Ethical investing has become increasingly popular in today’s world as investors look toward assets that promote positive environmental, social, or governance changes. Not only is ethical investing appealing from a moral standpoint, but this approach is often financially rewarding over the long term.
With that in mind, this guide takes an in-depth look at what ethical investing actually is, covering the various ethical asset classes and the benefits of investing in them. We’ll also present some popular trading strategies before highlighting where investors can begin investing ethically today – from as little as $10.
Best ESG Investment 2025

IMPT is currently in the presale phase – although due to the project’s innovative use case, demand is already ramping up for the token allocation. Investors looking to get involved early can buy IMPT tokens at a discounted rate of $0.018, the lowest price they’ll be made available. We’ll discuss IMPT later in this article for those who want to learn more.
Ethical Investing Explained
First thing’s first – what is ethical investing? Broadly speaking, ethical investing refers to the process of filtering potential assets based on certain moral principles. These principles will vary from person to person, but all relate to having a positive impact on the world.
There are many different ways to determine what ethical investments actually are, which we’ll explore later in this guide. For example, investors may opt to buy stocks in green energy companies as a way to promote the slowdown of global warming. This approach clearly has an environmentally-conscious filter, so it would be considered ethical stock investing.
According to The Times, although ethical investing means investors seek securities that make positive social, environmental, or governance changes, they are still looking to generate a return on their capital. This can make ethical investing slightly more challenging, as using these filters reduces the universe of potential assets that can be considered for investment.
Those who invest ethically also avoid securities that could be construed as ‘harmful’ or have a moral compass that doesn’t align with the investor’s own. A typical example is ethical investors opting to sidestep tobacco or firearms stocks, as these companies generate revenue (and profit) based on the sale of products that many consider unethical.
Whether someone is wondering how to invest $1,000 or any amount, ethical investing can be a great way to ensure the investor remains socially responsible and sticks to their values. Humans are individualistic, so one person’s values may differ from another’s. Thus, there is no ‘guideline’ for what an ethical investment is, as it can vary depending on the investor.
How Does Ethical Investing Work?
Investing ethically works the same way as regular investing – yet investors must be much more stringent when choosing the assets to be added to their portfolios. The most common way this is achieved is by creating a sort-of ‘filter’ based on the investor’s principles and values.
For example, someone may wish to only invest in stocks of companies involved in the healthcare or education sectors, as these companies often aim to make positive changes in the world. Other ethical investments may include ESG/SRI funds, which we’ll explore later in the article.
However, the key way that investing in ethical funds, stocks, and other asset classes works is by the investor performing extensive prior research. It’s not enough for the target asset to describe itself as ethical – it must BE ethical.
So how can investors do this? This will depend on the chosen asset, although most have supporting documentation that can help investors understand whether they are ‘ethical’ or not. For example, ethical investment funds tend to have a file detailing the criteria the fund manager employs when choosing the assets to be included in the fund.
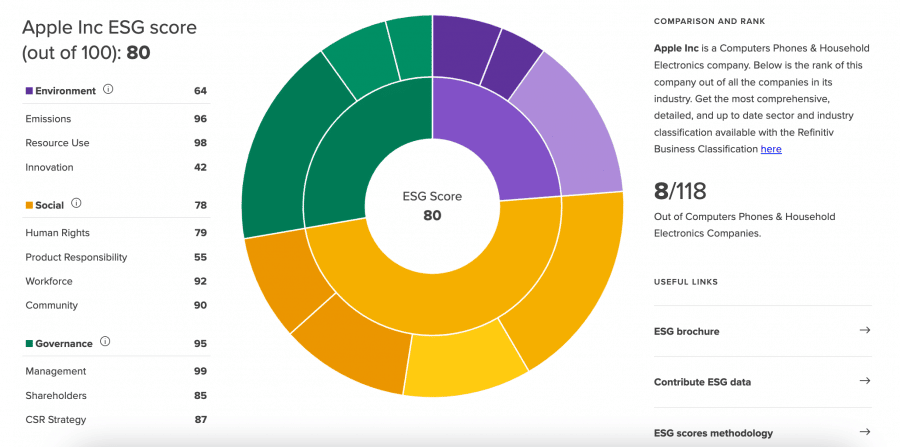
Those interested in ethical stock investing can also review a company’s environmental, social, and corporate governance (ESG) score. Leading financial data firm Refinitiv is an excellent resource for finding accurate ESG scores on most publicly-listed companies. Using this, investors can weed out companies that don’t meet their criteria for an ethical asset.
