A key player in the aviation industry, Delta Air Lines has grown to become one of the world’s largest airlines. Since its beginnings in 1928, Delta’s net worth and reach has expanded, becoming a leader in both passenger and cargo services.
As of September 2024, Delta Air Lines had a market value of $30.44 billion, cementing its position as a major force in global aviation.
Our team at Business2Community has taken a deep dive into Delta’s history, key financial achievements, challenges, and continued growth. Read on to explore the major milestones and the journey behind Delta’s rise to prominence.
Delta Air Lines Key Company Data
Delta Airlines Net Worth: $30.44 billion
Date Founded: December 1928
Founded By: CE Woolman
Current CEO: Ed Bastian
Industries: Aviation
Delta Airlines Stock Ticker: NYSE: DAL
Dividend Yield: 1.32%
What Is Delta Air Lines’ Net Worth?
As of September 2024, Delta Air Lines’ net worth or market cap was $30.44 billion based on a share price of $47.16 and 645.42 million shares outstanding. The company has been listed on the New York Stock Exchange under the ticker symbol DAL since 2007.
Delta’s fiscal year ends on December 31 each year and the company typically releases its annual financial results in the following January.
Following several years of difficult financial performance, the company filed for bankruptcy in 2005 and emerged in its current form in 2007.
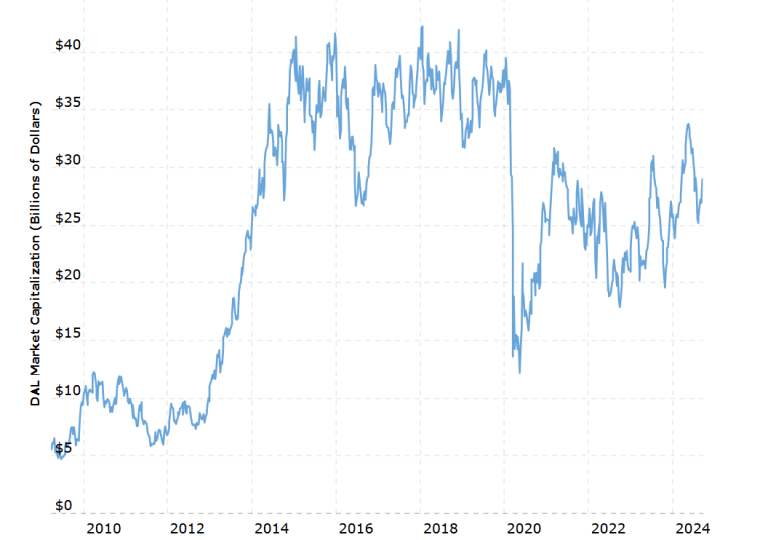
Delta Air Lines’ stock began trading once again on the New York Stock Exchange at $20 a share in May 2007. After several years of steady growth, its shares were going for over $40 each in early 2015 for the first time, giving the company a valuation of around $38 billion.
Delta’s ability to bounce back from bankruptcy and become one of the healthiest, most profitable airlines in the world has been attributed to the innovative approach taken by its leaders. For example, it launched an employee profit-sharing program and stock ownership plan, and took the unusual step of acquiring its own oil refinery in a bid to control fuel costs.
Between 2015 and 2020, Delta Air Lines’ stock price and net worth were relatively stable, gradually reaching an all-time high of $61.48 per share in July 2019.
However, along with carriers in the airline segment across the world, Delta was hit hard by the COVID-19 pandemic. With flights grounded, the company’s market cap dropped 70% from around $40 billion at the start of 2020 to just $12 billion by April that same year.
Since the easing of lockdown measures and a return to pre-pandemic passenger levels, Delta Air Lines has seen its stock price and market cap steadily increase. The company’s share price peaked at $53.86 a share in May 2024 and sits at around $46 as of September 2024.
