC and Telemundo broadcast company, with 11 national cable networks.
Within the NBC Universal division, Comcast further extends its influence through ownership of 5 film studios dedicated to the development, production, acquisition, marketing, and global distribution of filmed entertainment.
Additionally, Comcast NBC Universal controls 4 entertainment television studios that produce content licensed to cable, broadcast, premium networks, and direct-to-consumer (DTC) streaming service providers.
Expanding beyond the screen, Comcast NBC Universal owns 4 international theme parks.
| Category | Assets |
| National Cable Television Networks | USA Network E! Syfy Bravo MSNBC CNBC Oxygen Golf Channel Universal Kids Universo CNBC World |
| Film Studios | Universal Pictures Illumination DreamWorks Animation Focus Features Working Title |
| Television Studios | Universal Television Universal Content Productions Universal Television Alternative Studio Universal International Studios |
| Theme Parks | Universal Orlando Resort Universal Studios Hollywood Universal Studios Japan Universal Beijing Resort |
Furthermore, Comcast owns Peacock, the direct-to-consumer streaming service under NBC Universal, launched in 2020. Comcast also owns Comcast Spectacor, a sports and entertainment subsidiary that includes notable properties and partnerships.
| Sports & Entertainment | Wells Fargo Center in Philadelphia The Philadelphia Flyers NHL Team Philadelphia Wings Maine Mariners Spectacor Events & Entertainment |
| Gaming | Seoul Infernal |
| Partnerships | Learfield IMG College T1 Entertainment & Sports Nerd Street Gamers The Cordish Companies |
History of the Comcast Logo
Comcast introduced its first logo in 1969 during the formal rebranding process from American Cable Systems.
The original logo showcased two stylized “C” letters, nested within each other in a solid black square. This design emphasized a sense of connection, symbolizing the company’s dedication to communication.

In 2000, Comcast had its first company rebranding, adopting a completely different style. The logo featured “Comcast” in all lowercase letters.

Furthermore, the emblem was simplified, showcasing a stylized red letter “C” positioned around the initial letter of the wordmark.
After this, Comcast made slight modifications to the logo in 2007, introducing a modified typeface for the wordmark.

Following the update, the logo featured all-capitalized letters and a thinner font compared to its previous design. The Comcast logo has maintained its design integrity since, showcasing its established presence and strong connection to NBC.

The Future of Comcast
As Comcast advances into the future, it says that it remains committed to embracing technological progress. Cable may be dying off but its smart, timely pivot to high-speed internet is already paying off. With a primary focus on uninterrupted connectivity, the company has invested significantly — $20 billion over the past five years — to expand its network, providing multi-gig speed service to 15 million homes and businesses.
Looking forward, Comcast will elevate its business operations by incorporating cutting-edge AI developments. In a pivotal collaboration with Broadcom in October 2023, Comcast is at the forefront of creating the world’s first AI-powered access network. Through the integration of AI and ML into its network components, Comcast aims to enhance automation and elevate customer experiences.
Additionally, in January 2024, Comcast NBC Universal introduced “One Platform Total Audience”, an AI-powered media planning solution. As a result, this tool utilizes machine learning to craft a unified plan across both linear and streaming platforms, leveraging NBCU’s data and advertisers’ datasets for widespread consumer reach and transparent program-level insights.
Driven by a dedication to innovation and strategic partnerships, Comcast will continue to shape the digital landscape, delivering unparalleled experiences for millions of users globally.