SRI, ESG & Impact in Ethical Investing
Many investors that ponder how to invest in mutual funds or equities are opting to invest ethically. Due to the rise in popularity of this approach, various tactics and strategies have emerged that make it easier for investors to find ethical companies to invest in.
Socially responsible investing (SRI), environmental, social, and governance (ESG) investing, and impact investing are three of the main tactics employed by ethical market participants. Let’s take a closer look at these tactics:
- SRI – As defined by BNP Paribas, socially responsible investing (SRI) integrates environmental, social, and governance factors into the decision-making. Although this approach is similar to ESG investing, it focuses on avoiding assets linked to unethical practices (e.g. animal testing).
- ESG – Environmental, social, and governance (ESG) investing is very similar to SRI investing, yet has more of a ‘quantifiable’ aspect through a scoring system. Assets are evaluated based on how they relate to the three ESG elements, with more responsible investments given a higher score.
- Impact – Impact investing only considers companies proactively helping address a particular issue, thereby positively impacting the world. For example, impact investors may buy the stocks of a company helping rebuild people’s homes after a flood.
The critical thing to remember is that all three types are geared towards making a positive impact, yet they differ slightly in their approach. Impact investing is more clear-cut, seeking out companies that actively improve the world. SRI and ESG investing can be subjective and based on the individual’s unique values and beliefs.
Types of Ethical Investments
Most of the best trading platforms now provide an array of ethical investment opportunities, making it easy to adopt this approach. But what are the different types of ethical investments? Let’s answer this question by providing some popular examples:
Cryptocurrency
Cryptocurrency has become an increasingly-popular asset for ethical investors to consider. Most people buy cryptocurrency purely for financial gain, yet many crypto projects now employ technologies that help positively impact the world – particularly in an environmental sense.

Ethical cryptos include those that avoid energy-intensive processes in favour of ‘greener’ options, like Proof-of-Stake (PoS). In addition, many crypto projects also purchase carbon offsets to reduce their footprint. Leading blockchain network Polygon even has a ‘Green Manifesto’ detailing how the development team is helping the environment.
However, one ethical crypto investment worth keeping an eye on is IMPT. This brand-new carbon credits ecosystem leverages the power of blockchain technology to remove the transparency issues plaguing the market. Moreover, the IMPT whitepaper also makes it easy for individuals to acquire carbon credits through everyday shopping activities.

IMPT has partnered with 10,000 leading retailers, meaning that whenever an individual shops with them, they will acquire IMPT points which can be exchanged for carbon credits. These carbon credits, structured as NFTs, can then be traded or retired. These innovations have led many to suggest that IMPT could be one of the most promising cryptocurrencies of 2025 for ethical investors.
More information about this project is available on the IMPT Telegram channel.
Carbon Credits
Although many people focus on ethical investing companies and funds, one of the most socially-responsible investments worldwide is carbon credits. These carbon credits, sometimes called carbon offsets, are a type of ‘permit’ that allows an individual or company to emit one ton of carbon dioxide (CO2) into the atmosphere.
The fascinating thing about carbon credits is that they can be traded. A company that emits more CO2 than expected can buy carbon credits from another company emitting less. Both companies can benefit through this process, yet the net emissions remain the same.

Those wondering how to invest in carbon credits can do so either directly or indirectly. Investors can buy stocks in companies that deal in carbon credits or invest in an ETF that tracks carbon allowances. Advanced investors may also wish to invest in carbon offset futures, which provide exposure to the price of these assets without having to own them.
