The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) in education has emerged as a powerful catalyst, reshaping the landscape of learning and pedagogical practices.
There is plenty of research on how this new technology is impacting our educational systems, but with data scattered across reports and websites, navigating AI in education statistics can be overwhelming.
That’s why we’ve curated this comprehensive rundown of essential information and insights into the potential of AI in education.
Global Adoption: AI in Education Statistics Highlights
- The market size for artificial intelligence (AI) in education is anticipated to reach $30 billion by 2032.
- By January 2023, the global number of edtech unicorns had reached 30, collectively valued at $89 billion.
- Institutions worldwide, from Georgia State University to National Cheng Kung University, are implementing AI to streamline operations and enhance educational experiences.
- In just two months after its launch, over half (51%) of teachers had begun using ChatGPT, with 40% incorporating it weekly
- In 2020, the AI online education market in China reached a notable total of 368 billion yuan.
- As of February 2023, 30% of college students had integrated ChatGPT into their school assignments.
AI in Education: What You Should Keep in Mind
- Expansive Impact: AI significantly reshapes educational methods, enhancing personalized learning experiences and administrative efficiency. It’s becoming a fundamental component in modernizing education through tools like adaptive learning platforms and AI-driven administrative aids.
- Widespread Adoption: Major educational institutions and universities are integrating AI to improve both student learning outcomes and operational efficiencies, indicating a strong trend towards digital transformation in education.
- Ethical and Policy Considerations: The rapid adoption of AI in education necessitates clear policies and guidelines to manage its use effectively and ethically. Institutions need to consider data privacy, the risk of bias, and the proper integration of AI into educational settings to ensure it benefits all students equally.
How is AI Used in Education?
Artificial intelligence (AI) has rapidly found its way into the education sector, revolutionizing traditional teaching methods and enhancing the learning experience. From personalized learning to efficient administrative management, AI’s impact is far-reaching and includes multiple AI categories.
Examples of the diverse ways AI is used in education include:
- Adaptive learning: AI assesses students’ skill levels and tailors instructional experiences, nurturing their proficiency in basic and advanced subjects.
- Assistive technology: AI aids special needs students by providing equitable access, like reading passages aloud for visually impaired learners.
- Early childhood education: Interactive AI-powered games impart fundamental academic skills to young learners, fostering engaging educational experiences.
- Data and learning analytics: Teachers and administrators employ AI to analyze data, empowering informed decision-making and enhancing educational strategies.
- Scheduling: AI simplifies course scheduling for administrators and aids individuals in managing their busy academic calendars effectively.
- Facilities management: AI monitors power, Wi-Fi, and water services, promptly alerting facilities management to address any arising issues.
- Overall school management: AI streamlines school operations, overseeing student records, transportation, IT, maintenance, scheduling, and budgeting.
- Writing assistance: AI aids students in improving writing skills and even assists professionals, like authors, in producing grammatically sound content.
- Plagiarism detection: AI identifies instances of plagiarism, fostering academic integrity and originality.
- Exam integrity: AI safeguards the integrity of exams by detecting irregularities and preventing cheating.
- Chatbots for enrollment and retention: AI-powered chatbots streamline enrollment processes and support student retention initiatives.
- Learning management systems: AI enhances learning platforms, providing personalized content and feedback to students.
- Transcription of faculty lectures: AI transcribes lectures, ensuring accurate documentation of instructional content.
- Enhanced online discussion boards: AI-driven discussion platforms facilitate insightful and meaningful online student interactions.
- Analyzing student success metrics: AI analyzes student performance data, enabling educators to identify areas for improvement and tailor interventions.
- Academic research: AI aids researchers in analyzing vast datasets, accelerating the pace of academic discoveries.
- Connected campuses: AI promotes seamless communication across campuses, improving collaboration and access to resources.
As AI continues to advance, its role in education will undoubtedly expand further, offering novel solutions that empower educators and learners alike.
How can AI help students learn?
From a student’s viewpoint, AI can be a helpful resource that educators can employ to tackle the individualized ways in which students learn. Unlike conventional educational resources that typically target the average learner, AI can accommodate the entire range of learning disparities among students.
One example is the case of AI-incorporated educational tools: they possess the capability to adjust to the distinct English language proficiencies of students, furnishing each with tailored assistance that caters to the diverse aptitudes and necessities of English learners.
