Cybercrime continues to rise, amounting to billions of dollars in losses for businesses and individuals alike. Given today’s rapidly evolving digital economy and threat landscape, understanding the key aspects of cybersecurity is not only crucial for IT professionals and security experts but also for business owners, executives, and anyone concerned about protecting their sensitive information.
While cybersecurity data is abundant, it can be challenging to find the most relevant and up-to-date insights. That’s why we’ve done all the heavy lifting to bring you over 100 cybersecurity statistics. Keep reading to discover all you need to know about the cybersecurity landscape in 2025.
Cybersecurity – Key Stats
Cybersecurity Market Statistics
Estimates project that the Cybersecurity market will increase by $5.7 trillion or 69.4% between 2023 and 2028.
The market for cybersecurity includes revenues generated by cyber solutions and security services. According to Statista, costs in the cybersecurity market will continue to show positive growth and reach $13.82 trillion by 2028.
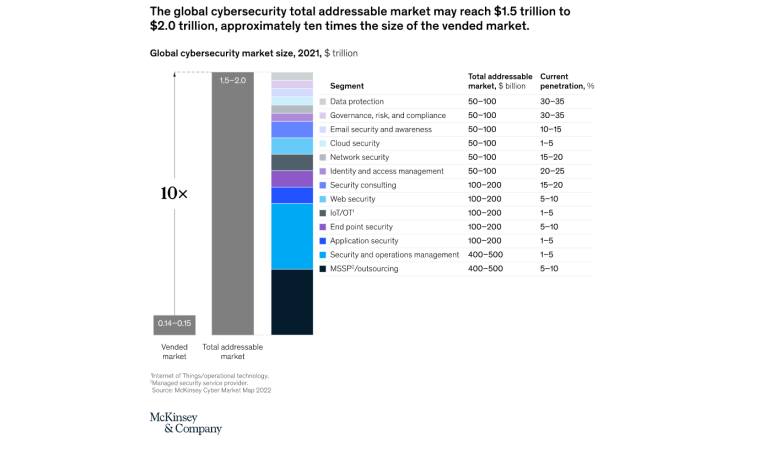
As of 2022, the fully addressable cybersecurity market amounted to between $1.5 trillion and $2.0 trillion, 10 times the size of the vended market.
The vended market amounts to $150 billion, which presents a massive opportunity for cybersecurity technology and service providers. According to McKinsey, growth in the market is driven primarily by a rapidly expanding digital economy.
Palo Alto Networks led the cybersecurity market in Q4 2022.
Palo Alto, which is the largest player in the cybersecurity space both by market share and valuation, led the market with a 7.9% share. Other key players included:
- Fortinet – 6.8%
- Cisco – 6.1%
- Check Point – 3.8%
- CrowdStrike – 3.2%
- IBM – 3.1%
- Okta – 3%
- Microsoft – 2.9%
- Trellix – 2.9%
- Symantec – 2.6%
- Splunk – 2.4%
- Trend Micro – 2.3%
According to the World Economic Forum (WEF), more than 39% of organization leaders globally agree that cybersecurity is a key enabler of business success.
Insights gathered by the WEF further confirm that a growing number of business leaders are championing the importance of cybersecurity.
Globally, the number of unfilled cybersecurity jobs grew by 350% between 2013 and 2021.
This was driven by a rapidly evolving threat landscape and a global shortage of trained cybersecurity professionals. Additionally, Splunk’s 2023 State of Security Report revealed that 88% of respondents reported talent challenges and that they struggled to hire and retain enough skilled staffers.
The average spend per employee in the cybersecurity market is expected to reach $46.54 in 2023.
Higher spending year-over-year is driven primarily by rapid market growth and the global cybersecurity skills shortage.
As of 2023, Cyber Edge also states that security experts are starting to assess the potential dangers of AI chatbots, deepfakes, and other AI-based tools. Major concerns include the risk that threat actors might use these tools to:
- Create realistic phishing emails tailored to specific industries or roles, mimicking individuals such as CEOs.
- Develop new malicious code and obfuscate existing malware variants.
- Use simulated voices, like those of CEOs, to persuade subordinates to transfer funds to fabricated accounts.
- Create deceptive videos that manipulate political figures or celebrities to announce sales and direct customers to fake websites for credit card information capture.
- Generate fake announcements from corporate executives regarding product recalls or accidents caused by the company’s products to sow confusion.
- Release fabricated videos of CEOs announcing extremely positive or negative news to manipulate stock prices.
- Spread fake videos of political candidates making controversial statements, exhibiting physical or mental weaknesses, or giving false endorsements to influence elections.
- Demand ransoms to refrain from carrying out any of the mentioned activities.
Cybersecurity Market Revenue Statistics
Revenue in the Cybersecurity market will reach $162 billion in 2023.
The largest market within cybersecurity is security services, with a projected market volume of $85.49 billion in 2023.
By 2028, cybersecurity revenue will reach $256.50 billion, representing an annual growth rate of 9.6%.
The US is projected to generate the most revenue, at $68.68 million for 2023.
Global spending on cybersecurity solutions is expected to increase by 12.1% in 2023.
According to data from the International Data Corporation, worldwide spending on cybersecurity solutions is projected to hit $219 billion in 2023.
Cybersecurity Statistics by Attack Type
Global cyberattacks increased by 125% in 2021 and are expected to cause $10.5 trillion in damages by 2025 at the current rate of growth. That’s a 300% increase from 2015.
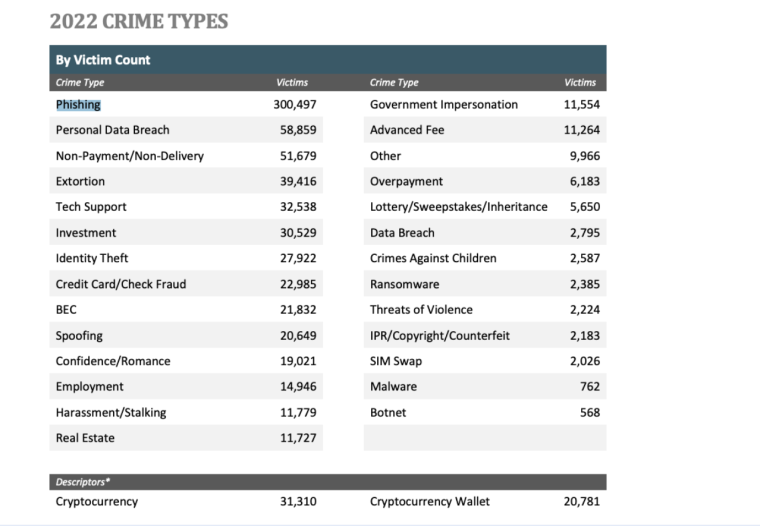
As of 2022, the top five cybercrime types as per the FBI’s Internet Crime Report were:
- Phishing: 300,497 victims, down 7.25% from 323,972 in 2021.
- Personal data breach: 58,859 victims, up 13.5% from 51,829 in 2021.
- Non-payment/non-delivery: 51,679 victims, down 59.6% from 82,478 in 2021.
- Extortion: 39,416 victims, up 0.14% from 39,360 in 2021.
- Tech support: 32,538 victims, up 36.1% from 23,903 in 2021.
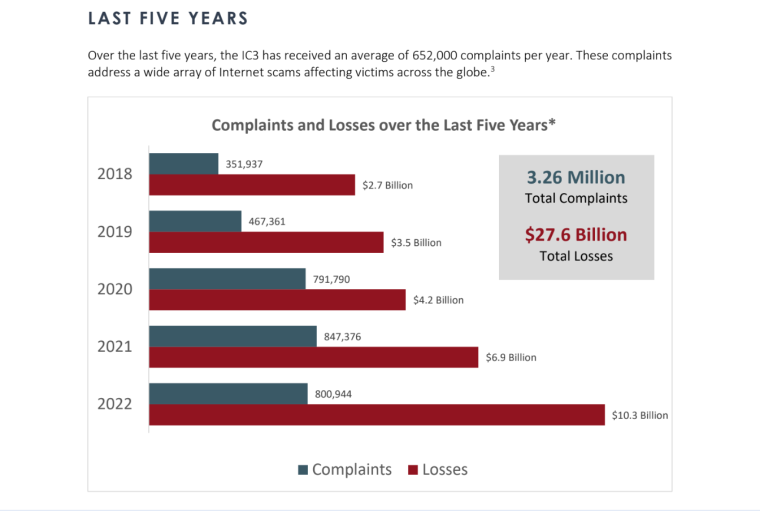
The IC3 has received over 7.3 million complaints since its inception in 2000.
