Comparable company analysis, also known as comps valuation or comparable companies analysis, is a popular analytical tool used by companies and investors to understand a firm’s value on the market. Conducting a comparable company analysis allows you to facilitate the investment process, structure your company better, and stay ahead of the competition.
Here at Business2Community, our team of financial experts has prepared this comprehensive guide to mastering comparable company analysis. From its applications to its limitations, we’ll cover everything you need to know. Follow this guide to build your next money-making financial model.
Comparable Company Analysis – Key Takeaways
- Comparable company analysis compares a company’s financial metrics against competitors to determine its value on the market.
- It is crucial for making investment decisions, helping you consider companies with similar characteristics like company size and share price to generate meaningful comparisons.
- When using this technique, you should bear in mind its limitations like the failure to consider qualitative elements to avoid being misled by the results.
What is a Comparable Company Analysis?
Comparable company analysis refers to the process of using financial data to evaluate similar companies in the same industry to better understand your firm’s value and position in the competition. It can help you understand if your or a competitor’s company is over- or undervalued.
This technique assumes that companies in the same industry classification will have similar operating metrics like revenue growth, net income, and gross profit.
Comparable companies are those engaging in production activities in the same sector with similar market value, size, and share price. When you conduct a comparable company analysis, these comparable companies belong to the peer group.
Choosing the right comparable companies can ensure the accuracy of your results. It’s meaningless to compare businesses with drastically different production sizes and funds.
For example, as a small company in the tech industry operating only in the US, you should aim to study similar companies in the same region so you can tell how your business is doing compared to competitors. Comparing yourself against global public companies like Microsoft will not give you actionable benchmarks to work with.
By considering financial metrics like enterprise value, market capitalization, stock price, and equity value, a comparable company analysis reveals if the target company is valued accurately.
This analytical tool helps your company to interpret market data and break down its business performance. With the analysis results, your firm can formulate more profitable business strategies, improve industry rankings, and allocate resources more efficiently to match your industry.
Do not confuse this quantitative analytical tool with a discounted cash flow analysis. The former looks at the relative valuation multiples to judge a company’s performance in a particular industry, whereas the latter analyzes the intrinsic value of the operation itself.
Who Needs to Do a Comparable Company Analysis?
Comparable company analysis offers critical insights into a firm’s worth – yours or one you may be planning to acquire, for example. It’s part of the company valuation process for financial analysts to grasp the true value of the company.
Investment bankers and decision-makers rely on these valuation multiples to make acquisition decisions. If the comparable analysis concludes that the target company demonstrates promising growth prospects compared to its peer group, investors will be more likely to give a green light to its acquisition process.
This technique is extremely important in the business world. It serves as a crucial benchmark for investors as well as an indicator for your internal operations. The financial data acquired demonstrates the profitability and market value of other comparable companies in the same period so you can align your vision and goals with reality.
Whether you’re an investment banker, business owner, or stock trader, learning about this analytical method gives you an edge over your competition. Market participants utilize the information extracted from a comparable company study to develop profitable plans. It can be helpful to emulate a successful comparable company you identify.
To make things easier, we’ve prepared a detailed step-by-step guide to creating a comparable company analysis in the next section.
How to Perform a Comparable Company Analysis
Comparable company analysis broadens your knowledge of company structure and profitability by directly comparing financial metrics with competitors. It should be one of the first analytical techniques you learn when you start your entrepreneurial journey.
To begin the analysis, you first need to learn about the components involved and how they assist you in generating reliable results.
Components of a Comparable Company Analysis
In theory, a comparable company analysis can consist of just one focus area like the enterprise value to market capitalization. However, going through the whole research process for just one factor isn’t cost-effective. Therefore, firms mostly choose to include a few valuation elements that they’re interested in.
Some common components you can compare include:
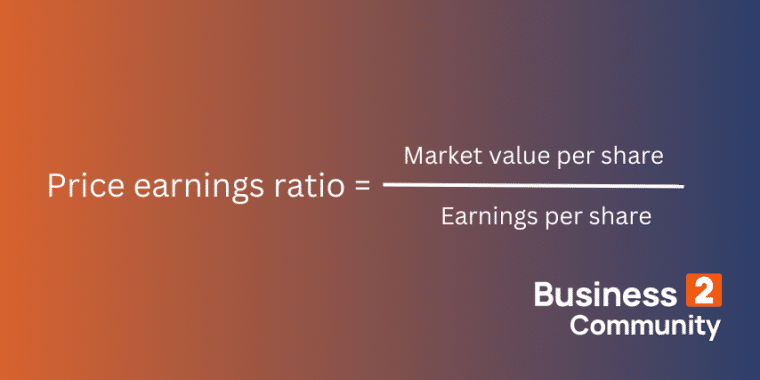
- Price-to-earnings ratio
- Enterprise value (EV) to its Earnings Before Interest, Taxes, Depreciation & Amortization (EBITDA) ratio
- Enterprise value-to-sales ratio
- Price-to-book ratio
- Price-to-sale ratio
- Enterprise value to gross profit ratio
These ratios identify the company’s profitability based on different aspects. When you’re creating an analysis, you need to select valuation multiples that speak to your research purposes.
