The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) in fintech, or financial technology, is already revolutionizing the sector and finance in general.
Fintech refers to the systems used to unbundle, digitalize, and simplify the delivery of financial services.
By leveraging AI, fintech companies have transformed the way financial services are delivered, easing the friction customers face with day-to-day financial transactions in the banking industry.
Key Takeaways
- AI Integration: AI’s integration into fintech has streamlined and enhanced the delivery of financial services, leading to advanced data analytics, improved customer service, and more robust fraud detection systems.
- Automation and Efficiency: Through automation, AI is transforming tasks like data processing and customer transactions into more efficient operations, minimizing errors and increasing security.
- Generative AI: The application of generative AI in fintech is innovating customer interaction and back-office functions, pushing the envelope on what can be automated and how data is utilized.
- Future Projections: With AI, fintech is expected to see significant growth in employment and innovation, as firms invest heavily in AI capabilities to stay competitive and meet regulatory demands.
As AI transforms the financial technology industry, keeping up with all the key developments is crucial for businesses and individuals alike.
That’s why we’ve compiled the latest data on AI in fintech, including how companies are leveraging AI, its key benefits, challenges, and more.
AI in Fintech Highlights
- 90% of fintech companies use artificial intelligence.
- 80% of fintech firms leverage machine learning.
- The most popular machine learning use case in fintech is advanced analytics.
- 80% of fintech companies say access to quality data is a major challenge to implementing AI.
- By 2030, AI in fintech is expected to boost employment in the finance industry by 20%.
How is AI Used in Fintech?
According to a joint report by the Cambridge Centre for Alternative Finance (CCFA) and the World Economic Forum, 90% of fintech companies use AI. Fintech companies use AI technologies differently compared to incumbents – well-established firms in the finance sector including banks, insurers, and asset managers. Fintech companies tend to:
- Create and sell AI-powered solutions.
- Use autonomous decision-making systems.
- Rely on cloud-based offerings.
Meanwhile, traditional financial institutions focus on harnessing AI systems to improve existing products.
The same report found that the most common specific use cases for AI are:
- AI-enabled data analytics – 43%
- Fraud/anomaly detection and surveillance – 42%
- AI-enabled customer communication channels – 36%
Over 75% of fintech firms have adopted at least one use case in ML, deep learning, and high-performance computing. This is according to a 2023 NVIDIA report on the state of AI in financial services. The report described the use of AI as “widespread” across all sectors of financial services including fintech. The top 6 use cases identified by the study were:
- Natural language processing (NLP)/large language models (LLMs) – 26%
- Recommender AI systems/next-best action – 23%
- Portfolio optimization – 23%
- Fraud detection: transactions/payments/KYC – 22%
- Algorithmic trading – 21%
- Conversational AI – 20%
Automation in Fintech
In a Netguru study, task automation was cited by 20% of respondents as their biggest motivator for adopting AI. Automation refers to the use of machines and computers that operate without human intervention.
Through the use of automation tools, fintech companies automate various tasks and processes, reducing the need for human intervention and the risk of human error. Artificial intelligence helps fintech companies streamline processes, improve accuracy, enhance security, and boost customer satisfaction through:
- Automated data processing: AI algorithms are used to process and analyze large datasets in record time and drive more accurate predictions.
- Automated payments: Automation is used to help fintech companies process payments faster and more securely through digital wallets, mobile apps, biometric authentication, and blockchain technology.
- Automated lending: Through the use of AI systems, lending fintech companies are able to support responsible lending and streamline risk assessment, credit scoring, underwriting, and management.
- Automated investing: Automation helps fintech businesses provide smarter portfolio management, asset allocation, and market data analysis. It is also used to execute and guide appropriate market trades.
Generative AI in Fintech
Generative AI refers to deep learning models that generate new text, images, and other content. For fintech businesses, generative AI goes beyond generating account statements, reports, and other documentation.