The IC3 has received an average of 652,000 complaints per year, with 800,944 in 2022 alone.
While the number of complaints the IC3 received decreased by 5% in 2022, losses increased by over 47%.
The potential loss from cyberattacks went up from $6.9 billion in 2021 to over $10.2 billion in 2022.
When it comes to organizations, the average dwell time for bad actors was 2.24 months.
Research by Splunk revealed that whatever the avenue, it took organizations about nine weeks from the moment a bad actor penetrated their systems until appropriate parties were aware of it.
Phishing Statistics
The number of phishing attacks continues to rise as cybercriminals use deceptive messages to trick users into providing sensitive information such as credit card numbers or installing malware on their computers. Phishing remains the most common cyber attack, accounting for over 3.4 billion daily spam emails.
There was a 61% increase in the rate of phishing attacks in the last six months of 2022.
As of 2023, attacks are getting more sophisticated, spreading beyond emails to text messages and other forms of personal communication.
In Q3 2022, 23% of phishing attacks worldwide were directed toward financial institutions.
In addition, web-based software services and webmail accounted for 17% of phishing attacks, making them the most-targeted industries.
Studies show a 50% increase in attacks on mobile devices, with scams and credential theft at the top of the list of payloads.
Cybercriminals are shifting their attacks to mobile and personal communication channels to reach users.
In 2022, internet users in Vietnam were most frequently targeted by phishing attacks.
The phishing rate in Vietnam was 17.03%. Macao ranked second, with an attack rate of nearly 14%, while Madagascar followed with 12%.
Malware Statistics
Malware is a type of harmful software created to gain control over or disrupt a computer system. It works by disguising itself as harmless files or links and tricking users into downloading it. Once installed, malware allows unauthorized individuals to access not only the affected computer but also an organization’s entire network. The reasons behind malware attacks include stealing personal information or company data so as to cause disruptions to normal operations.
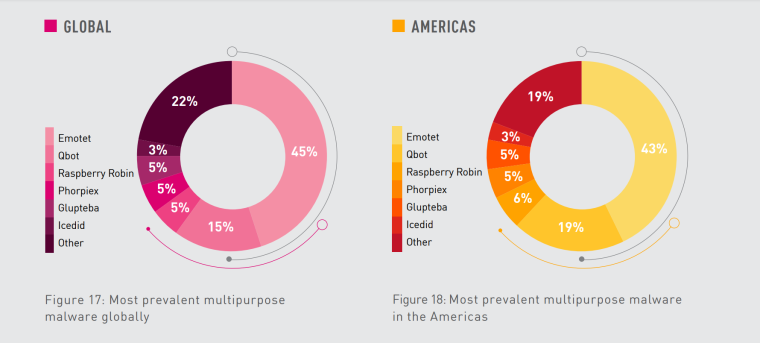
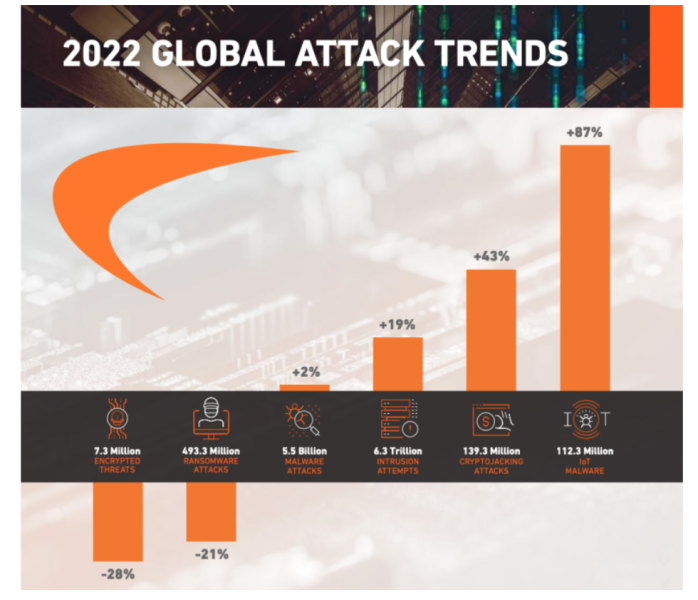
Globally, there were 5.5 billion malware attacks detected in 2022, mainly in the Asia-Pacific region.
Types of Malware include:
- Viruses
- Ransomware
- Scareware
- Worms
- Spyware
- Trojans
- Adware
- Fileless malware
As per IC3’s 2022 annual report, malware attacks between 2019 and 2020 increased by 358%.
Worms, viruses, ransomware, trojans, and backdoors were the most frequently blocked types of malware attacks. Email and websites were the two most common attack vectors, but websites were more often used for phishing attacks.
Ransomware Statistics
Ransomware, a form of malicious software or malware, is designed to encrypt computer data, rendering it inaccessible. Cybercriminals not only encrypt a network but often seize data from the system and keep it hostage until a ransom is paid.
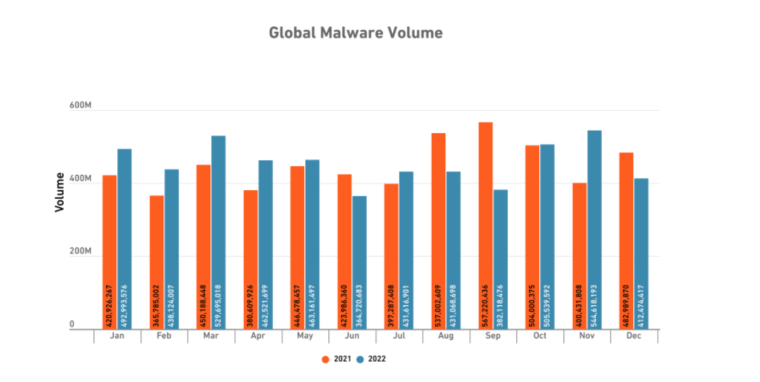
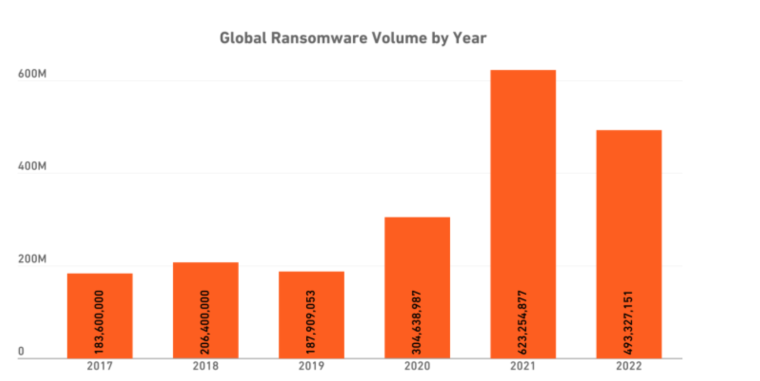
In 2022, 493.33 million ransomware attacks were detected by organizations worldwide.
Overall, the number of ransomware attacks increased during Q3 and Q4 of 2022, going from around 102 million to over 155 million cases, respectively.
In 2022, the IC3 received 2,385 complaints identified as ransomware with adjusted losses of more than $34.3 million.
Although cybercriminals used a variety of techniques to infect victims with ransomware, the top initial infection vectors for ransomware incidents reported to the IC3 in 2022 were
- Phishing emails.
- Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) exploitation.
- The exploitation of software vulnerabilities.
Ransomware attacks saw an increase of 41% in 2022.
11% of breaches in IBM’s Data Breach report were ransomware attacks, an increase from 2021, when 7.8% of breaches were ransomware.