Stocks
Investing in ethical companies is one of the most popular approaches for ethical investors. As touched on earlier, which companies are considered ‘ethical’ is decided by the individual, based on their own beliefs or values. However, most ethical companies avoid immoral practices and actively help promote positive change.
For example, the best biotech stocks help create more sustainable farming practices which require fewer pesticides. In turn, this makes these practices better for the environment – which is why many biotech stocks can be considered ethical investments.
ESG/SRI Funds
Ethical investing funds often use ESG or SRI-based criteria when choosing which assets to invest in. Due to the rise in popularity of ethical investing, funds are now available that exclusively target ethical investors. These funds only include assets that many consider environmentally, socially, and governmentally responsible.
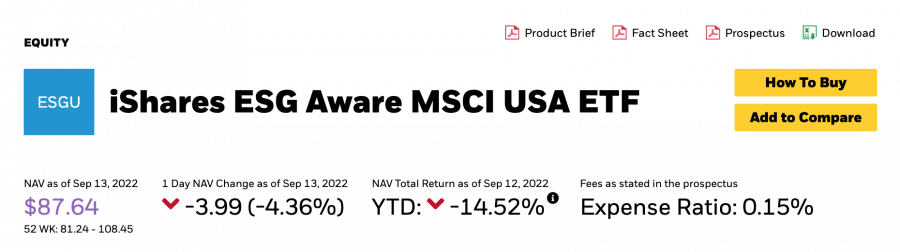
Notably, ESG and SRI funds may have a specific bias towards a particular type of asset. For example, a fund may invest in companies that promote ethical labor practices. Either way, these funds still aim to generate a return for investors.
Pre-made Portfolios
An alternative to investing in an ethical investment fund is to consider pre-made portfolios. These are similar to mutual funds but are assembled and offered by the best CFD brokers and online trading platforms.
‘Green’ ETFs
Finally, ethical investors focusing on environmental factors can opt to invest in ‘green’ ETFs. For those unaware, ETF stands for ‘exchange-traded fund’ and operates much like a mutual fund. However, the critical difference is that ETFs are publicly-traded, meaning investors can buy and sell their shares on the stock exchange.
ETF trading is a popular passive investment method, as a fund manager handles asset selection. Relating this to ethical investing, ‘green’ ETFs focus solely on assets that aim to affect the environment positively. For example, a green ETF may only invest in renewable energy stocks and avoid companies related to fossil fuels.
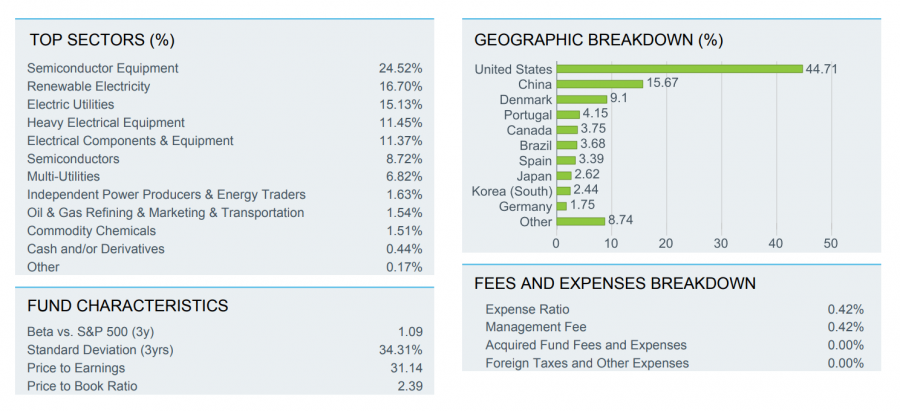
ETFs tend to be more accessible than investing in ethical funds, as they are available through leading brokers and trading platforms. Moreover, ETFs often have lower barriers to entry – since mutual funds tend to have high fees and a minimum investment threshold.