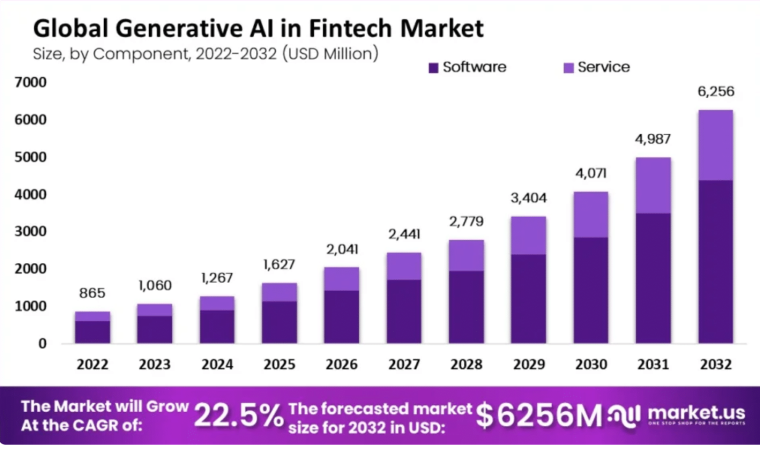
Market.us forecasts that generative AI in Fintech alone will become a $6.25 billion market by 2032 with a predicted compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 22.5%.
According to McKinsey, 75% of the value that generative AI could deliver falls across four key areas:
- Customer operations
- Marketing and sales
- Software engineering
- R&D
Key examples of generative AI in fintech include:
- Conversational finance: Generative AI is used to generate natural and engaging responses to customer queries, bringing significant efficiencies to customer service teams in labor-intensive fields like insurance and wealth management.
- Financial analysis: Generative AI is also used to generate insights and reports from financial data, such as market trends, sentiment analysis, news classification, and risk assessment.
- Synthetic data generation: Generative AI is used to create synthetic data to address data quality challenges and train machine learning (ML) algorithms. Synthetic data sets mimic real-world financial data, such as transactions, activities, and behaviors, augmenting and anonymizing existing data sets.
- Fraud detection: Generative AI is used to detect unusual patterns, simulate cyberattacks, and generate decoy data that helps train fraud prevention models.
Machine Learning in Fintech
80% of fintech companies are leveraging ML. In fact, it remains the top AI use case for the sector. A report by Netguru further found that the top three most popular use cases for ML in fintech are:
- Advanced analytics – 55.75%
- Forecasting – 44.30%
- Fraud detection and prevention – 38%
Machine learning, a branch of artificial intelligence (AI), focuses on harnessing the power of data and algorithms. ML AI models imitate the way humans learn while enhancing their capabilities over time with iterative learning.
ML has many applications in the fintech industry, such as:
- Process optimization: Fintech companies in investment, insurance, lending, payments, and cryptocurrency use ML to automate their operations for greater efficiency and cost reductions.
- Underwriting: AI-powered underwriting systems analyze multiple data points to support responsible lending and root out bogus insurance claims.
- Predictive analysis and forecasting: Fintech organizations use AI algorithms to uncover deeply buried insights and make accurate recommendations based on massive swaths of data. ML algorithms are also used to improve customer engagement and forecast demand for products and services.
- Trading and investment: Machine learning models are used to automate and optimize trading and investment decisions. By analyzing large volumes of market data, identifying patterns, and learning over time, machine learning algorithms enable better trading and investment strategies.
- Fraud detection and prevention: Machine learning algorithms are used for monitoring transactions, analyzing millions of data points, and improving fraud detection mechanisms over time. This offers dynamic defense against evolving threats, safeguarding customers’ assets and reducing the costs associated with fraud.
Natural Language Processing in Fintech
NLP refers to machine learning technology that allows computers to interpret, manipulate, and understand human language. NLP has many applications in the fintech industry, such as:
- Advanced sentiment analysis: NLP helps fintech companies analyze the emotions and opinions of customers, investors, and market participants from data such as social media, news articles, reviews, and feedback. This, in turn, helps drive marketing campaigns, protect brand reputation, ensure compliance, and predict market trends.
- Customer service: NLP powers chatbots and virtual assistants that interact with customers to provide relevant information and solutions in a conversational way. This increases customer engagement and satisfaction.
- Document classification: NLP helps fintech companies optimize document classification, processing, compliance checking, fraud detection, and risk management.
