Learning how to invest in carbon credits is likely to be the next big theme in the financial markets. While they have been available to trade since the 1997 Kyoto protocol only recently has the global carbon futures market exceeded an annual trading volume of $683.9 billion.
With the price of carbon expected to surge over the next few years to reach the 1.5℃ global warming limit agreed upon in the Paris agreement, now could be an interesting time to capitalise on the growth of carbon credit investing.
But what is the best way to invest in carbon credits? In this article, we take a deep dive into the world of carbon credits.
How to Invest in Carbon Credits – 4 Easy Steps
One of the most popular ways to invest in carbon credits is by using IMPT – the innovative blockchain-powered ecosystem that allows seamless trading between individuals and companies. Detailed below are the four steps that investors need to take to acquire $IMPT tokens so that they can exchange them for carbon credits:
- Step 1 – Set Up a Crypto Wallet: Investors must first set up a crypto wallet compatible with ERC-20 tokens. We recommend using MetaMask as it’s free to use and can be set up in minutes.
- Step 2 – Purchase Crypto (Optional): If an investor wishes to buy IMPT using crypto, they’ll have to acquire some beforehand. This can be done using a leading crypto exchange.
- Step 3 – Connect Wallet to Presale: Head to IMPT’s website and click ‘Connect Wallet. Choose the relevant wallet provider (e.g. MetaMask) and follow the instructions to make the link.
- Step 4 – Buy IMPT: In the order box that appears, enter the number of IMPT tokens to be purchased. Once everything has been double-checked, confirm the transaction.
How Does Investing in Carbon Credits Work?
In December 1997, an international agreement on carbon emission reduction was agreed upon among 192 countries and called the Kyoto Protocol. So, how do carbon credits work? The concept allows businesses to sell unneeded carbon credits for the amount of carbon gas allowed to be emitted under the Kyoto Protocol.
But what exactly is carbon credit trading? Businesses that buy carbon credits from other companies are then permitted to release more carbon emissions through their operations. Effectively, this means carbon credits act like a certificate to help with the reduction of a carbon footprint. One carbon credit represents one metric ton of carbon dioxide.
Carbon Credits Explained
Carbon credits are known as a ‘cap and trade’ policy. It’s also one of the ways investors can engage with common impact investing practices.
- The cap is the amount of carbon emissions a company is permitted to produce under the Kyoto Protocol.
- The trade reflects the buying and selling of carbon credits by companies to increase or decrease their permitted carbon emission release.
The concept of carbon credits is in response to climate change and the need to reduce carbon dioxide emissions and greenhouse gas emissions (GHG) which have resulted in global warming.
While much of carbon credit investing has been done by institutional traders on behalf of global corporations and governments, retail investors can also now invest in carbon credits and green investment funds through carbon credit brokers and the carbon instruments they provide.
Research Carbon Credits
A common question among investors is why buy carbon credits? The research on the growth of the carbon credit industry is compelling and one which has attracted many readers interested in socially responsible investing.
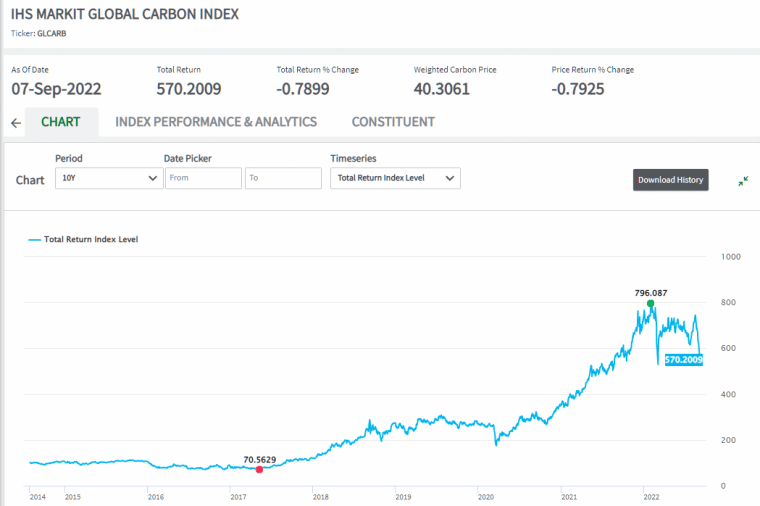
The price of carbon is predicted to reach $147 per ton of CO2
According to research from the IHS Markit institute, the global price of carbon was trading at around $51 per ton of CO2. Analysts believe that in order to achieve the sustainability of the 1.5℃ global warming target, the price of carbon will need to reach $147 per ton of CO2.