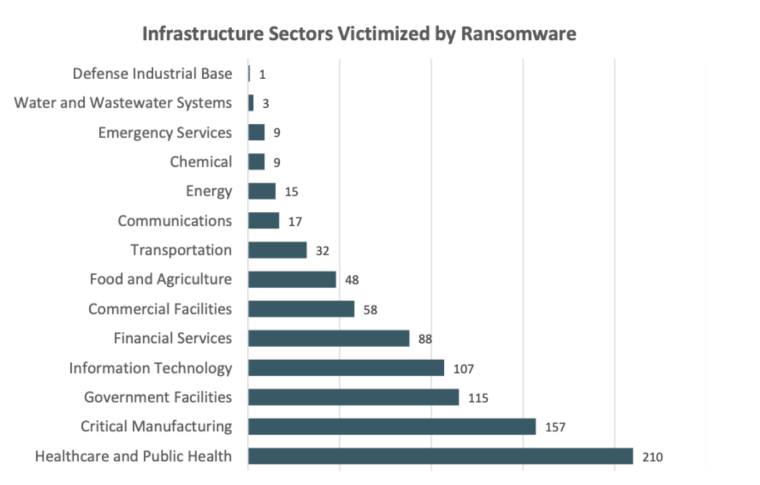
The IC3 received 870 complaints which indicated that organizations belonging to critical infrastructure sectors had fallen victim to ransomware attacks.
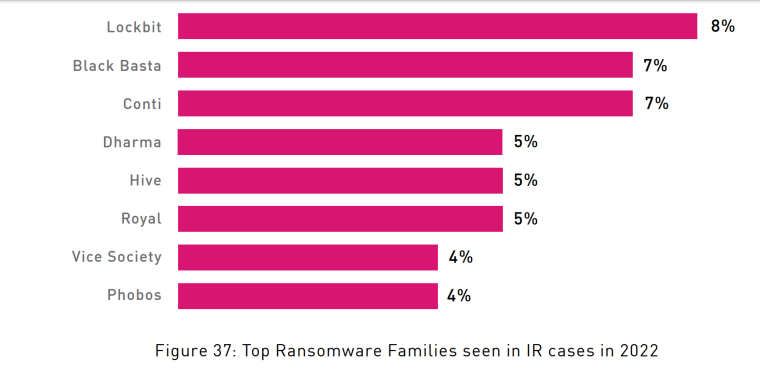
Additionally, the top-three ransomware variants reported to have targeted members of a critical infrastructure sector were Lock bit, ALPHV/Blackcoats, and Hive.
According to IBM, the average cost of a ransomware attack in 2022 was $4.54 million not including the cost of the ransom itself.
The average cost of a ransomware attack excluding the cost of the ransom was $4.54 million, while the average cost of a destructive or wiper attack was $5.12 million. Both were higher than the overall average total cost of a data breach of $4.35 million.
Ransomware breaches took 16.3% or 49 days longer than average to identify and contain.
A ransomware attack took 237 days to identify and 89 days to contain, amounting to a lifecycle of 326 days. A destructive attack took 233 days to identify and 91 days to contain, for a total lifecycle of 324 days. This is compared to the overall average lifecycle of 277 days.
According to findings compiled by Comparitech in 2022:
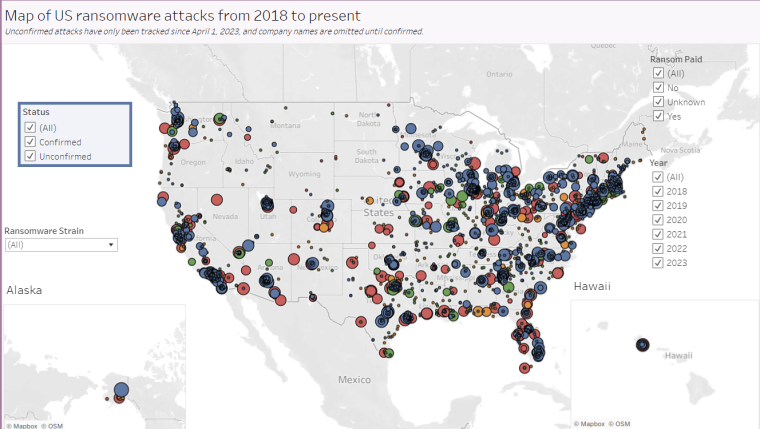
- There were 795 ransomware attacks compared to 1365 recorded in 2021 in the USA.
- The average ransom demand was $7.2 million, lower by just over $1 million compared to $8.2 million in 2021.
- A total of 115,856,886 records were impacted, over double the number impacted in 2021.
- On average, each attack impacted 559,695 records, which is nearly five times the average of 119,114 records in 2021.
Password Cracking Statistics
Passwords remained the most used security method by companies worldwide in 2022.
This is despite the vulnerability of password security currently in the face of evolving cyber breaches and cyberattack techniques.
According to a study from Statista, 50% of respondents from countries such as the US, Germany, and Australia report that passwords are too weak for security.
However, despite the rising concerns surrounding passwords, they remained the most popular security authentication measure taken to protect online accounts in 2022.
According to the LastPass Psychology of Password’s 2021 report:
- 45% of respondents said they hadn’t changed their passwords in a year, despite a security breach.
- 79% of respondents thought compromised passwords were a concern.
- 51% relied on their memory to keep track of passwords.
- 65% always or mostly still used the same password or a variation.
A hacker can attempt 2.18 trillion combinations of passwords and usernames in 22 seconds.
Adding a single uppercase letter to a password dramatically transforms its potential. An eight-character password can be broken within one second, however, this can increase to 22 minutes by adding one upper case letter.
Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) Data
DDoS attacks are malicious attempts to disrupt a network, service, or website by flooding it with internet traffic. As a result, the target’s resources and infrastructure are disrupted, causing substantial downtime and financial losses. Overall, there was a 74% year-on-year increase in the number of DDoS attacks in 2022. The power of botnets also surged in the year, powering over 2 Tbit/s attacks that stretched up to 3 days.
According to Cloudflare, ransom DDoS attacks increased by 67% between 2021 and 2022.
They also saw a quarter-on-quarter increase of 24%. Notably, online industries experienced a significant rise in application-layer DDoS attacks, with a quarter-on-quarter increase of 131% and a year-on-year increase of 300%.
In 2022, Microsoft mitigated an average of 1,435 DDoS attacks daily.
- The maximum number of daily attacks was 2,215 on September 22, 2022.
- The minimum number of daily attacks was 680 on August 22, 2022.
- The total number of unique attacks mitigated in 2022 was over 520,000.
In Q1, 2023, Israel took the lead as the country most targeted by HTTP DDoS attack traffic.
Just short of a single percent of all HTTP traffic that Cloudflare processed in the first quarter of 2023 were attacks targeting Israeli websites. Following closely behind Israel were the US, Canada, and Turkey.
Top targeted industries included internet companies, which saw the largest amount of HTTP DDoS attack traffic.
In second place were the marketing and advertising industry, computer software industry, gaming / gambling, and telecommunications.
Business Email Compromise Data
Business email compromise (BEC) is a sophisticated scam targeting both businesses and individuals performing transfers of funds.
The IC3’s Recovery Asset Team (RAT) had a 73% success rate in 2022.
In 2022, the RAT initiated the Financial Fraud Kill Chain (FFKC) on 2,838 BEC complaints with potential losses of over $590 million. While the RAT saw a 64% increase in FFKCs initiated compared to 2021, a monetary hold was placed on $433 million, which represents a 73% success rate.
Internet of Things (IoT) Hack Data
The Internet of Things (IoT) is a network of physical objects or devices that are interconnected. IoT hacks target devices connected to the internet, instead of servers, and systems such as cars, smart home appliances, and medical devices.
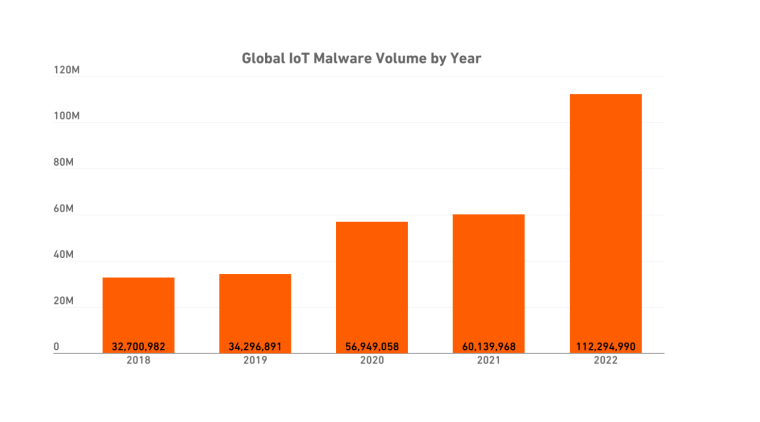
IoT malware surged by 87% in 2022 compared to 2021, reaching an all-time high of 112.3 million cases.