Examples of Ethical Investment Assets
Those interested in investing in ethical companies or placing their capital in socially-responsible funds must conduct extensive prior research to ensure the target asset is as moral as claimed. Detailed below are some prominent examples of ethical investment assets that investors can look to for inspiration:
IMPT

Through IMPT’s partnerships with leading brands, this project aims to actively make a positive change to the environment. What’s more, IMPT’s social platform incentivizes positive change even further, giving points to individuals and companies that are the most impactful.
IMPT even ensures its own emissions are as low as possible by being hosted on the Polygon blockchain. This blockchain network uses a Proof-of-Stake (PoS) consensus mechanism, meaning that energy requirements are minimal. Combine this with IMPT’s carbon-reduction goals, and it’s clear why the project has already made a name for itself in the ethical investing space.
NextEra Energy

Many investors believe NextEra Energy is one of the most undervalued stocks on the market since the company is primed to benefit from the US government’s push toward renewable energy. What’s more, NextEra energy has also pledged to remove CO2 emissions from its operations entirely by 2045.
Due to this, NextEra energy is a popular company amongst ethical investors with a bias toward eco-friendly assets. The company’s share price is up 32% since May 2022, highlighting that it may also be popular from a capital gains perspective.
iShares Global Clean Energy UCITS ETF
The iShares Global Clean Energy UCITS ETF is an exchange-traded fund that invests in companies involved in clean energy production. These companies are based in both developed and emerging markets, providing broad global exposure. Moreover, the iShares Global Clean Energy UCITS ETF actively avoids investing in companies that exceed a specified carbon emissions threshold.
Some of the companies that this fund invests in include Enphase Energy, Solaredge Technologies, and Plug Power. The iShares Global Clean Energy UCITS ETF has a total annualized return of 14.79% over the past ten years, with an expense ratio of just 0.65%.
Vanguard FTSE Social Index Fund
The Vanguard FTSE Social Index Fund aims to track the FTSE4Good US Select Index – an index composed of securities demonstrating specific environmental, social, and governance practices. These securities have transparent management and are thoroughly researched, ensuring they can be considered ethical.
As such, the Vanguard FTSE Social Index Fund excludes gambling, alcohol, cannabis, firearms, and nuclear weapons stocks. Moreover, the fund also appeals to SRI-focused investors by avoiding companies with poor labor practices or human rights violations. It even shuns firms that do not meet specific diversity criteria.
European Union Allowance (EUA) Futures
Finally, European Union Allowance (EUA) Futures are a type of futures contract based on Europe’s emission allowances. One EUA contract is the equivalent of one ton of CO2 or greenhouse gas equivalent. Corporations often buy and sell these futures contracts to hedge their price risk over the longer term.
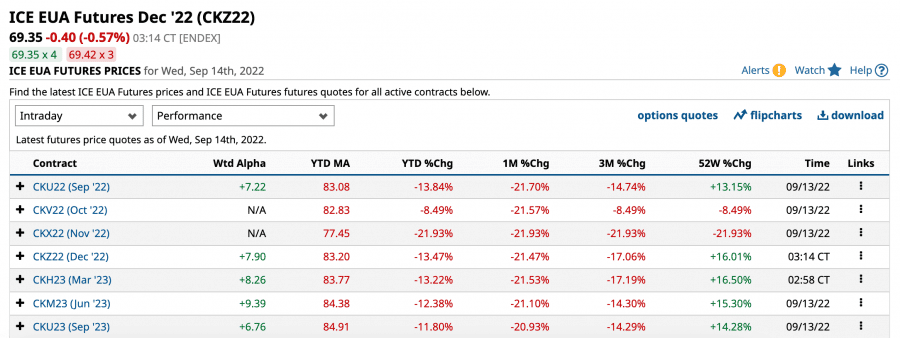
However, many of the best futures brokers also allow individuals to trade EUA futures. Although this approach is focused on capital gain rather than actually making positive change, it does provide a viable option for investors who no longer wish to utilize ‘unethical’ securities.