Step 1: Choose Your Comparable Companies
The first thing in a comparable company analysis is to form your peer group. As we’ve noted, a peer group should consist of similar companies that operate in your industry.
There are several criteria for choosing peer companies. You can look at factors like operating regions, size, share price, and equity value to locate companies with similar characteristics. Since you’re going to rely on publicly available information to calculate the ratios, your comparable companies are going to be public companies.
Step 2: Collect Financial Data
There are many ways to collect the financial data of a target company. You can find the annual and quarterly reports on the company’s website and equity value and share price in company filings.
You can find the company’s debt and net income through financial statements like balance sheets and income statements. As a researcher, you need to decide the relevant factors in the study and collect the data accordingly.
Step 3: Organize Your Data
Once you’ve collected all the data, it’s time to organize the information for further analysis. Organizing your data points into a table can meticulously separate them for easy access. Not only does it facilitate the current analysis process but it also makes it easier for you or your team to come back later for revisions or updates.
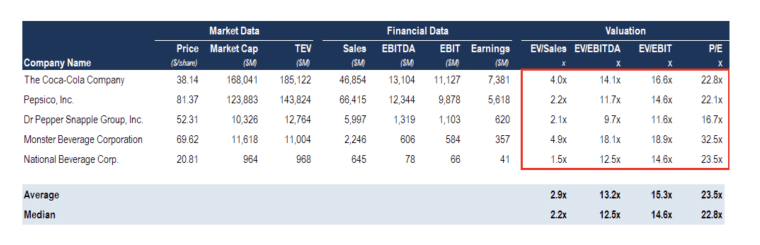
The first row of the table shows the categories you are studying such as net income and share price. As you can see in the example below in step 4, the second row presents your company’s financials in those categories and in the subsequent rows, you can list other companies’ values.
Step 4: Calculate Comparable Ratios
Use the information in your table to calculate the valuation multiples. Since there are many numbers to process, it’s important to select an appropriate multiple for each aspect you’re studying.
Calculate enterprise value and other metrics with the corresponding valuation methods. Create a new table to present the ratio analysis results. You can separate the results by their characteristics like market value vs company value and put the calculated valuation metrics in the respective column.
To make things easier, here is a comparable company analysis template you can model your report after:
Step 5: Share Your Findings with Your Team Members
Share your results with your team members and discuss possible strategies to make your firm more competitive. You can target key areas that are underperforming and allocate resources to improve performance.
The analysis results will identify the strongest and weakest comparable companies in your field. With that in mind, you can present your results to potential investors and go forward with potential collaborations. It can also help your company target others for acquisition or even help you decide who to collaborate with.
Examples of Comparable Company Analysis
Comparable company analysis penetrates most areas of the business spectrum, making it one of the most powerful tools for assessing the competitiveness and state of the company. Since this technique is so widely used, you’ll be able to find lots of ways to utilize this method for your firm.
Let’s take a look at a few common ways of incorporating this analytical technique in your company to refine the process and deliver a better user experience for your audience.
Example 1: Study Your Peer Group to Evaluate Pricing Strategies
You are a consultant in the investment banking field and you’re trying to help your client assess their pricing strategies compared to other public companies in their sector. Investment bankers rely heavily on comparable company analysis to deliver professional, top-notch advice to their clients. Various valuation tools can reveal the metrics of the target companies.
With the numbers to hand, you can evaluate if your client has been underpricing or overpricing their products, offering expert advice to polish their pricing strategies. You can also focus on a target company with similar performances and use it as a benchmark.
Example 2: Use Comparable Company Analysis to Determine Company Strategy
By studying the enterprise value to market capitalization, preferred stock valuation, and other financial multiples of your peer group, you can gain a better understanding of how your firm is valued. A thorough comparable company analysis allows your business to identify its worth among competitors and formulate tactics appropriately.
Based on the results, you can choose a target company based in the same region with similar production activities to the model. Mimicking a successful peer company often saves you costs and resources in experimenting with different strategies.
However, you should be aware of the differences between the two companies and only adopt quality metrics that reflect your business reality.
Example 3: Understand if Your Company is Expanding Appropriately
Your balance sheet says a lot about your business’ debt and asset situation. On a balance sheet, you can find out if your or a target company is currently borrowing funds from private equity firms, its valuation measure, and its capabilities to repay the debts based on its asset valuations.
The information is useful in determining if your company is expanding too fast or too slow. A company that expands too fast by being in debt can bring disastrous outcomes in the future whereas a company not expanding quickly enough can miss out on the profitable opportunities available on the market.