- Topic clustering: Through topic clustering, NLP is used to help fintech companies discover new insights, identify emerging trends, and optimize information retrieval.
| Fintech Sub-sector | Description |
| Investment | Cost-effective and easily accessible apps, robo-advisors, and online platforms that allow consumers to invest their money automatically. |
| Trading | Accessible, cost-effective platforms that allow customers to buy and sell stocks, exchange-traded funds (ETFs), and cryptocurrency from their mobile devices. |
| Payment | Platforms or apps that enable automatic and cost-effective payment processing platforms for consumers and businesses. |
| Personal Finance | Platforms or apps designed to help consumers view and manage their finances conveniently in one place. |
| Lending | Platforms or apps designed to simplify and revolutionize the lending space by providing customers with more credit options. |
| Cryptocurrency | This includes exchanges, wallets, and payment applications that allow customers to transact using cryptocurrencies and digital tokens |
| Insurance | Tech and systems specifically designed to transform and streamline operations in the insurance space. |
Computer Vision in Fintech
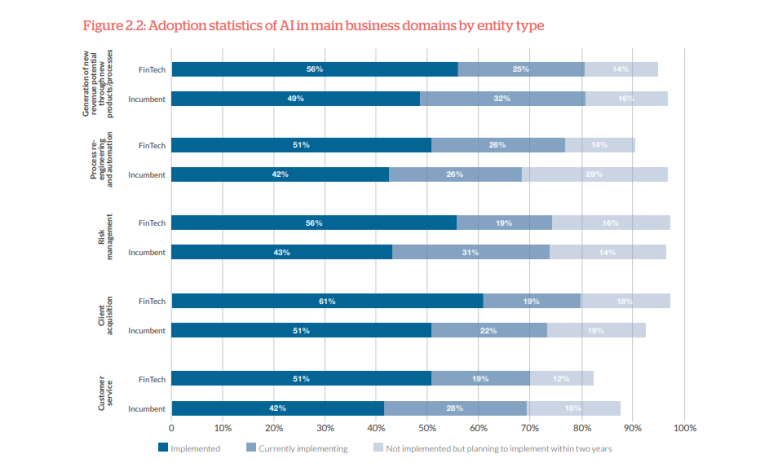
Computer vision refers to applications such as image and video recognition and object tracking. Among the fintech companies studied in the previously mentioned CCFA study, computer vision is quite popular. 36% of respondents have adopted it and another 42% are planning to implement it within two years. This AI technology helps fintech companies improve efficiency and security through:
- Biometric authentication
- Facial recognition
- Document verification
Who is Using AI in Fintech?
The fintech industry encompasses financial education, payments, lending, insurance, cryptocurrencies, investment management, and many other functions traditionally fulfilled by the banking sector.
According to a 2023 BCG report, there are now over 32,000 fintech companies across the world consisting of startups, established financial institutions, and technology companies. These fintech companies remain at the cutting edge of AI adoption, using AI to:
- Develop innovative solutions.
- Enhance fraud detection.
- Increase customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Mastercard

Mastercard uses AI to provide better services for customers, merchants, and partners. The global payment processing giant considers artificial intelligence a foundational technology, employing it across a wide range of business operations. Mastercard is focused on increasing financial security through the use of AI. Its AI-powered suite of security solutions has prevented over $35 billion in fraud losses since 2020.
Mastercard also uses AI to support its recruitment efforts. Its HR team uses generative AI for job descriptions. They also use an AI-based game that doesn’t record demographic data to vet candidates. This advances competent candidates while helping reduce the risk of unconscious bias in hiring.
| Company | Mastercard |
| Location | New York, US |
| Type of Fintech | Payment Processor |
| Types of AI Used |
|
Chime
Chime is a fintech company built on the premise that basic banking services should be helpful, easy, and accessible. It’s a neobank, a fintech company challenging the traditional retail and business banking giants, that relies on a dedicated machine learning team that regularly deploys sophisticated models.
Chime owes its growing success to a features-based marketing strategy powered by artificial intelligence. The fintech company uses artificial intelligence to uncover customer insights, guide product decisions, and determine which marketing tactics to employ.
| Company | Chime |
| Location | California, US |
| Type of Fintech | Neobank |
| Types of AI Used |
|
SoFi
SoFi’s product-based approach offers customers various services, from student loan refinancing to mortgages and wealth management services. It leverages customer data and AI to transform the lending process. Through its efficient credit underwriting model, SoFi gives borrowers more confidence in their applications and guarantees greater customer satisfaction.