Why Do People Make Ethical Investments?
Discussions on the best way to invest $100k (or any amount) tend to focus solely on financial gain – yet when investing in ethical assets, there are other benefits to consider. Let’s take a closer look at four of the main ones:
Potential for High Returns
A key reason that people invest in ethical investing funds and stocks is that these securities often provide a pathway toward high returns. The basis for this is that ‘ethical’ industries, such as renewables and biotechnology, are often considered high-growth areas.
What’s more, the pressing need for alternatives to the ‘traditional’ ways of doing things means that ethical investments are often in high demand. This helps drive their price up and creates positive returns for investors.
Helps Make a Positive Impact
Ethical investors also choose these assets since it allows them to make a positive impact indirectly. For example, if an ethical investor buys shares in a company that helps with humanitarian aid, the capital generated by the company can be put to good use.
The same goes for SRI/ESG funds and carbon credits, as the more people invest in these assets, the more publicity they garner. This then creates a snowball effect leading to more capital inflows, which expands their positive impact.
Supports High-Growth Industries
As noted above, many ‘ethical’ industries are considered high-growth areas. For example, a report by McKinsey & Company pointed out that the average share price of a company in the biotechnology sector increased at more than twice the rate of the S&P 500 between January 2020 and January 2021.
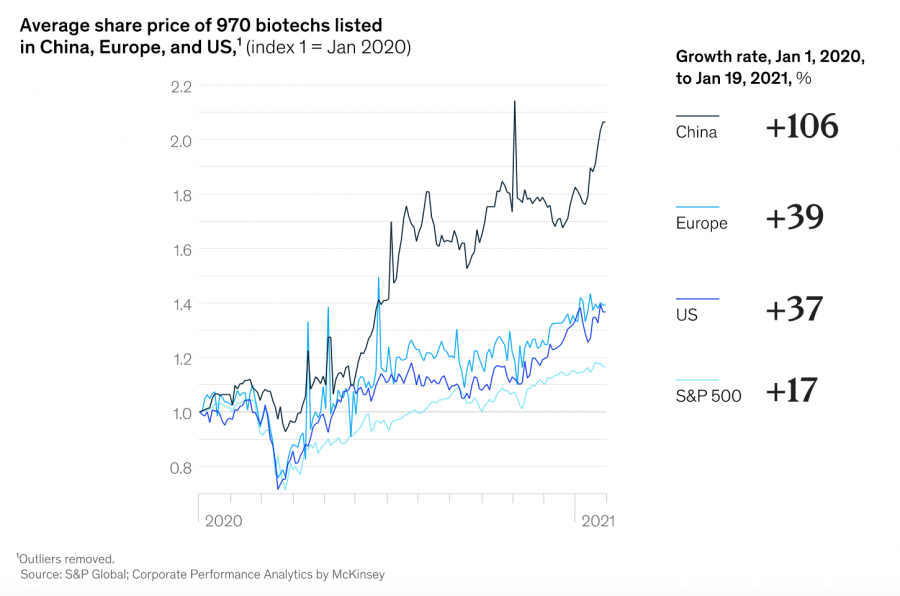
This growth can also be seen in the renewables sector, which has experienced an uptick in demand due to the threat of global warming. On a more micro level, investors continue to buy Tesla stock due to the rapid growth of the EV industry.
Makes ‘Unethical’ Assets Less Popular
Finally, the act of ethical investing has the added side-effect of making ‘unethical’ assets less popular. As more people veer towards socially-responsible investments, those involved in morally-troublesome industries, such as tobacco and firearms firms, become less favoured.
When this trend is extrapolated over a long period, it can really begin to affect these companies’ bottom line – which tends to harm the share price.
How to Find Ethical Investment Assets
Finding ethical assets to invest in is easier than ever, thanks to the explosion of information on the internet over the past two decades. However, detailed below are some popular strategies that investors can use to uncover assets with a high moral standard:
Keep Tabs on Current Affairs

For example, a statement from the leading fashion brand Levi Strauss in March 2022 highlighted that the company would donate more than $300,000 in humanitarian aid for refugees in Eastern Europe. Thus, ethical investors may find the company more appealing, thanks to this announcement.