Through a comparison table, you can see if your company is growing proportionally with competitors to determine the next steps.
How to Adjust a Comparable Company Analysis
Comparable company analysis is a form of relative analysis that compares similar companies. Since the analysis results are crucial for investment decisions, you will want to learn about how to control the results better to strategically present your company in financial meetings.
Adjusting a comparable company analysis is also a fantastic way to examine the effectiveness of a new business strategy
You can adjust the components involved in the comparable company analysis to observe their effects on the results. You can do this by replacing the updated numbers on the table and calculating all the ratios again.
Once you have updated the values, you can compare them against your competitors’ ratios to draw a new conclusion. It offers guidance for businesses to decide the best tactic to adopt to maximize success.
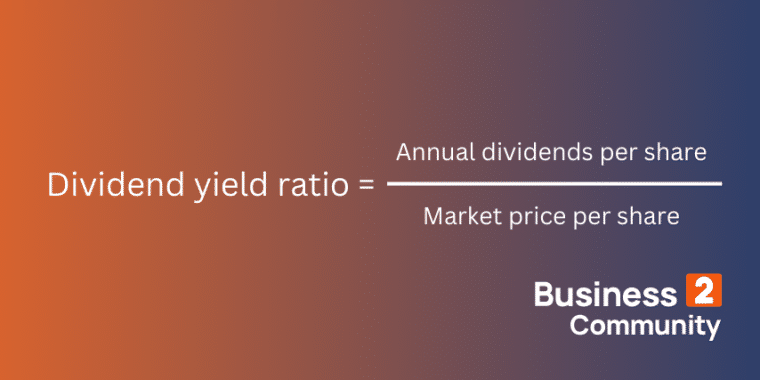
Not only you can adjust a comparable company analysis by making changes to existing components but you can also include new ratios to change the results such as the dividend yield ratio.
As a form of relative analysis, you can gain more favorable results for your firm if you choose to include high-performing ratios based on your company’s performance. Create new columns on the analysis table and include the new ratios for comparison to get a broader and deeper view of your market position.
While you can change a comparable company analysis from your side to control the results, you can’t control the ratios obtained from peer companies.
You can use the new numbers to update the table and draw a conclusion about your findings. The most important thing is to make sure you gather your data points from legitimate sources like official annual reports and public filings from companies that are indeed in your company’s peer group.
Limitations of Comparable Company Analysis
A comparable company analysis is useful in assessing the state of your company against competitors. However, despite its effectiveness in offering insights into the business environment, this tool comes with several disadvantages.
When utilizing this technique in your decision-making process, you need to keep these shortcomings in mind so you don’t get misled by the results.
It Doesn’t Consider Qualitative Factors
Comparable company analysis is a quantitative analytical tool that strictly looks at the numbers of a company. It fails to take into account important qualitative factors like company goodwill, brand history, and customer loyalty that can influence a company’s valuation. These factors are vital to a company’s success and should be considered when valuing a company’s worth.
For example, a startup in the same field may have garnered a large loyal following due to its sustainable practices, therefore, it can easily outperform competitors. If you simply look at the figures and blindly follow their approach, it’ll be difficult to grow your brand because you fail to take into account these qualitative elements.
Conducting a qualitative analysis is an excellent way to measure these non-tangible factors and understand how they impact your company.
It Doesn’t Make an Estimation About the Future
Comps valuation only looks at historical financial metrics from the past. It doesn’t offer predictions about future trends or how these numbers will change. It is up to you as the researcher to determine the appropriate way to interpret these numbers and make financial projections.
Without making inferences, historical data can be challenging for businesses to fully be aware of future opportunities and threats. You can incorporate inferential statistics techniques to get an estimated value of future sales, costs, and other figures.
It Can be Difficult to Find Truly Comparable Companies
The whole idea of a comparable company analysis is based on finding comparable companies. In reality, it can be tough to find similar companies in your field. Depending on your niche and size, you may not be able to find enough comparable companies to create a meaningful analysis.
You can utilize other analytical techniques like PESTEL analysis, which considers the influence of external factors on your operations. It allows you to gain a clearer idea of your company’s position in the industry.
The Value of Comparable Company Analysis
Comparable company analysis is an effective valuation tool for comparing your company’s worth against competitors so you can strategize accordingly. Investment bankers also rely on the analysis results to make investment decisions. This widely adopted tool is an essential business technique that you should familiarize yourself with.
You need to work to find companies that are appropriate to make a direct comparison with. The work it takes can offer great value. Not only can you see where you sit in your market, you can also figure out if a competitor is ripe for a buy-out, if you should be collaborating with similar companies, or if you need to be pushing your business harder to innovate and connect with buyers.
Despite its advantages, this technique fails to address the qualitative elements that add value to your business, which can undervalue your company. Therefore, when using this tool, it is important to incorporate other analytical techniques to generate the best results.