In terms of its wealth management services, SoFI makes use of a robo advisor to help customers with investment planning, rebalancing, diversification, and recurring deposits. On August 8, 2023, SoFi Technologies announced that it had integrated Galileo Financial Technologies’ conversational artificial intelligence engine into its personal finance app to improve response time and customer satisfaction.
| Company | SoFi |
| Location | California, US |
| Type of Fintech | Personal Finance/Banking |
| Types of AI Used |
|
Stripe
Stripe, an online payment processor, uses artificial intelligence to enhance customer experience, manage fraud, and increase conversion rates. In March 2023, Stripe introduced OpenAI’s new natural language technology, GPT-4, into its products and services. By adopting this technology, Stripe is able to enhance user experience.
One of the first instances of GPT-4 use at Stripe is Stripe Docs. This enhancement allows developers to ask questions in natural language and receive relevant, summarized answers. It also allows developers to extract specific pieces of information, helping them spend more time building instead of reading.
| Company | Stripe |
| Location | San Francisco, US |
| Type of Fintech | Financial SaaS |
| Types of AI Used |
|
Affirm
Affirm is a fintech startup that provides point-of-sale (POS) loans and buy-now-pay-later (BNPL) financing for consumers via e-commerce retailers. The startup aims to democratize financing and provide an alternative to predatory lenders.
Affirm uses artificial intelligence and other data modeling techniques to vet consumers’ credit history, credit risk, and ability to repay. It also uses efficient AI systems to adjust loan amounts, interest, or repayment terms.
Through its AI-powered underwriting system, Affirm identifies more credit-deserving consumers than traditional scoring systems. By accurately assessing customers’ ability to repay and fairly pricing risk at the point of sale, the startup reduces fraud rates and defaults while giving customers wider access to credit.
| Company | Affirm |
| Location | San Francisco, US |
| Type of Fintech | Lending: BNPL/POS Loans |
| Types of AI Used |
|
What Are the Advantages of AI in Fintech?
Cost Reductions
44% of fintech companies in the previously mentioned Netguru survey reported significant cost savings in areas where artificial intelligence was deployed. Financial institutions have saved an estimated $447 billion as of 2023, with front and middle office operations accounting for $416 billion of the cost savings.
AI enables cost reductions through:
- Improving operational efficiency, increasing productivity, and reducing costly errors.
- Reducing losses from poor investment or lending decisions.
- Reducing operational, marketing, and employee costs.
- Avoid regulatory fines and the costs associated with manual compliance efforts.
- Enhancing fraud detection and reducing financial losses.
Innovative Solutions
The average consumer uses three fintech or banking apps, with payments, bill pay, tax filing, online banking, investing, budgeting, and lending being the most common uses. AI technologies such as machine learning, generative AI, NLP, and computer vision allow fintech firms to build attractive solutions that compete with traditional banks and other financial institutions.
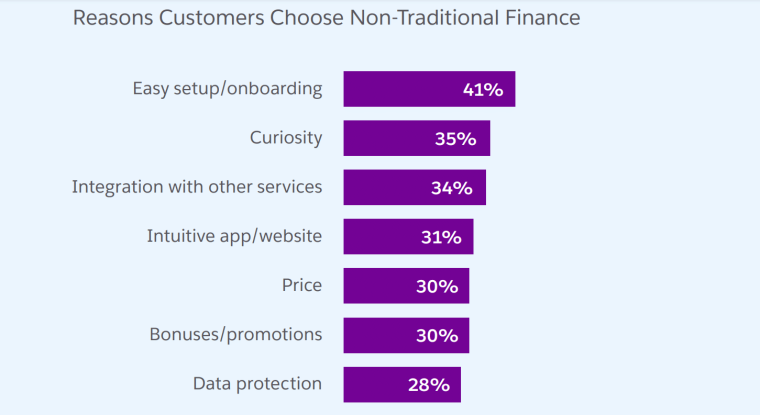
A few of the most important advantages that fintech apps have according to customers include great ease-of-use, easy integration with a wide range of services and apps, great user interfaces, and better pricing.
77% of all respondents in the CCFA survey stated that AI capabilities were of very high strategic importance to their businesses. The data-driven insights enabled by AI play a crucial role in developing actionable business strategies. They also allow companies to keep track of market trends to deliver AI-powered solutions that appeal to consumers’ growing need for convenient, integrated financial solutions.