The drop in market confidence is largely linked to Delta Air Lines’ handling of a global technology outage caused by a software update from the cybersecurity firm CrowdStrike in which thousands of flights were grounded. It is thought that the company’s handling of the situation led to unnecessary additional disruption compared to its competitors.
Delta Air Lines Revenue
In its first year after bankruptcy, Delta Air Lines posted pre-tax income of $1.8 billion. However, with jet fuel prices rising significantly, the company also reported a pre-tax loss for the final quarter of 2007 of $105 million.
Delta Air Lines merged with Northwest Airlines in 2008 increasing revenue considerably. For 2008, the combined companies reported total revenue had grown to $22.7 billion. However, including pre-merger data from Northwest in the comparison showed operating revenue was flat for the fourth quarter compared to the previous year.
At this point, with economies around the world suffering a global recession, Delta Air Lines remained unprofitable, reporting a loss of $8.9 billion.
High fuel prices and low consumer confidence continued to pose a significant challenge for Delta Air Lines for several years. 2010 marked a turning point, however, as the company’s turnaround plans began to make an impact and the world slowly recovered from the global economic crisis. In January 2011, the company announced full-year revenue of $31.75 billion and net income of $593 million for the 2010 financial year.
“Our 2010 results are among the best in Delta’s history. They would not have been possible without the dedication and determination of Delta employees worldwide and we are pleased we will pay more than $300 million in profit sharing for 2010,” said Richard Anderson, Delta’s CEO at the time.
These results are a direct reflection of the success of our merger, cost discipline, and debt reduction strategy and give us momentum to deal with the rising fuel prices we face in 2011
The next 10 years of Delta Air Lines’ financial performance were somewhat unremarkable but solid. Between 2010 and 2019, revenue grew from $31.75 billion to $47 billion, an increase of 48%. The company also remained profitable during this time, increasing net income from $593 million in 2010 to $4.8 billion in 2019.

However, Delta’s balance sheet took a huge hit in 2020 with the arrival of the COVID-19 pandemic. With international and domestic air travel more or less eliminated during the peak of the pandemic, air carriers had no source of income. In January 2021, Delta announced annual revenue of $17 billion and a loss of $12.8 billion for the 2020 financial year. This was against a profit of $4.8 billion in 2019 and ended a 10-year run of profitable years.
“Our December quarter results capped the toughest year in Delta’s history. I want to thank the Delta people who have risen to the occasion, focusing on delivering results for all of our stakeholders by putting our customers at the center of our recovery,” said Ed Bastian, Delta’s CEO. “While our challenges continue in 2021, I am optimistic this will be a year of recovery and a turning point that results in an even stronger Delta returning to revenue growth, profitability and free cash generation.”
After another challenging year in 2021, Delta Air Lines bounced back in style in 2022 with annual revenue up to $50 billion and a net income of $1.3 billion.
In 2023, the company’s annual results showed further solid operational performance, with revenue of $58 billion and profit up 350% to $4.6 billion. Adjusted operating margin for the full year was 11.6%, with pre-tax margin of 9.5%. Delta also reported liquidity of $6.8 billion at year-end, including cash and cash equivalents, short-term investments, and undrawn revolving credit facilities
The table below shows Delta Air Lines’ annual revenue for the past 10 years:
| Year | Revenue ($ billions) |
| 2014 | 40.36 |
| 2015 | 40.7 |
| 2016 | 39.45 |
| 2017 | 41.44 |
| 2018 | 44.44 |
| 2019 | 47.01 |
| 2020 | 17.1 |
| 2021 | 29.9 |
| 2022 | 50.58 |
| 2023 | 58.04 |
Aside from revenue, Delta focuses on other metrics such as free cash flow because the company’s management believes this metric is helpful to investors. It defines free cash flow as net cash from its operating and investing activities adjusted for:
- Net redemptions of short-term investments to give investors a better understanding of the company’s free cash flow generated by its operations.
- Cash flows related to investments in and transactions with other airlines, to provide a more meaningful comparison to industry peers.