As of 2023, IoT devices are estimated to number 17 billion worldwide, all of which are susceptible to hacking. IoT devices are a key entry point for many attacks as security in IoT has lagged behind.
Check Point Research reported a sharp increase in cyberattacks targeting IoT devices. Key findings for Q1 2023 included:
- The first two months of 2023 saw a 41% increase in the average number of weekly attacks per organization targeting IoT devices, compared to 2022.
- 54% of organizations suffered from attempted cyber attacks targeting IoT devices.
- IoT devices in European organizations were the most targeted, followed by those in APAC and Latin America-based organizations.
The top-5 exploits seen in the wild since the beginning of 2023 are:
- MVPower DVR Remote Code Execution – impacts an average of 49% of organizations every week.
- Dasan GPON Router Authentication Bypass (CVE-2018-10561) – impacts 38% of organizations weekly.
- NETGEAR DGN Command Injection – impacts 33% of organizations weekly.
- D-Link Multiple Products Remote Code Execution (CVE-2015-2051) – impacts 23% of organizations weekly.
- D-Link DSL-2750B Remote Command Execution – impacts 14% of organizations weekly.
Cloud Threat Statistics
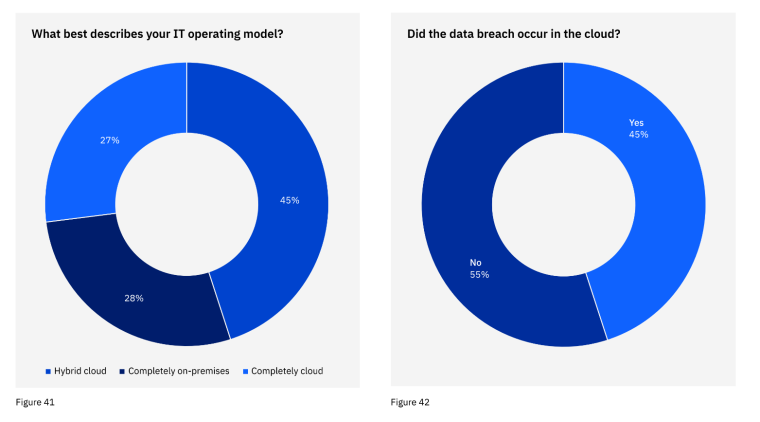
In 2022, around 98% of organizations used cloud-based services, and 76% had multi-cloud environments that incorporated services from two or more cloud providers.
Between 2021 and 2022, the number of attacks on cloud-based networks per organization increased by 48%.
Although the overall number of attacks on cloud-based networks was 17% lower than non-cloud networks, newly disclosed vulnerabilities were exploited more frequently on cloud-based than on-premise environments.
45% of breaches in IBM’s study occurred in the cloud.
Breaches that happened in a hybrid cloud environment cost an average of $3.80 million, compared to $4.24 million for breaches in private clouds and $5.02 million for breaches in public clouds. Additionally, organizations with a hybrid cloud model also had shorter breach lifecycles than organizations that solely adopted a public or private cloud model.
Data Breach Statistics
According to IBM, 83% of organizations experienced more than one data breach in 2022.
Of these organizations, 17% said this was their first data breach and 60% stated that they increased the price of their services or products because of the data breach.
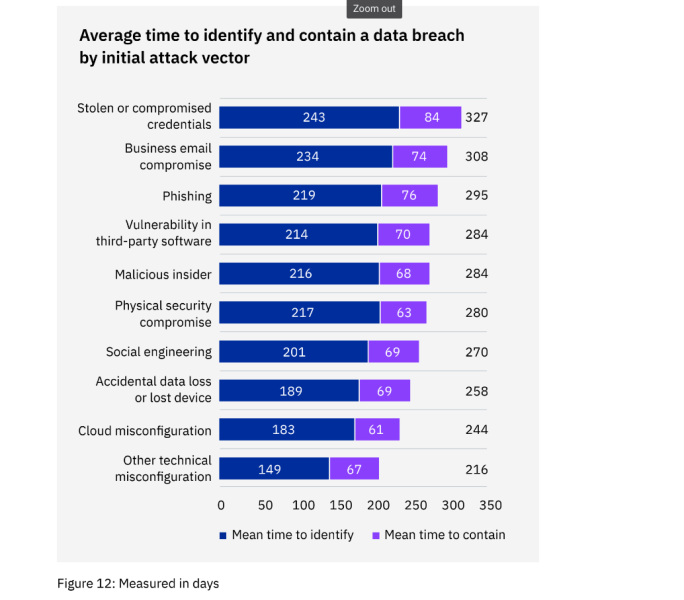
19% of breaches were caused by stolen or compromised credentials.
Use of stolen or compromised credentials remains the most common cause of a data breach. Breaches caused by stolen or compromised credentials had an average cost of $4.50 million and the longest lifecycles — 243 days to identify the breach, and another 84 days to contain the breach.
The average time to identify and contain a data breach fell from 287 days in 2021 to 277 days in 2022, a decrease of 10 days or 3.5%.
In 2022, it took an average of 207 days to identify a breach and 70 days to contain it, while it took an average of 212 days to identify a breach and 75 days to contain it in 2021.
Remote Work Compromise Data
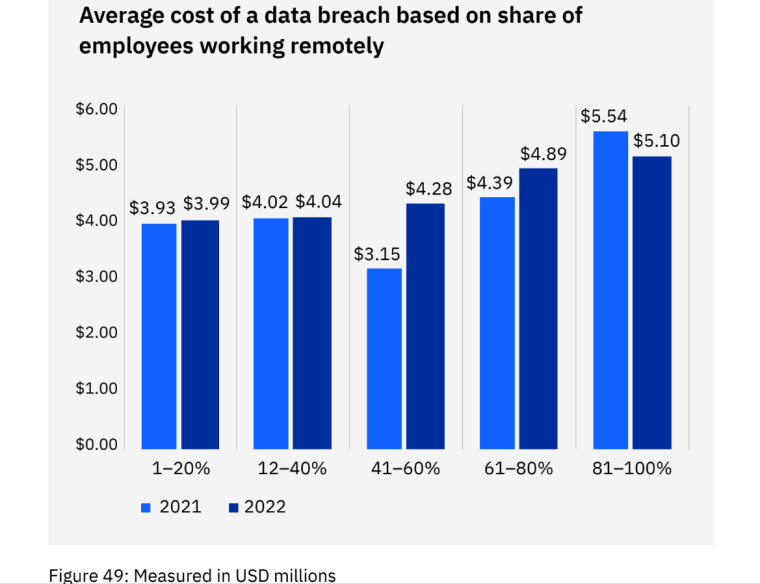
When remote work contributed to a breach, such as a remote-working employee having credentials stolen, this impacted the cost of the breach considerably.
IBM’s study found that breach costs were highest for organizations with most of their employees working remotely. For those with 81% to 100% of remote workers, the average cost of a data breach was $5.10 million compared to $3.99 million for those with less than 20% of remote employees.
The average total cost of a data breach was nearly $1 million greater when remote work was a factor in causing the data breach.
Organizations that indicated remote work was a factor in a breach experienced an average cost of a data breach of $4.99 million compared to the average cost of a data breach of $4.02 million when remote work wasn’t a factor in causing the breach.
Supply Chain Compromise Data
IBM’s research found that close to 20% of breaches were caused by a supply chain compromise and that this resulted in more expensive breaches with longer lifecycles.
A supply chain attack occurs when a business partner, such as a supplier, is compromised.
Research by IBM revealed that a supply chain breach took 9% or 26 days longer to identify and contain than the global average of 277 days.