In 2022, the Russia-Ukraine conflict caused a global energy crisis. This led to governments moving back to producing energy from carbon-emitting methods. As a result, the price of carbon was trading around $66 by the middle of 2022.
Global carbon futures market volume has surged
The IHS Markit Global Carbon Index tracks four of the world’s largest global carbon futures markets which include:
- European Union Allowances (EUA)
- UK Allowances (UKA)
- California Carbon Allowances (CCA)
- Regional Greenhouse Gas Initiative (RGGI)
Data shows that trading volume has surged across the board in these markets with annual trading volumes exceeding $680 billion. This has also led to a significant increase in price for carbon credits with more growth expected.
China launches its own national emissions trading scheme (ETS)
In 2021, China launched its own national emissions trading scheme (ETS). This made more than 2,000 of the largest carbon emitters to be accountable for their emissions. While the ETS has only just launched it already accounts for around 40% of China’s total CO2 emissions.
While activity has been limited with only 412.05 million tones of allowances being traded in 2021, it is expected to grow significantly. In the first year of the EU’s ETS launch, only 321 million allowances were traded. By 2021, this had grown to more than 12 billion giving significant potential for China’s ETS launch.
How to Find the Best Carbon Credits in 2025
Investors have a variety of options when investing in the best carbon credits ETFs. This includes investing directly in carbon emission futures contracts, or carbon ETFs which invest in multiple carbon offset companies or by finding individual businesses that are focused on carbon offsetting.
Invest in carbon offsetting organizations
In order to find high-quality carbon offset programs or businesses, it is important to make sure their projects have been independently verified. Some of the most well-known voluntary carbon market certification standards include the Climate Action Reserve and American Carbon Registry.
Investors may also consider where the project is located to make sure it can have the most amount of impact on carbon reduction. For example, the Carbonfund.org Foundation has four projects located in the Amazon rainforest called the Reducing Emissions from Deforestation and Forest Degradation (REDD+) project.
However, most of the carbon offsetting organizations are not publicly traded companies that are easy for investors to access. This also means they’re not available for fund managers focused on ESG principles.
Invest in carbon credit futures contracts
Alternatively, investors can invest in carbon direct directly by investing in carbon credit futures contracts. These products are more easily accessible as they trade on futures exchanges such as the Intercontinental Exchange (ICE).
When choosing which carbon credit futures contract to trade on there are some factors to take into consideration, such as:
- How accessible is the market?
- What is the minimum amount to trade the market?
- Is there enough volume to transact easily?
Below is a list of the best five carbon credits to watch right now.
6 Best Carbon Credits to Watch Right Now
Carbon credits allow investors to speculate on the price direction for the demand to offset credits by larger institutions. Investors can invest directly in the carbon credit futures contract or choose a carbon ETF for a more diversified approach.
1. IMPT – Blockchain Project Supporting Carbon Offset Programs
When assessing how to buy carbon credits in the UK, it is worth exploring innovative blockchain projects related to this space. In this regard, we found that IMPT is a project that has plenty to offer for socially responsible investors in the UK.
According to the IMPT whitepaper, this is an emerging blockchain project that offers tokenized versions of carbon credits. It allows investors and companies to support a curated selection of carbon offset programs. The project has launched its own native digital token, which allows investors to buy and sell carbon credits via the IMPT marketplace.
These carbon credits are offered in the form of NFTs. Companies can choose to burn them in order to offset their own carbon emissions, whereas investors can hold on to their tokens for speculative purposes.
Given the rising demand for carbon credits, there is every possibility that IMPT NFTs will be worth more in the coming years.
The project is still in its early stages of development and is in the process of adding credible carbon offset programs to its catalog. In the meanwhile, early investors can gain access to IMPT digital tokens via a presale launch.
The first stage of the presale is already over, with the project successfully selling 90 million tokens. Nonetheless, in the next stage of the public presale, a new batch of IMPT digital tokens will be available for $0.06 each – starting from October 1st, 2022.

Crucially, IMPT allows investors to contribute to a carbon offset program directly by funding the project. Moreover, the project plans to add more features to its marketplace – such as a shopping platform and social network, offering token holders several ways to earn passive income.