- Net cash flows related to certain airport construction projects to help investors better understand the company’s free cash flow and capital expenditures.
- Financed aircraft acquisitions that are leased as capital expenditures based on their original contractual purchase price or an estimate of the aircraft’s fair value to provide a better view of its investing activities.
The company reported a free cash flow of $2 billion for the 2023 financial year.
Delta Air Lines Dividend History
Delta Air Lines typically pays quarterly dividends to its shareholders. The most recent dividend paid was $0.15 in August 2024. The company didn’t pay a dividend at all between March 2020 and August 2023 as it navigated the financial impact of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Delta’s dividend payout ratio is based on:
- 8.63% on the preceding 12 months of earnings
- 10.02% on the current year estimates
- 8.31% on the next year’s estimates
- 5.93% on cash flow
Delta Air Lines has a dividend yield of 1.32%, which is considerably lower than the average for a transport company. While Delta increased its quarterly dividend from $0.10 in June 2024 to $0.15 in August 2024, the amount paid to shareholders is still significantly below pre-pandemic highs of $0.40. Before the pandemic, the company also had a solid record of quarterly stock buybacks.
Here’s a list of Delta’s annual dividend payments since 2014:
| Date | Stock Price ($) | Payout ($) | Dividend Yield (%) |
| 11/16/2017 | 46.99 | 0.94 | 2.01 |
| 2/22/2018 | 49.23 | 1.05 | 2.13 |
| 5/10/2018 | 49.05 | 1.16 | 2.36 |
| 7/25/2018 | 49.01 | 1.49 | 3.04 |
| 11/6/2018 | 52.95 | 1.25 | 2.36 |
| 2/28/2018 | 47.66 | 1.29 | 2.72 |
| 5/1/2019 | 55.31 | 1.34 | 2.42 |
| 7/24/2019 | 61.48 | 1.40 | 2.27 |
| 10/23/2019 | 52.77 | 1.46 | 2.79 |
| 2/19/2020 | 57.77 | 1.52 | 2.62 |
| 7/14/2023 | 46.00 | 0.10 | 0.22 |
| 10/11/2023 | 35.70 | 0.20 | 0.56 |
| 2/23/2024 | 41.50 | 0.30 | 0.72 |
| 5/13/2024 | 52.81 | 0.40 | 0.75 |
| 7/30/2024 | 43.23 | 0.45 | 1.04 |
| 9/23/2024 | 47.16 | 0.45 | 0.95 |
Who Owns Delta Air Lines?
Delta Air Lines, Inc. is a publicly-traded company on the New York Stock Exchange. Over 78% of Delta’s stock is owned by institutional investors, such as The Vanguard Group (11.2%), and BlackRock, Inc. (6.59%). A further 21% of the company’s stock is owned by the general public, including current and former employees under its employee stock ownership plan.

Delta Air Lines can be traced back to Delta Air Service which was first incorporated in December 1928 and led by CE Woolman after acquiring the assets of a crop dusting business. The company became Delta Air Lines, Inc. in 1945.
Who is the Delta Air Lines CEO?
Ed Bastian was appointed as Delta Air Lines’ CEO in 2016. He joined Delta in 1998 and was appointed chief financial officer in 2005 and President in 2007. During his tenure, both as CEO and in his previous roles, Bastian has had to navigate some of the most challenging periods in Delta Air Lines’ history, including 9/11, bankruptcy, and COVID-19.
Under Bastian’s leadership, Delta has won many awards, including:
- Wall Street Journal: Top US airline
- Air Transport World: Airline of the Year
- Fortune: World’s Most Admired Companies
- Cirium: Platinum Award for operational excellence
- Fast Company: Most Innovative Companies
Bastian himself has also been recognized for his leadership. He was included in Fortune’s World’s 50 Greatest Leaders and the Top 10 CEOs of 2021 in Glassdoor’s Employees’ Choice Awards, and named Chief Executive magazine’s 2023 Chief Executive of the Year.