On average, organizations took 235 days to identify and 68 days to contain a supply chain compromise, which is a total lifecycle of 303 days compared to the average data breach lifecycle of 277 days.
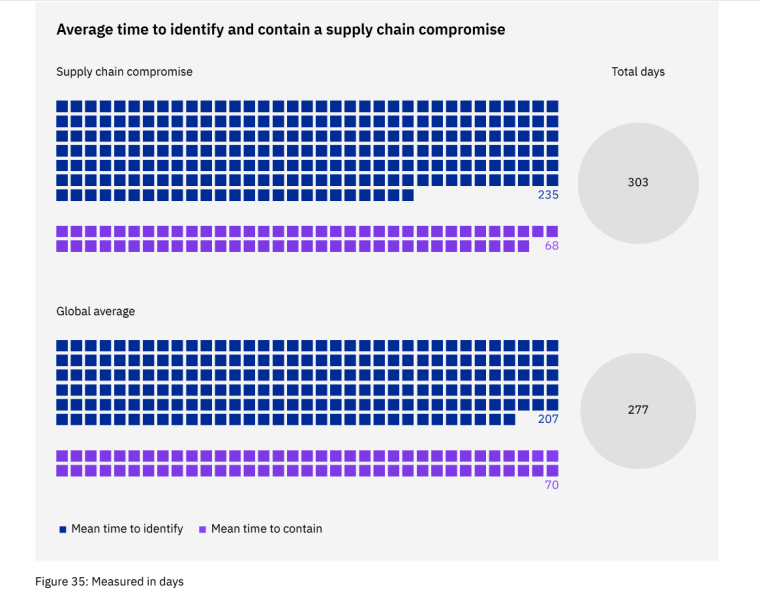
The average total cost of a supply chain compromise was 2.5% more than the overall average cost of a data breach.
A supply chain breach cost $4.46 million which was $0.11 million greater than the overall average cost of a data breach of $4.35 million.
Costs of Cybersecurity Data
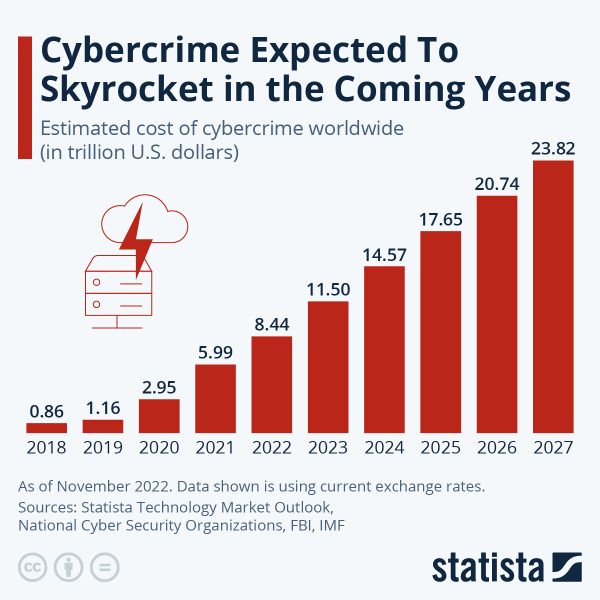
The cost of global cybercrime increased by 41% in 2022.
The cost of global cybercrime increased from $6 trillion in 2021 to $8.4 trillion in 2022. Costs of cybercrime continue to rise, with costs expected to hit $11.5 trillion in 2023 and $23.8 trillion by 2027.
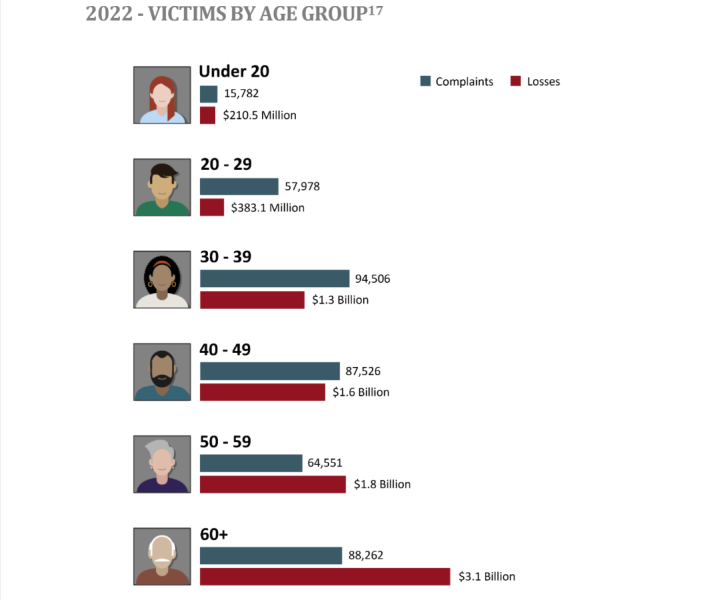
With over $3.1 billion in losses incurred, the over-60 age group suffered the most losses from cybercrime in 2022.
This was followed by the 50 to 59 age group and the 40 to 49 age group, which had $1.8 billion and $1.6 billion in losses respectively. Those under 20 suffered the least amount of losses ($210.5 million).
According to the IC3, investment scams were the most costly scheme in 2022.
Investment fraud complaints increased by 127% from $1.45 billion in 2021 to $3.31 billion in 2022. Among those complaints, cryptocurrency investment fraud jumped from $907 million to $2.57 billion in 2022, a spike of 183%.
Losses from BEC complaints amounted to over $2.7 billion.
After investment schemes, BEC complaints were the second most costly. This is followed by tech support scams which amounted to $807 million.
According to McKinsey, spending on products and services from cybersecurity vendors is set to increase by 13% annually up to 2025.
This is up from 10% between 2019 and 2023 and with services set to increase much faster than products.
Cybersecurity Business Cost Statistics
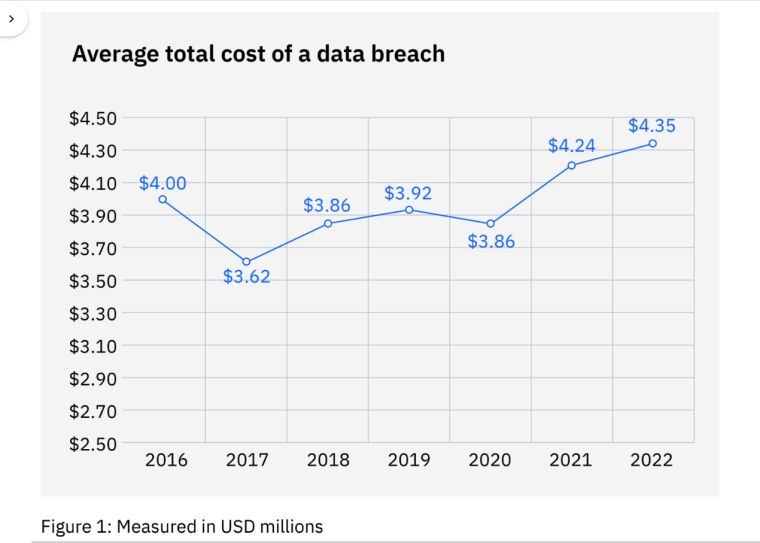
According to IBM’s 2022 Cost of a Data Breach Report, the average cost of a data breach was $4.35 million in 2022.
This all-time high represents a 2.6% increase from 2021’s average cost of $4.24 million and a 12.7% increase from $3.86 million in 2020.
The same report revealed that the average cost of a critical infrastructure data breach was $4.82 million.
This is a $1 million jump from the average cost for organizations in other industries.
The report also revealed that the average cost savings associated with fully deployed security AI and automation were 65.2% or $3.05 million.
Companies with fully deployed security AI and automation were also able to identify and contain a breach 74 days faster than those without. The adoption of security AI and automation increased by almost 20% from 59% in 2020 to over 70% in 2022.
A report by Deloitte uncovered seven potential hidden costs associated with a cyberattack, namely:
- Insurance premium increases.
- Increased cost to raise debt.
- Operational disruption with destruction.
- Lost value of customer relationships.
- The value of lost contract revenue.
- Devaluation of trade name.
- Loss of intellectual property.
95% of security budgets will increase over the next two years.