Improved Customer Data Analysis
Leveraging datasets to generate novel insights is a key benefit of harnessing AI. Machine learning algorithms allow fintech businesses to evaluate unstructured data as well as analyze historical and current data to drive more informed decision-making.
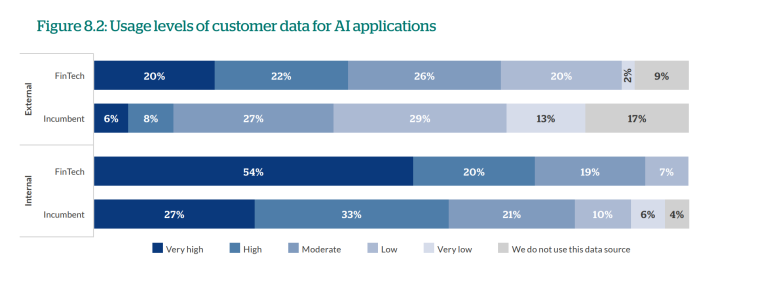
54% of fintech organizations surveyed by Netguru cited extracting better insights from their data as their main driver for adopting machine learning. Compared to other players in the financial sector, fintech organizations rely on and invest heavily in customer data analysis.
60% of all respondents in the CCFA survey used new or alternative forms of data in artificial intelligence. The most frequently used alternative data sources include social media, data from payment providers, and geolocation data.
Better Funding Opportunities
Venture capitalists and investors of all kinds are looking for innovative, profitable companies on the cutting edge. Using AI intelligently makes fintech companies more attractive to VCs than others that have yet to embrace the tech.
Fintech businesses that use artificial intelligence secure higher AI venture funding. Financial institutions that leverage AI, ML, computer vision, NLP, and virtual assistants/chatbots as their primary technology solution raise 20% more investment each year.
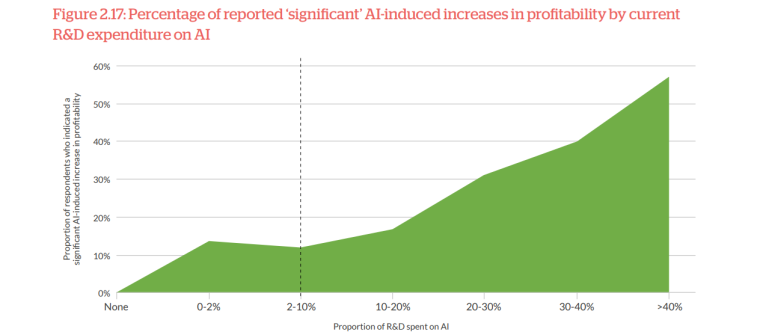
30% of respondents in the CCFA study indicated a significant AI-induced increase in profitability compared to only 7% of incumbents. Compared to incumbents, artificial intelligence has a higher positive impact on fintech industry profitability. Additionally, 63% of respondents in the Netguru survey reported increases in revenue from adopting AI.
Better Fraud Detection and Management
The use of artificial intelligence enhances fraud detection capabilities. In fact, McKinsey estimates that machine learning algorithms can help reduce the number of false reports by 20 to 30%. According to fraud analysts, attacks targeting financial institutions are becoming more complex and widespread. AI-powered security solutions offer fintech businesses dynamic fraud detection and management systems that adapt and get better over time.
Better Customer Experience
73% of customers expect fintech organizations to understand their unique needs and expectations, up from 66% in 2020. By leveraging artificial intelligence, fintech companies are able to reduce operational costs, increase efficiency, and boost customer satisfaction.
What Are the Challenges of Integrating AI in Fintech?