Use Social Media as a Resource
Investors can also keep track of social media trends to uncover ethical assets. Twitter, Reddit, and YouTube have become great resources for investors, as they provide a quick and easy way to gain insight into various investments.
These platforms are also great for keeping track of a company’s ethical agenda. If there’s a company that an investor is interested in, they can look up the official Twitter page and scan the tweets to uncover any information that points to it being morally responsible.
Look for Technological Innovations
Technological innovations happen all of the time in ethical industries. The electric vehicle sector is just one example of the rate of innovation, which has increased exponentially since Tesla burst onto the scene in 2009.

A recent example of technological innovation is in the case of fuel cell electric vehicles (FCEVs), which are powered by hydrogen. Many believe this technology is even more eco-friendly than electric cars, providing another option for ethical investors.
Be Aware of ‘Greenwashing’
Finally, it’s also essential that ethical investors are aware of ‘greenwashing’. This is the immoral practice of using false claims to make a company appear more virtuous than it actually is.
A famous example of this is the Volkswagen scandal that emerged in 2015. As reported by the BBC, this scandal saw Volkswagen cheat emissions tests to make their cars look more environmentally friendly than they actually were. There are many other examples of similar greenwashing attempts, so investors must conduct thorough research before making an investment decision.
Ethical Investing Strategies
Now that we’ve covered what ethical investing is and the various types of ethical assets, let’s turn our attention to some popular strategies that investors can employ. Detailed below are three well-researched approaches that could help ethical investors make the most of their capital:
Dollar-Cost Average into Ethical Assets
A popular approach for those wondering how to invest during inflation is to dollar-cost average. This approach involves building up a position over time by investing equal amounts at regular intervals – regardless of the underlying price.
Relating this to ethical investing, investors could place $100 per month into an ethical investment fund over a period of five years. This helps remove emotion and essentially ‘automates’ the process, meaning investors don’t have to worry about timing the market.
Avoid Assets in ‘Unethical’ Industries
As mentioned earlier, a key strategy is avoiding assets in unethical industries. This can be a little more challenging for fund and ETF investors, as it means they must thoroughly review all of the holdings to ensure each meets the investor’s ethical criteria.

On a more micro level, investors can also avoid goods and services offered by unethical firms. For example, an investor focused on animal rights can avoid makeup brands that test on animals. If this is extrapolated on a large scale, bypassing the company’s products can significantly impact its bottom line.
Buy-and-Hold an Ethical Stock
Another popular ethical investment strategy is to simply buy-and-hold ethical stocks. As the name implies, this strategy means that investors hold a security over the long term, regardless of price fluctuations or governance changes.
This strategy works best with companies operating in high-growth industries. For example, a report from Fortune Business Insights notes that the global solar power market is expected to value over $293 billion by 2028. Thus, buy-and-hold investors may wish to check out companies that operate in this market.
Brokers Offering Ethical Investments
Those interested in adding ethical investing companies (or other securities) to their portfolio must create an account with a safe and respected trading platform. There is an abundance of platforms to choose from, so investors must complete extensive research to find one that suits their needs.
What is Ethical Investing? – Conclusion
In conclusion, this guide has taken a comprehensive look at ethical investing, discussing what it entails and some examples of assets that are often considered virtuous.
The practice of ethical investing continues to grow in popularity, thanks to the increasing need for environmental and social change. This trend shows no signs of slowing down, meaning ethical investors will continue to see their universe of suitable assets expand as the years go on.
Those looking to begin ethical investing today may wish to consider IMPT. This pioneering carbon credits ecosystem looks to streamline the process of buying, selling, and trading these credits – all using the power of the blockchain. Although the project is still in development, investors can buy IMPT tokens at a discounted rate through the presale phase.