Who Is Using AI in Education?
Colleges and Schools Using AI
Colleges are increasingly harnessing the power of AI to improve learning, research, administration, and student support. AI technology is reshaping higher education, creating new opportunities for students and institutions.
Below, we take a closer look at how five universities are using AI and how it’s being integrated into all aspects of education.
Georgia State University
Georgia State University employs a chatbot called “Pounce” to aid in admissions, financial aid, class registration, and campus resources, among other functions.
| University | Georgia State University |
| Location | Georgia, US |
| Type of AI | AI chatbot |
| AI Tasks | Admissions, financial aid, class registration, and campus resources |
| AI Name | Pounce |
University of California
Since 2021, The University of California, Berkeley, has offered the Berkeley Chatbot, an AI-powered assistant catering to both current and prospective students’ inquiries.
During its initial week of operation, the AI-powered chatbot managed over 1,500 conversations, addressing inquiries spanning financial aid, registration, REC sports, billing, and payments.
| University | University of California, Berkley |
| Location | California, US |
| Type of AI | AI-powered chatbot |
| AI Tasks | Answering administrative and financial inquiries |
| AI Name | The Berkley Chatbot |
Deakin University
Another successful chatbot implementation comes from Deakin University in Australia. Back in 2017, the university introduced Deakin Genie, a chatbot accessible through a voice-activated mobile app.
This AI-driven companion effectively supports students in multiple dimensions of their academic journey, including course choices, enrollment procedures, study planning, assignment aid, and feedback. Deakin Genie delivers personalized assistance tailored to each student’s academic and personal aspirations.
| University | Deakin University |
| Location | Victoria, Australia |
| Type of AI | AI-powered chatbot |
| AI Tasks | Answering student inquiries |
| AI Name | Genie |
Staffordshire University
Staffordshire University was the first university in the UK to introduce a digital assistant (chatbot) to aid students with their studies and campus life.
As part of Staffordshire University’s comprehensive Digital Vision, this chatbot, known as “Beacon”, served as an innovative digital coach and assistant for students.
A particularly interesting aspect of the university’s approach with Beacon was its focus on supporting new students. It employed various gentle reminders (“nudges”) to ensure students were connected with essential services and activities.
| University | Staffordshire University |
| Location | Staffordshire, UK |
| Type of AI | AI-powered chatbot |
| AI Tasks | Admissions, financial aid, class registration, and campus resources |
| AI Name | Beacon |
National Cheng Kung University
In 2020, National Cheng Kung University (NCKU) in Taiwan was the first university in the country to incorporate AI into the university’s security center. The initiative combined surveillance technology, an emergency notification system, and campus police dispatch.
NCKU established the Research Center for Campus Security (the Security Center), which strategically placed 18 red emergency booths equipped with security cameras throughout the campus. When the emergency button was activated, the system swiftly connected to the Security Center, considerably reducing the response time from an average of 10 minutes to an impressive 3 minutes.
Within a span of six months, the Security Center played a pivotal role in addressing several incidents, including traffic accidents and emergencies that occurred on the NCKU campus.
| University | National Cheng Kung University |
| Location | Tainan, Taiwan |
| Type of AI | AI-powered surveillance and emergency notification system |
| AI Tasks | Surveillance, emergency notifications, campus police dispatch |
| AI Name | Research Center for Campus Security |
ITS and AI In Universities
Many universities employ intelligent tutoring systems (ITS) to personalize learning. These systems utilize machine learning to analyze individual learning patterns, address student needs, monitor progress, and offer tailored feedback, ultimately enhancing academic performance and engagement.
Examples of intelligent tutoring systems employed in education include:
- Carnegie Learning – focused on mathematics education
- Duolingo – dedicated to language learning
- Smart Sparrow – an adaptive platform spanning multiple disciplines
- Knewton – an adaptive solution seamlessly integrating with existing learning frameworks
AI In E-Learning
In 2021, the e-learning market reportedly exceeded $315 billion, and experts predict it could grow to $1 trillion by 2028. This expansion is largely fueled by cutting-edge technologies such as artificial intelligence and machine learning.
The integration of AI in e-learning is revolutionizing education by crafting intelligent and tailored learning journeys for students. This not only accelerates content accessibility but also enhances efficiency.
AI also simplifies educators’ tasks by facilitating progress tracking and pinpointing specific areas where students require additional assistance.