Regulatory Challenges
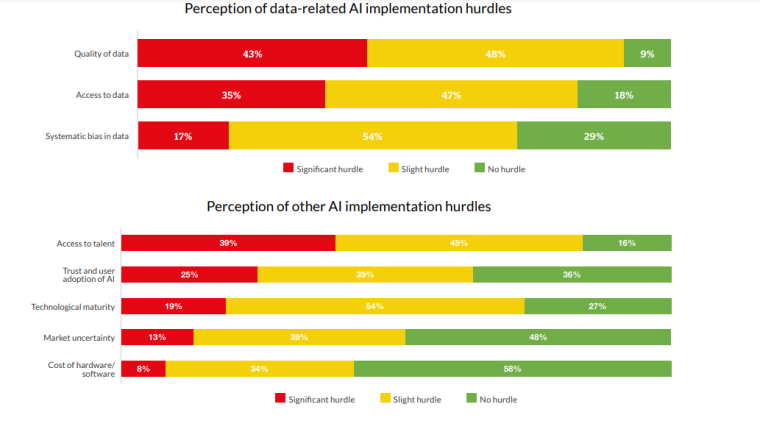
40% of respondents in the CCFA study felt that regulation negatively affected their implementation of artificial intelligence while just over 30% stated that regulation facilitated or enabled it. Fintech companies were most affected by data-sharing regulations between jurisdictions and entities. Regulatory complexity and uncertainty was also cited as a major challenge.
20% of fintech firms in the same study felt they were not ready to mitigate the potential market-wide risks and biases caused by the widespread adoption of AI. Artificial intelligence may amplify biases in decision-making, or expose fintech companies to mass data and privacy breaches.
Data Quality Challenges
As artificial intelligence relies on vast amounts of data to learn and make predictions, inaccurate, incomplete, or biased data can affect the performance and reliability of AI models. Additionally, financial data is often sensitive and personal, which raises ethical and legal issues regarding data protection and consent.
80% of fintech businesses cite access to quality data as a major roadblock to implementing AI. Imperfect data quality poses several threats to fintech businesses including potentially undermining existing methods, unfair credit scoring, and other discriminatory outcomes.
Customer Experience Challenges
In a Salesforce study of the financial industry, a high rate (39%) of customers stated they weren’t satisfied with AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants. The same study found that poorly integrated or non-intelligent chatbots were the most commonly reported area of digital friction.
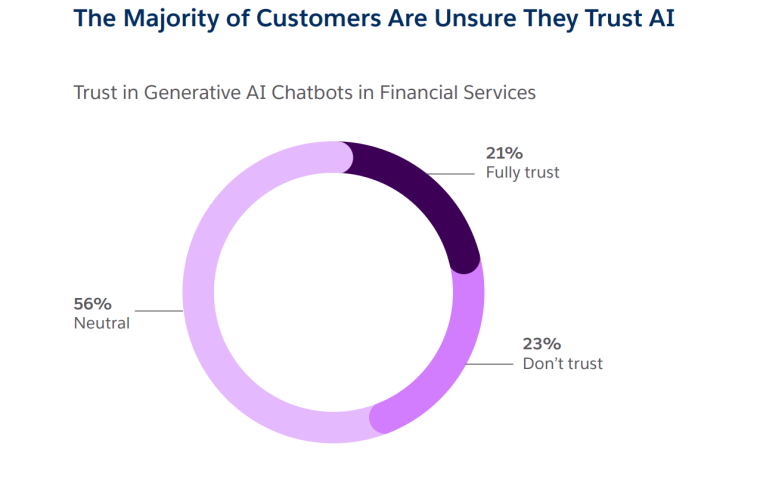
It’s not surprising that AI chatbots are very popular. Many people just don’t trust AI yet. 23% of customers don’t trust it and another 56% are neutral towards it.
86% of customers prefer to interact with a human agent and 71% would be less likely to use a brand if it didn’t have human customer service agents available. So although chatbot adoption is on the rise, fintech companies still face customer acceptance challenges.
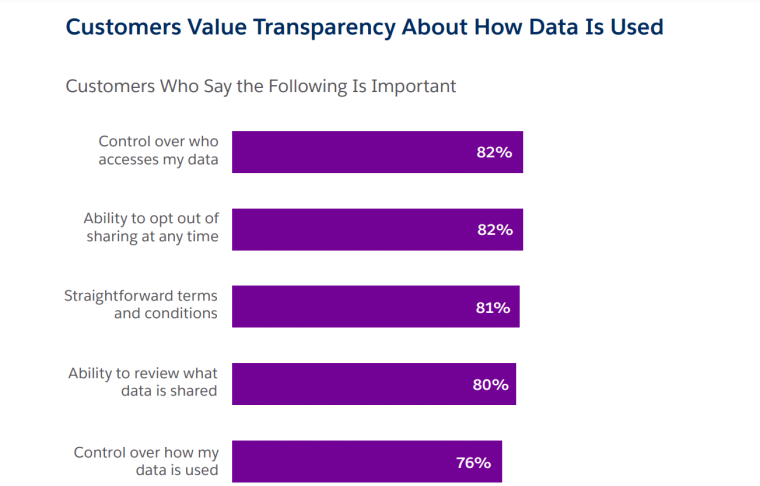
Privacy and Security Challenges
A staggering 78% of customers would switch financial service providers if they felt their data was mishandled or compromised. Therefore, fintech businesses must ensure that they collect and process customer data ethically and securely and focus on the issues that customers value the most.