56% of organizations surveyed in Splunk’s State of Security Report state that increases will be significant. A report by the Cyber Edge group goes on to reveal that 87.7% of respondents expect their IT security budget to increase by an average of 5.3% in 2023.
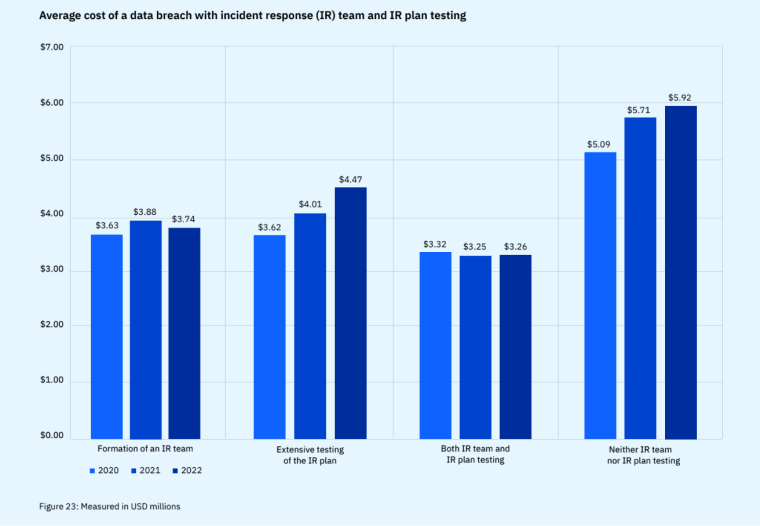
The average cost savings associated with an incident response (IR) team and regularly tested IR plan came up to about $2.66 million in 2022.
Having an IR team and a regularly tested IR plan resulted in significant cost savings of about 58% from a total of $5.92 for organizations without IR capabilities.
The average cost of a breach in the US was $9.44 million, the highest of any country or region for 12 consecutive years. This was followed by:
- The Middle East at $7.46 million
- Canada at $5.64 million.
- The UK at $5.05 million.
- Germany at $4.85 million.
Shorter data breach lifecycles were associated with 26% lower data breach costs.
A data breach lifecycle of 200 days or less was associated with an average cost of $3.74 million in 2022, compared to $4.86 million for breaches with a lifecycle longer than 200 days.
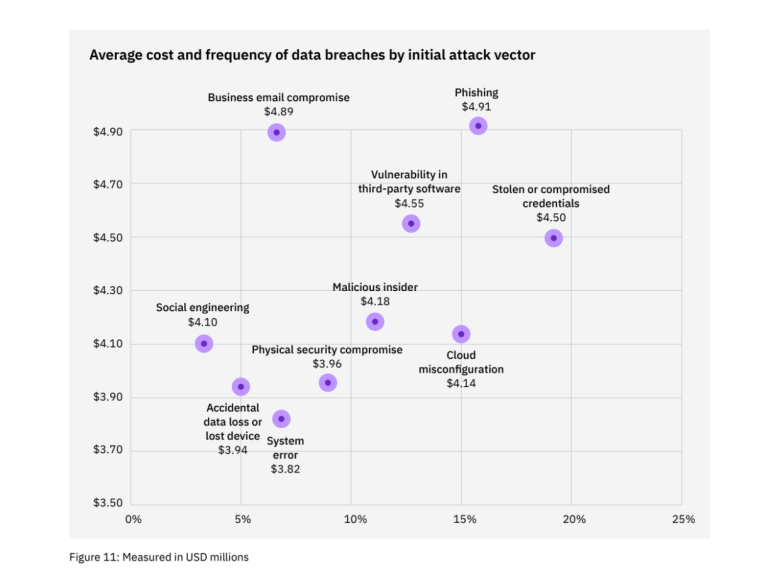
During 2022, stolen or compromised credentials were the most common initial attack vector, responsible for 19% of breaches with an average cost of $4.50 million.
Other attack vectors included:
- Phishing – 16%
- Cloud misconfiguration – 15%
- Vulnerability in third-party software – 13%
At $4.91 million, phishing was the most costly initial attack vector in 2022.
As per IBM, this was followed by BEC at $4.89 million, a vulnerability in third-party software at $4.55 million, and compromised credentials at $4.50 million.
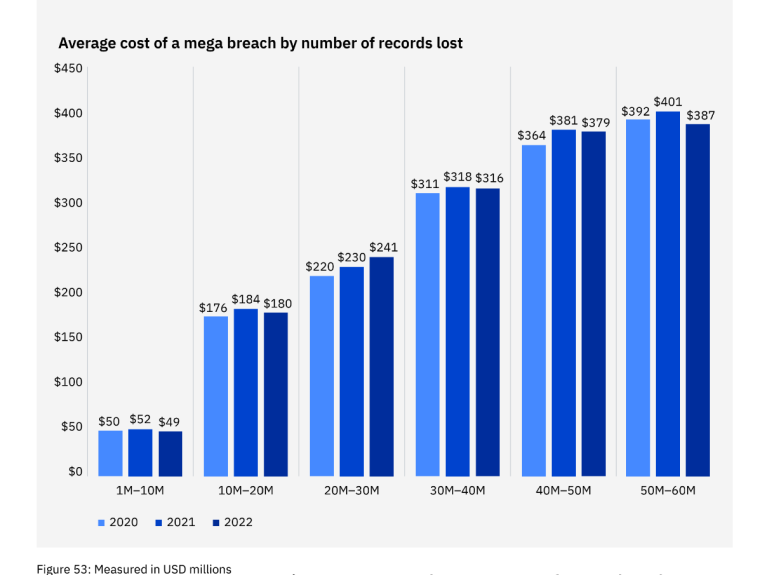
The average cost of a mega breach decreased slightly in 2022.
Mega breaches are those with more than 1 million compromised records. Mega breach costs fell slightly from 2021 in six of seven breach-size cohorts surveyed by IBM. The 50 million to 60 million record cohort saw the largest drop of 3.6% from $401 million in 2021 to $387 million in 2022. The 20 million to 30 million record cohort was the only one that saw an increase in 2022. In that cohort, the average total cost of a mega breach increased by 4.8% or $230 million to $241 million.
When compared with organizations without zero-trust deployed, organizations with zero-trust deployed saved close to 20% in average breach costs.
Zero-trust frameworks are becoming core organizing models for many IT security programs. The average cost of a data breach was $4.15 million at organizations with zero-trust deployed, while the cost of a breach was an average of $5.10 million at organizations without zero-trust deployed. This represents a $0.95 million or 20.5% saving for organizations with zero-trust deployed. In addition, having a mature zero-trust deployment was associated with increased savings of 35.9% or $1.5 million compared to early adoption of zero-trust.
Cybersecurity Statistics by Country
As of 2020, the US ranks first in the Global Cybersecurity Index (GCI).
With a score of 100 index points, the US is the country most committed to cybersecurity. Among the countries with the highest commitment to cyber security, the UK and Saudi Arabia are tied for second with 99.54 GCI scores each.
With 479,181 victims, the US had the highest number of cybercrime victims in 2022.
California was the US state with the highest number of victims (80,766). The IC3 revealed the top 5 victim countries for 2022 as follows:
- United States – 479,181 victims
- United Kingdom – 284,291 victims
- Canada – 5,517 victims
- India – 2,550 victims
- Australia – 2,489 victims
For the 12th consecutive year, the United States ranked highest for the average cost of a data breach.
The US had the highest average total cost of a data breach at $9.44 million up from $9.05 million in 2021.
The top five countries or regions with the highest average per data breach were:
- The United States – $9.44 million
- The Middle East – $7.46 million
- Canada – $5.64 million
- The United Kingdom – $5.05 million
- Germany – $4.85 million
According to Cyber Edge Group’s 2023 Cyberthreat Defense Report, over 50% of organizations surveyed in Mexico, Australia, and Germany reported six or more successful cyberattacks during 2022.
In the US, it was 48% while the countries which had the least amount of organizations with six or more successful attacks were:
- Japan (15.6%)
- France (16.5%)
- Colombia (20.0%)
- Italy (22.0%)
- Brazil (22.6%)
- China (24.0%)
The same report revealed that respondents in the countries surveyed planned to increase their spending on cybersecurity by between 4% and 7% in 2023.