- Personalized learning paths: AI tracks student behavior and performance, creating customized learning paths tailored to their needs.
- Adaptive learning: AI adjusts material based on students’ understanding, allowing flexible pacing and focused review.
- Intelligent tutoring: AI-powered tutors provide instant help and engaging activities, enhancing learning experiences.
- Natural language processing: AI uses NLP to interact naturally, answering queries promptly and accurately.
- Predictive analytics: Students visualize progress, aiding teachers in planning, feedback, and insightful evaluation.
- Content automation: AI swiftly generates course content based on data, streamlining updates and knowledge integration.
- VR and AR integration: AI enables immersive learning through virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR).
- Gamification: AI gamifies courses for interactive, tailored learning, utilizing performance metrics for personalized experiences.
Benefits of AI in Education
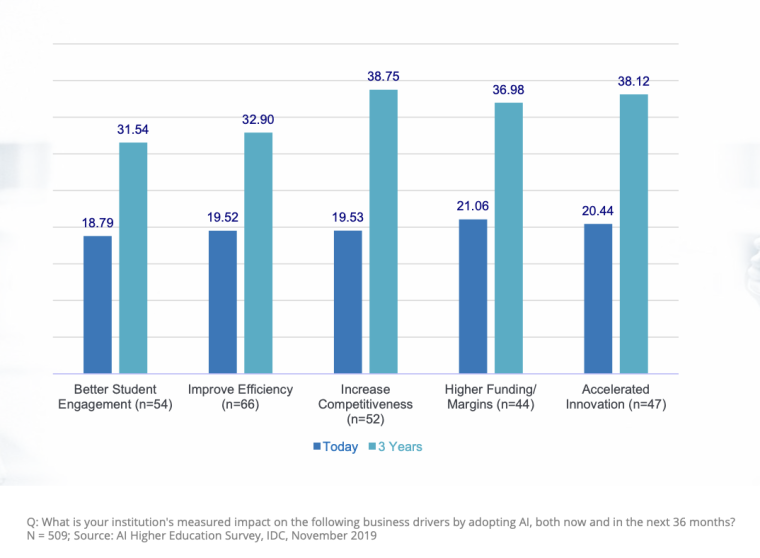
In a 2019 survey, IDC in conjunction with Microsoft asked institutions about the measured impact of adopting AI over the course of three years.
The top 5 benefits returned were:
- Better student engagement
- Improved efficiency
- Increased competitiveness
- Higher funding/margins
- Accelerated innovation
Unrestricted 24/7 Learning
AI-driven tools ensure learning is available to every student, wherever and whenever they choose.
Each student progresses at their individual speed, and constant accessibility empowers them to discover effective methods without dependency on educators’ availability. Moreover, students worldwide can access top-tier education without the need for costly travel and accommodation expenses.
Automation of Tasks
66% of teachers reported that they spent over half of their working time on tasks other than teaching, when surveyed by the UK Department for Education in 2023.
AI’s capability for automation can handle mundane and repetitive responsibilities, such as grading papers, assessing learning patterns, and responding to general queries. This shift toward task automation enables educators to streamline manual processes, freeing up valuable time to concentrate on teaching essential skills.
Adaptive Learning
Thanks to AI, students are now benefiting from tailored learning programs that cater to their distinct backgrounds and preferences.
AI has the ability to adjust to individual knowledge levels, learning speeds, and objectives, ensuring optimal educational outcomes. AI-driven solutions can also analyze past learning records, pinpoint areas of weakness, and recommend courses for enhancement, thus offering ample prospects for a personalized learning journey.
Assistance Beyond Hours
An AI-driven chatbot can provide responses to student queries in as little as 2.7 seconds.
Many students need additional support beyond classroom hours, but teachers often lack the availability. AI tutors and chatbots serve as ideal solutions in such situations. While no chatbot can fully substitute an educator, AI tools aid students in honing their abilities and enhancing areas of weakness beyond formal learning. They offer personalized learning interactions, addressing inquiries even outside regular teacher availability.
Continuous and Automated Optimization
AI can extract data from a learning management system (LMS), student performance, and feedback, enabling comprehensive analytics.
Schools can utilize this data to gain insights into their learning processes. They can assess course effectiveness, pinpoint areas for improvement, and uncover important trends. These insights drive the enhancement of content, courses, and training strategies for better results. AI’s automated data collection further streamlines this process.