The average cost of a data breach in the financial industry was $5.72 million in 2020. The cost of fraud is rising and AI is increasingly being used by malicious actors to launch sophisticated cyber attacks. As such, it is crucial for financial institutions to invest in their cybersecurity measures and capabilities.
Explainability Challenges
Automated systems and their outputs are often called “black boxes” as their internal workings are difficult to explain. Various solutions, such as game-theory-based methods and local model approximations have been explored. However, a universally applicable and scalable approach, irrespective of model complexity, is yet to be found.
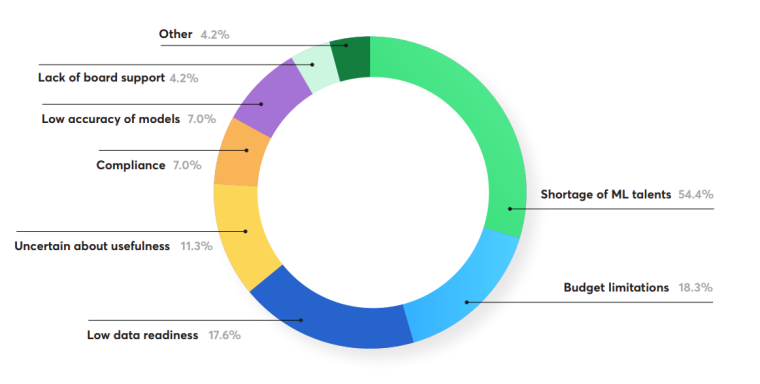
Talent Challenges
A Netguru report revealed that 54% of fintech industry respondents saw the shortage of AI talent as their biggest challenge. Recruiting talent in AI remains one of the most significant obstacles to AI implementation.
Similarly, a 2023 Nvidia study found that over a third of respondents (36%) cited challenges in recruiting and retaining AI talent as a key challenge. That’s an 80% jump from 2022 and the first time in the survey’s three-year history that recruiting AI talent emerged as the top challenge.
What Is the Future of AI in Fintech?
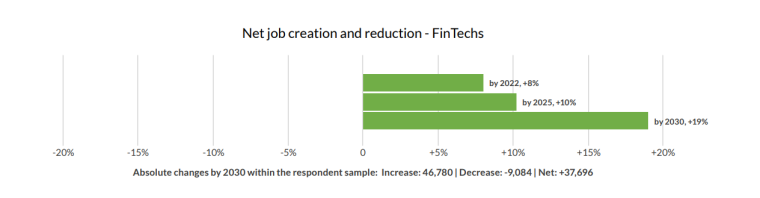
The AI in fintech market is expected to grow at a rate of 28.6% to reach $31.71 billion in 2027. By 2030, the use of AI could reduce operating costs in the financial services industry by 22%.
Within the financial sector, the financial services industry is set to experience a 9% replacement of jobs by 2030. However, this is expected to be offset by the creation of new jobs in the fintech industry where employment is expected to grow by 20% because of AI.
According to BCG, generative AI will power digital financial concierges that will complete tasks such as:
- Paying bills
- Sending remittances
- Checking budgets
- Disputing charges
The World Economic Forum predicts that by 2025, AI will replace significant functions including call center inquiries, data entry, and reconciliation. New jobs will be created to help AI interfaces be more personable and human-like in their behavior.
To help fintech businesses in their efforts, experts from non-traditional areas such as psychology will be recruited. Ultimately, cross-functional, AI personal assistants will become a key part of customers’ lives, organizing their finances, making purchases, and more.