Averages ranged from around 7% for:
- Brazil
- Turkey
- South Africa
and 4%-5% for:
- Germany
- Italy
- The US
- Japan
- Canada
Despite a 48% year-over-year drop, the US had the highest ransomware attack volume of any country in 2022.
In second place, the UK experienced a 112% increase in ransomware attacks. Meanwhile, ransomware attacks in Germany decreased by 42%, moving it from the second-highest attack volume to fifth.
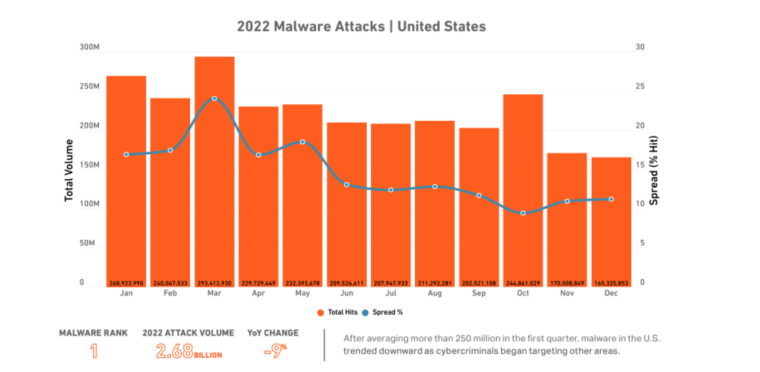
The US also experienced the highest volume of malware attacks in 2022.
With 2.68 billion malware attacks in 2022, the US took the lead in Sonic Wall’s Cyber Threat Report. The UK took the second spot with 432.9 million malware attacks. With 335.4 million attacks, India ranked third on the list, up 31% from 2021. Despite overall declines in 2022, India’s attack volume grew the most among those included in the report.
The number of malware attempts in North America reached a record low of 158.9 million in February 2022, marking the lowest monthly volume since 2018.
This indicates a decline in malware activity in the region and suggests cybercriminals may be shifting their focus to other regions worldwide.
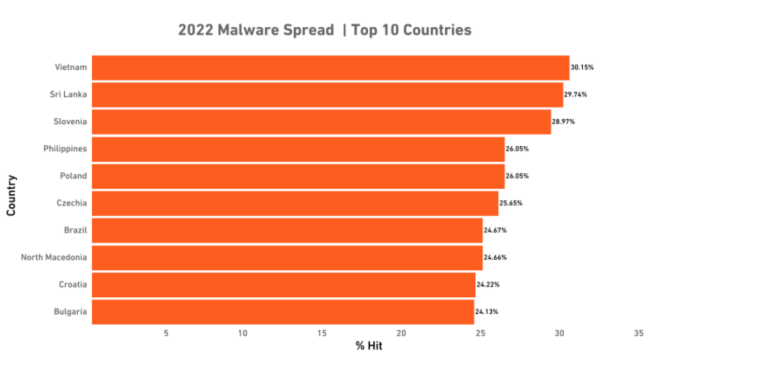
According to Sonic Wall’s malware spread percentage, Vietnam was the number one country targeted by malware at 30.15%.
Sonic Wall’s malware spread percentage represents the calculation of the sensors that detected a malware attack, indicating the extent of the malware’s reach in that particular region.
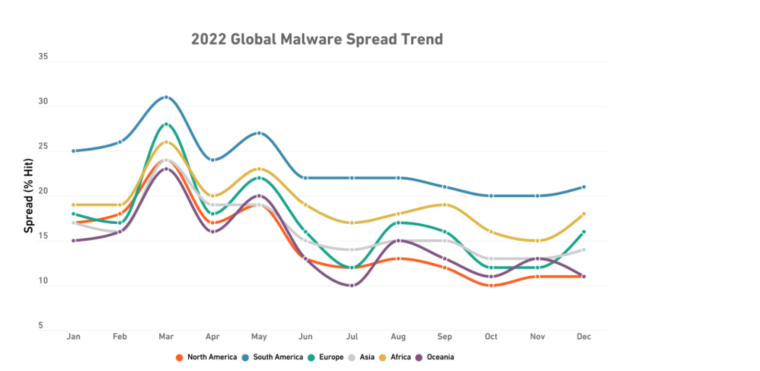
As per the same report, Europe emerged as a cybercrime hotspot, with the number of European countries on Sonic Wall’s list doubling since 2021, accounting for the majority of the top 10.
The same report also noted that LATAM and Asia experienced double-digit growth rates of 17% and 38% in 2022, respectively.
Cyberwarfare Statistics
Almost 500 geopolitical cyberattacks have been documented worldwide since 2009, with 26.3% directed at the United States.
Together, China and Russia account for nearly 35% of global attacks, making them the dominant aggressors in the cyberwarfare space.
The two countries have frequently targeted national governments, with 79 confirmed attacks from China and 75 from Russia.
The White House released a statement in July 2021 expressing concern over the People’s Republic of China’s irresponsible conduct in cyberspace.
“As detailed in public charging documents unsealed in October 2018 and July and September 2020, hackers with a history of working for the PRC Ministry of State Security (MSS) have engaged in ransomware attacks, cyber-enabled extortion, crypto-jacking, and rank theft from victims around the world, all for financial gain.”
America’s Cyber Defense Agency frequently updates its advisories, alerts, and malware analysis reports (MARs) on Russian malicious cyber activities.
“The Russian government engages in malicious cyber activities to enable broad-scope cyber espionage, to suppress certain social and political activity, to steal intellectual property, and to harm regional and international adversaries.”
74% of ransomware revenue went to Russia-linked hackers in February 2022, according to the BBC.
According to researchers, cryptocurrency payments worth over $400 million were directed to groups widely believed to be Russia-affiliated.
Russian intelligence services reportedly increased attacks against governments and NGOs in June 2022.
The attacks targeted over 42 countries supporting Ukraine with the goal of obtaining sensitive information.
In 2022, the heads of UK and US security services, FBI and MI5 made an unprecedented joint appearance to issue a warning about the threat posed by China.
FBI director Christopher Wray said China was the “biggest long-term threat to our economic and national security” and had interfered in politics, including recent elections. He went on to warn the audience – which included chief executives of businesses and senior figures from universities – that the Chinese government was “set on stealing your technology” using a range of tools. MI5 head Ken McCallum said his service had more than doubled its work against Chinese activity in the last three years and would be doubling it again.
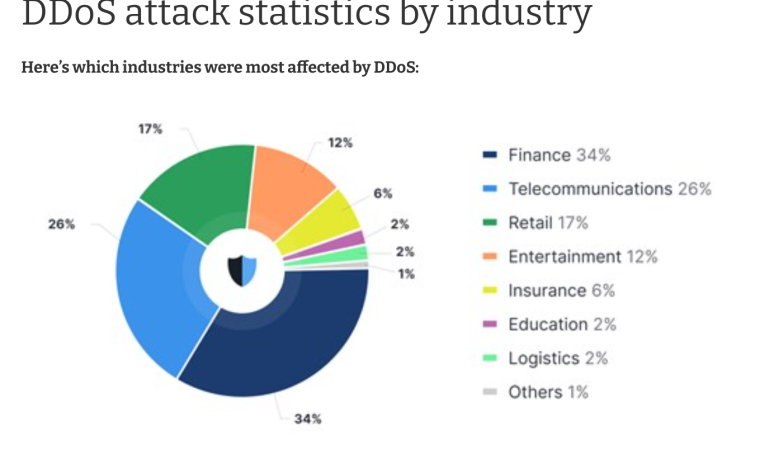
Cybersecurity Stats by Industry
The demand for healthcare, manufacturing, and government cybersecurity services has grown exponentially since the pandemic. Check Point Research found that global attacks increased by 28% in the third quarter of 2022, with education/research as the most attacked industry overall, and the healthcare sector the most targeted industry in ransomware attacks.
The IC3 found that 28% of critical infrastructure organizations had experienced a destructive or ransomware attack in 2022.
Meanwhile, 17% experienced a breach because of a business partner being compromised.