Challenges of AI in Education
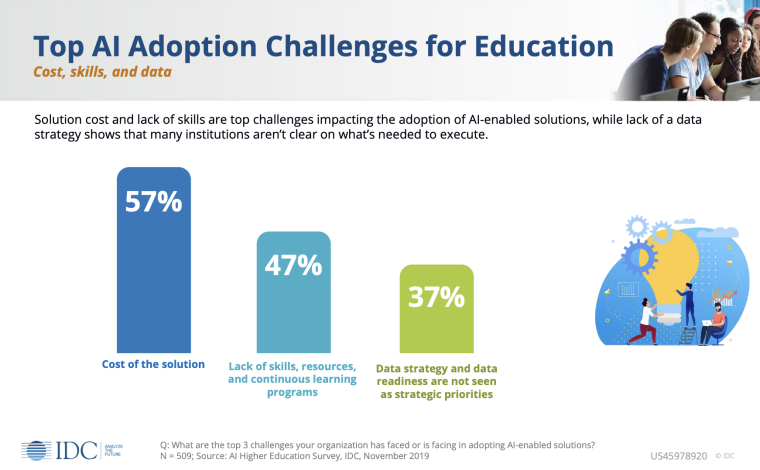
Insufficient Digital Maturity and Data Readiness
Artificial intelligence is dependent on the data it is trained with. However, when surveyed for a 2020 IDC study, 37% of educational professionals did not consider data strategy and data readiness as significant strategic focal points for their organization. This suggests an absence of understanding about the essential components required to effectively implement an AI strategy.
Lack of AI Policies and Guidance
Less than 10% of schools and universities have established formal policies or guidance for the utilization of generative AI applications, according to a recent global survey conducted by UNESCO, involving more than 450 educational institutions.
As AI continues to become more accessible and adopted among students, policies and regulations are lagging behind. Around 40% of educational institutions that did claim to have guidance revealed that it was conveyed orally, rather than in written form. This highlights the spontaneous and unplanned approach often seen in educational policy responses.
A 2023 survey, undertaken by Junior Achievement in collaboration with research firm Big Village, aimed to illuminate the increasing dependency of teenagers on AI for their schoolwork. 44% of the surveyed teens indicated that they intended to use AI for tackling their schoolwork in the upcoming 2023-2024 academic year.
At the same time, a significant majority of teens (60%) viewed relying on AI for schoolwork as a form of “cheating”, revealing a noteworthy contradiction in their attitudes.
The survey delved into motivations behind teens’ embrace of AI for schoolwork, revealing a range of factors:
- 62% considered AI as just another tool for completing assignments.
- 24% turned to AI due to dissatisfaction with school or schoolwork.
- 22% believed that AI eliminates the necessity to acquire knowledge.
- 22% succumbed to peer pressure, influencing their decision to rely on AI.
- 17% feared poor performance without AI assistance.
- 8% perceived subject knowledge to be unimportant.
These numbers illustrate the multifaceted factors driving teens’ adoption of AI and the underlying attitudes shaping their choices. They also showcase some of the challenges that the educational system will need to address.
Other findings on this topic, from a 2023 survey by the Walton Family Foundation, include:
- Teachers were 4x more likely to allow students to use ChatGPT (38%) than to catch unauthorized use (10%).
- 15% of students admitted using ChatGPT without their teachers’ permission.
- 63% of students and 72% of teachers agreed that ChatGPT’s is part of a modern approach to education.
- 68% of students believed ChatGPT improves learning.
- 75% of students experienced faster learning with ChatGPT.
- 73% of teachers affirmed ChatGPT’s positive impact on student learning.
The Future of AI in Education
The total value of AI in education is expected to reach $6 Billion by 2024, according to Unesco.
By 2032, the total market size of artificial intelligence in education is projected to reach $30 billion, according to research by Global Market Insights Inc.
AI holds the promise to tackle prominent educational challenges, drive innovation in teaching and learning methods, and ultimately expedite progress towards achieving Sustainable Development Goals 4.