The Delta Air Lines HQ is based at Hartsfield–Jackson Atlanta International Airport where it has been since 1941. There are also nine Delta Air Lines bases, or hubs, across the United States, including Atlanta, Boston, Detroit, New York, Salt Lake City, and Seattle.
Delta Air Lines’ Company History
Delta Air Lines is a major US air carrier based in Atlanta, Georgia. It’s the oldest US airline still in operation and one of the biggest airlines in the world, with a fleet of almost 1,000 commercial aircraft. Delta operates more than 4,000 flights each day, across 290 destinations around the world.
Below, we explore Delta’s journey from a humble crop dusting operation to becoming a global leader in the aviation industry.
1928-2005: From Louisiana Crop Dusting Company to 100 Million Passengers
Delta Air Lines’ company history begins with a crop dusting business based out of Monroe, Louisiana. The original company’s CEO, CE Woolman, backed by local investors, acquired its assets and founded Delta Air Service in 1928.
Delta began to run passenger flights in the summer of 1929 between Texas and Mississippi. The Delta Air Corporation was set up in December 1930 and secured an airmail contract in 1934. Delta moved its headquarters to Atlanta in 1941.
The company changed its name to Delta Air Lines in 1945. It acquired Chicago and Southern Air Lines in 1953 and began flying international routes for the first time. In 1972, Delta acquired Northeast Airlines.
Delta launched its transatlantic service in 1978, flying non-stop between Atlanta and London. In 1981, Delta launched its frequent-flyer program, which became SkyMiles in 1995.
In 1991, Delta acquired transatlantic routes from Pan Am and the Pan Am Shuttle. This was the biggest acquisition of flights in aviation history and made Delta the leading airline across the Atlantic.
In 1997, Delta became the first airline to carry over 100 million passengers in one year.
2005-2016: Delta Emerges From Bankruptcy to Become a Global Airline
Against a backdrop of rising fuel costs, Delta Air Lines filed for bankruptcy in 2005. The company’s liabilities included around $28.3 billion in total debt. The company’s leaders estimated that it would be worth between $9.4 billion and $12 billion after emerging from bankruptcy.

With a goal of returning to profitability by 2007, Delta began to work towards an additional $3 billion in annual cost cuts from debt relief, facility costs, fleet modifications, and lay offs. Staff pay was also reduced, including a 15% cut for the company’s leaders and 25% for CEO at the time Gerald Grinstein.
After resisting a hostile takeover bid from US Airways, the company emerged from bankruptcy in 2007 and its shares were relisted on the New York Stock Exchange. Despite its troubles, Delta was the leading carrier in on-time performance for 2007.
In 2008, Delta acquired Northwest Airlines, which it operated as a wholly-owned subsidiary until the end of 2009. The merger created a truly global airline, with an enterprise value of $17.7 billion and significant operations in every part of the world. Around 15% of stock in the new company was awarded to employees.
In 2009, Delta became the first US airline to operate in six continents following the launch of non-stop flights between LA and Sydney. Delta announced an investment of more than $2 billion in 2010 to improve customer experience, including installing beds and in-seat video systems, and creating more First Class cabins. It also revealed plans for a $1.2 billion project to expand and renovate its facilities at JFK.

In 2012, Delta’s subsidiary, Monroe Energy, acquired the Trainer oil refinery in Pennsylvania for $180 million. As part of the deal, Delta acquired the refinery, pipelines, and transportation assets to provide fuel to its Northeastern operations.
To improve its access to the transatlantic market, Delta acquired a 49% stake in the UK-based airline Virgin Atlantic from Singapore Airlines in 2013 for $360 million.
In 2015, the carrier introduced five different onboard ticket options for passengers:
- Delta One
- First Class
- Delta Comfort+
- Main Cabin
- Basic Economy
In 2016, the company added a Delta premium economy option, which became Premium Select.