Cyber Edge noted the following key insights:
The most targeted industries by cybercriminals as per its 2023 report were:
- Finance (95.7%)
- Telecom and technology (88.9%)
- Retail (85.6%)
- Healthcare (79.2%)
- Education (78%)
- Manufacturing (77.5%)
- Government (74.4%)
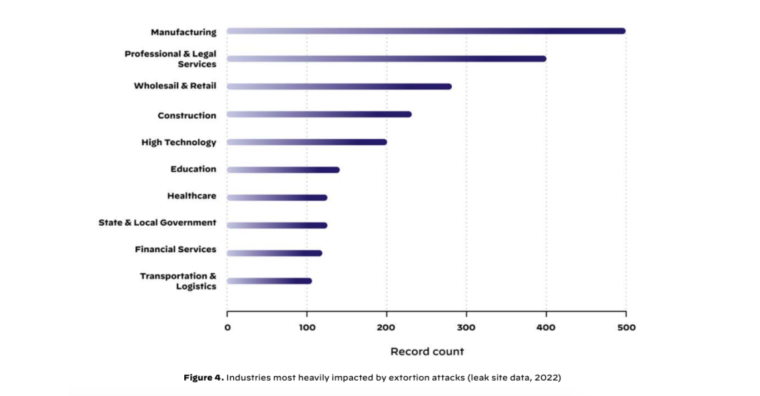
According to Palo Alto Network’s 2023 Ransomware and Extortion Report, manufacturing was severely affected by extortion attacks in 2022.
The manufacturing sector had 447 recorded victims across different platforms, the highest of all industries. This was followed by professional and legal services, with 343 reported victims.
Compared to 2021, attacks on the healthcare industry in 2022 increased by 74%.
Hospitals, clinics, and research facilities have been targeted by attackers since the COVID-19 pandemic began. In 2022, 89% of healthcare organizations reported cyberattacks, costing an average of $4.4 million.
The healthcare industry has had the highest average cost of a breach for 12 consecutive years.
Healthcare breach costs hit a new record high in 2022. The average breach in healthcare increased by nearly $1 million to $10.10 million. Over the past 12 years, healthcare breaches have had the highest costs, increasing by 41.6% since 2020. Other costly industries include:
- Financial at $5.97 million.
- Pharmaceuticals at $5.01 million.
- Technology at $4.97 million.
- Energy at $4.72 million.
Ransomware groups reported to target healthcare organizations include Lockbit, BlackCat, Cuba, Zeppelin, and others.
The most notable reported attacks in 2022 include:
- CommonSpirit Health, the second largest non-profit hospital chain in the US reported that the data of more than 600,000 patients was stolen, resulting in medical damage to patients.
- Hospitals in New York were hit by ransomware in November 2022, leaving medical systems down for weeks after the attack.
- An attack on Dallas, Texas, based Tenet HealthCare caused disruption to acute care operations.
- Hackers disrupted operations at an Indian hospital in November 2022 by cutting off access to its online networks and patient records. It took hospital officials and federal authorities nearly two weeks to regain access to hospital servers and recover lost data.
In 2022, malware attacks on educational institutions saw the largest spike among overall sectors.
Check Point Research found that global attacks increased by 28% in the third quarter of 2022, with education/research as the most attacked industry overall, and the healthcare sector the most targeted industry in ransomware attacks.
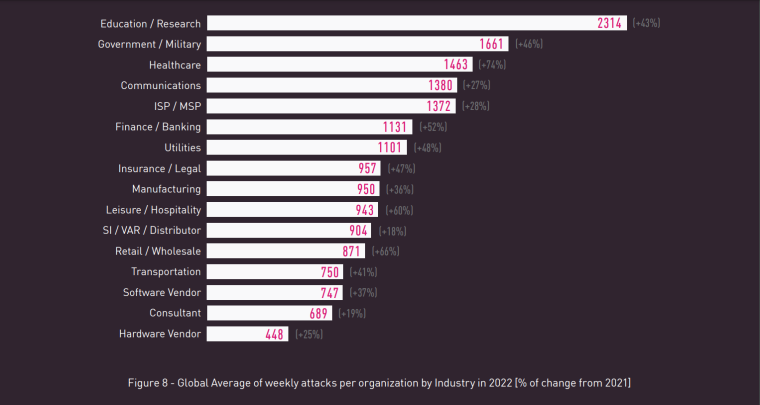
Threat actors are increasingly targeting educational institutions. In fact, the education sector experienced the highest average weekly number of cyber attacks in 2022.
In 2022, educational and research institutions experienced a growing number of attacks with an average of 2,314 attacks per week per organization. This is an increase of more than 40% from 2021.
Notable cyberattacks in the education sector in 2022 and 2023 included:
- In January 2023, Hackers launched a ransomware attack against Technion University, Israel’s top technology education program. Hackers demanded 80 bitcoins to decrypt the university’s files.
- In May 2022, Lincoln College, a 157-year-old institution in Illinois, announced its indefinite closure after a ransomware attack crippled its operations.
In February 2022, a significant Ransomware attack disrupted the operations of oil port terminals in Belgium, Germany, and the Netherlands.
The attack affected at least 17 ports and resulted in difficulties in loading and unloading refined product cargoes.
Research by Check Point revealed that the technology industry was most frequently affected by brand phishing in 2022, followed by shipping and social networks.
The top-10 brands ranked by their overall appearance in brand phishing events during Q4 2022 include:
- Yahoo – 20%
- DHL – 16%
- Microsoft – 11%
- Google – 5.8%
- LinkedIn – 5.7%
- Wetransfer – 5.3%
- Netflix – 4.4%
- Fedex – 2.5%
- HSBC – 2.3%
- WhatsApp – 2.2%
Yahoo moved up 23 spots in Q4 2022, due to a malicious phishing campaign designed to gather personal and banking details. Using Yahoo’s branding, victims were sent emails that they had won prize money and that they needed to provide their details to claim their winnings.
In October 2022, Aurubis, the largest copper manufacturer in Europe fell victim to a cyberattack.
The attack targeted its IT systems and forced the company to shut down many of its sites’ systems.
As a result of a ransomware attack in May 2021, Colonial Pipeline’s fuel distribution pipeline was completely shut down.
In only two hours, cybercriminals belonging to a group known as DarkSide managed to extract 100 gigabytes of data from Colonial Pipeline. The company consequently paid $5 million to hackers from Russia to facilitate the restoration of the nation’s largest fuel pipeline.
In June 2021, JBS, the world’s largest meatpacking company, suffered a significant ransomware attack by Russian hackers.
As a result of the breach, JBS paid a ransom of $11 million to the hackers.
Notable Attacks on Government Entities
- In April 2023, NSA cyber authorities reported evidence of Russian ransomware and supply chain attacks against Ukraine and other European countries that have provided Ukraine with humanitarian aid during the war in Ukraine.
- In February 2023, hackers disabled Italy’s Revenue Agency website. While the website was disabled, users received phishing emails directing them to a false login page that mirrored the official agency site.
- In December 2022, China-linked hackers launched phishing attacks containing malware designed for espionage against government, education, and research sector victims across the Asia Pacific.
- In May 2022, Costa Rica declared a State of Emergency following a crippling ransomware attack by the Conti gang. The attack affected many governmental organizations, including The Finance Ministry, The Costa Rican Social Security Fund, and The Ministry of Science, Innovation, Technology, and Telecommunications. An estimated $200 million was lost due to disruptions related to the tax and customs platforms.
- In July 2022, both Norway and Lithuania were victims of large-scale DDoS attacks. The attacks were assumed to have been carried out by separate pro-Russian hacker groups with the goal of discouraging the nations’ support of Ukraine.
References
- Statista
- McKinsey & Company
- Reuters
- World Economic Forum
- Fortune
- Splunk
- Cyber Edge
- Statista
- Reuters
- IC3 2022 Report
- CNBC
- Statista
- Statista
- Statista
- Comparitech
- Statista
- Last Pass
- Onelogin
- Infosecurity Magazine
- Cloudflare
- Microsoft
- Cloudflare
- Sonic Wall
- Check Point
- IBM
- Statista
- Deloitte
- Statista
- Privacy Affairs
- The Whitehouse
- CISA
- BBC
- BBC
- Palo Alto Networks
- Statista
- Statista
- Bloomberg