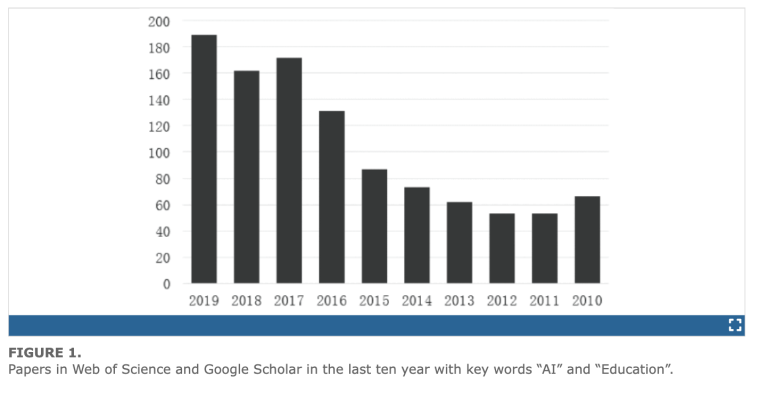
The academic interest in the integration of AI algorithms and systems into education has been growing for a long time. As illustrated in the chart below, the volume of papers published on the intersection of “AI” and “Education” has been steadily rising since 2010, with a notable concentration of publications occurring between 2015 and 2019, making up 70% of the indexed papers.
In the 2023 report “Artificial Intelligence and the Future of Teaching and Learning”, the US Department of Education listed 4 imperative focus areas that needed attention with the continued implementation of AI in the education system. According to the report, to ensure ethical and safe use of AI in education, it’s essential to implement the following:
- Harness automation to enhance learning outcomes while preserving human decision-making and judgment.
- Scrutinize the foundational data quality in AI models, ensuring impartial and unbiased pattern recognition and decision-making within educational contexts. This entails using accurate information suitable for the specific pedagogical scenario.
- Facilitate the evaluation of how specific AI technologies, integrated into broader educational systems or edtech platforms, might either amplify or compromise equity for students.
- Take proactive measures to uphold and promote equity. This involves incorporating mechanisms for human oversight and balance and setting limits on AI systems and tools that could potentially undermine equity.
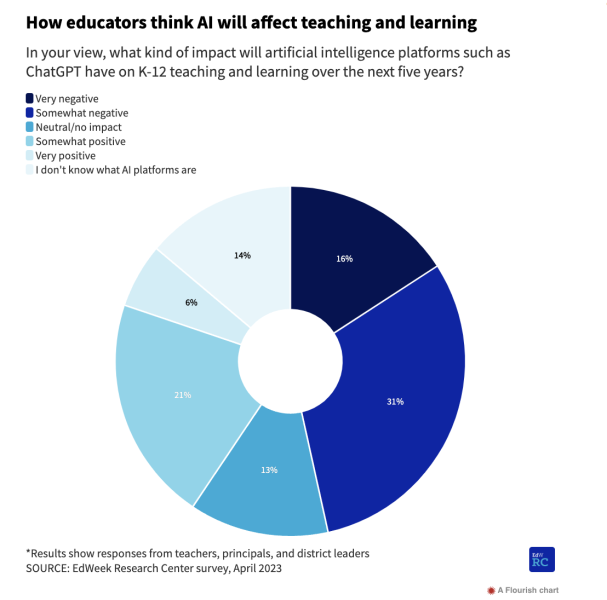
Educators’ perspectives on AI span a range of viewpoints. Some educators express concerns about the potential misuse of AI-powered tools such as ChatGPT by students for academic dishonesty, while others are adopting these innovations to streamline tasks such as email communication and rubric development, ultimately saving them valuable time.
Almost 50% of educators participating in an April 2023 survey conducted by the EdWeek Research Center expressed concerns about AI, expecting a detrimental or highly unfavorable influence on the realm of teaching and learning within the next five years.
In contrast, 27% of respondents held an optimistic view, believing that AI’s effect would be beneficial or exceptionally positive.
Final Thoughts: The AI Revolution
AI’s integration into education is reshaping the landscape, offering tailored educational experiences and operational efficiencies. As AI continues to evolve, its potential to enhance both teaching and learning will expand, promising a future where education is more accessible, personalized, and effective.
FAQs
What are examples of AI in education?
How will AI impact education?
What is the main role of AI in education?
References
- Global Market Insights
- Global Market Insights
- Walton Family Foundation
- Statista
- The US Department of Education
- Berkeley University
- Deakin University
- Inside Higher Ed
- AsiaToday
- EdTech Review
- UNESCO
- Junior Acheivement USA
- UNESCO
- IEEE.org