2016-2024: Navigating the COVID-19 Pandemic
Ed Bastian was appointed CEO, succeeding Richard Anderson in 2016. It was during this year that Delta paid out $1.5 billion in profit sharing to its employees, in the biggest payout of its kind in US history.
In 2018, Delta revealed that its third-party refinery sales for quarter two, which covers the sale of non-jet fuel produced at its refinery, increased to $216 million from $67 million in 2017. The company said that it used this income to manage rising fuel costs and keep fares down.
Following a sharp drop in air travel due to the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic, Delta Air Lines announced it was reducing flight capacity by 40% in March 2020. The company also said it would reduce investment and park hundreds of aircraft.
“The speed of the demand fall-off is unlike anything we’ve seen,” said Ed Bastian. “We are moving quickly to preserve cash and protect our company. And with revenues dropping, we must be focused on taking costs out of our business.”
Delta’s finances (and its stock price) were hit hard in 2020, with international and domestic travel more or less eliminated during the peak of the pandemic. The company’s 2020 full year results showed annual revenue of $17 billion, down from $47 billion, and a loss of $12.8 billion against a profit of $4.8 billion in 2019. With this performance, Delta ended a 10-year run of profitable years.
Ongoing weak demand and an increase in lower-margin leisure travel led to an imbalance between Delta’s costs and revenue per available seat mile. In the first quarter of 2021, costs per seat mile were up by 13% while revenue per seat mile fell by 46%. It wasn’t until the second quarter of 2021 that Delta reported a quarterly profit again, but finances remained tight as many flight schedules remained unfilled.
Delta Air Lines Controversies
Delta’s largely positive reputation has helped it grow to become one of the world’s biggest airlines. Its history is not one riddled with controversies, but some notable stories include:
Carbon Offsetting
In 2023, the US government announced that it would be taking action against Delta for misleading claims about its carbon neutrality. Delta had revealed its carbon neutral plans in 2020, pledging $1 billion to offset all its emissions by 2030 by buying carbon credits, decreasing its fuel usage, and increasing aircraft efficiency.
The lawsuit claimed that the carrier’s carbon neutral claims were false due to the company’s reliance on offsetting measures which was misleading to customers. In response, Delta called for the case to be thrown out.
2024 CrowdStrike Incident
In July 2024, Delta was forced to cancel over 7,000 flights during a meltdown following a routine software upgrade from the cybersecurity provider CrowdStrike. The company’s recovery from the incident was so out of sync with other airlines, that the US government launched an investigation into the events. More than 500,000 passengers were inconvenienced and the government received more than 3,000 complaints.
Delta claimed that it lost $500 million and plans to sue CrowdStrike.
Has Delta Air Lines Ever Crashed?
Delta Air Lines has recorded one fatal crash in its history, the crash of flight 191 in 1985. This accident, caused by severe weather conditions, resulted in 137 fatalities.
The most recent incident was in 2015 when flight 1068 skidded off the runway while landing in heavy snow at LaGuardia Airport. 29 passengers were treated for minor injuries, but there were no fatalities.
What Can We Learn From Delta Air Lines?
Delta Air Lines’ net worth growth and business evolution to become one of the world’s largest airlines truly highlights the power of adaptability and strategic growth. By responding to shifting market demands, adopting new technologies, and expanding its global network, Delta has firmly taken its place as a leader in the aviation industry.
Throughout its history, Delta’s resilience has been key to its ability to overcome challenges such as economic downturns, the global pandemic, and industry disruption. Strategic decisions to form alliances, expand international routes, and invest in customer experience, have fueled Delta’s growth and helped it to stand out in a highly competitive market.
As Delta turns to the future, it looks likely to maintain its leadership through continued innovation, a commitment to sustainability, and further investment in passenger comfort. However, like other major airlines, Delta faces challenges around regulatory scrutiny, environmental concerns, and the constantly evolving needs of travelers.
By balancing growth with a focus on efficiency, safety, and sustainability, Delta Air Lines should be able to build on its legacy while navigating the complex modern aviation landscape.