Investors wanting to get the latest information about this project can stay up to date by subscribing to the IMPT Telegram channel.
2. KraneShares Global Carbon Strategy ETF (KRBN)
The KraneShares Global Carbon Strategy exchange traded fund aims to track the performance of the IHS Markit Global Carbon Index. This sustainable investing fund provides a way tracks the cap and trade carbon allowances by measuring the performance of the most traded carbon credit futures contracts.
The fund trades on the New York Stock Exchange and has net assets of $826,180,951. Since its inception in 2020, the fund has performed well. In fact, at the beginning of 2021, the fund traded at around $25 before surging to a record high of $55 by early 2022.
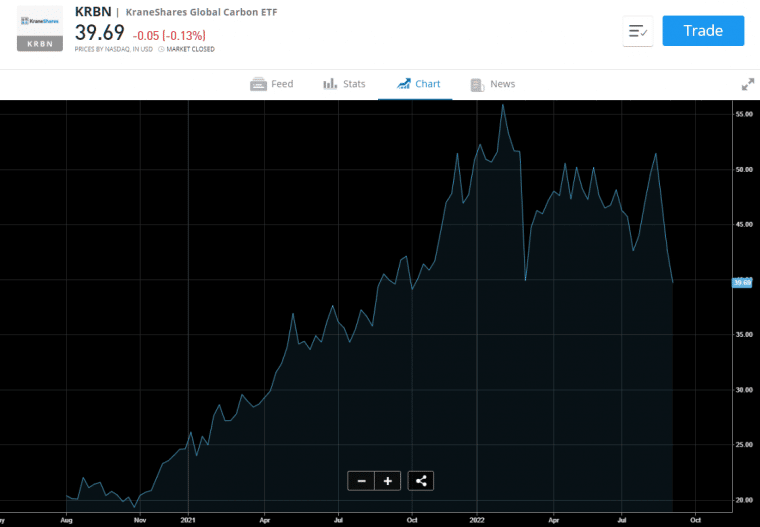
In 2022, the fund has trended lower in line with a global stock market sell-off. However, this could present an interesting opportunity for those wishing to gain exposure to sustainable investing via carbon credit investment funds.
3. European Union Allowance (EUA) Futures Contracts
The European Union Allowance (EUA) is the official name for emission allowances in Europe defined by the Kyoto Protocol. One EUA gives the holder permission to emit one ton of carbon dioxide.
The European Union issues new EUAs every year on 28 February. EUA futures include a day future contract and a quarterly futures contract for 2021 – 2027. The contracts trade in euros (EUR).
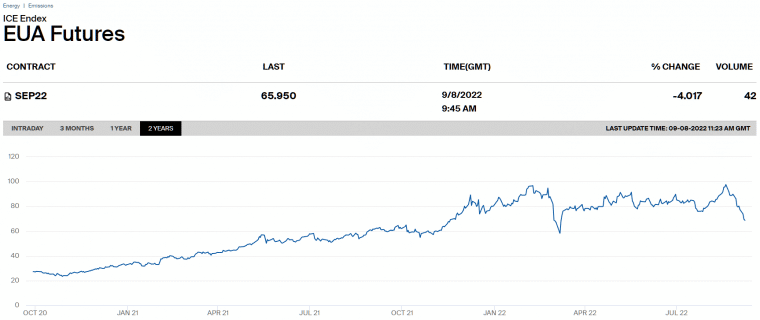
Over the past few years, the price of a EUA carbon credit futures contract has performed well. At the start of 2021, the EUA price was trading at EUR 33.85. By the start of 2022, the price of the futures contract had surged to EUR 83.88.
While there had been a steady price rise from 2020 to 2022, the global energy crisis affected the carbon credit market. The price of the EUA went as low as EUR 58.19 in March but then rallied to an all-time high of EUR 95.72 by August.
4. UK Allowance (UKA) Futures Contract
The UKA futures contract only launched in May 2021 but has already had 775 million tonnes of carbon dioxide gas traded through the InterContinental Exchange (ICE). Each lot of the UKA futures contract is the equivalent to 1,000 UK allowances where each allowance is the equivalent to emit one ton of carbon dioxide gas.
In October 2022, ICE plan to launch UKA Options which will provide the ability to trade options on the futures contract that will be listed up to March 2024. The UKA contracts are traded in GBP.
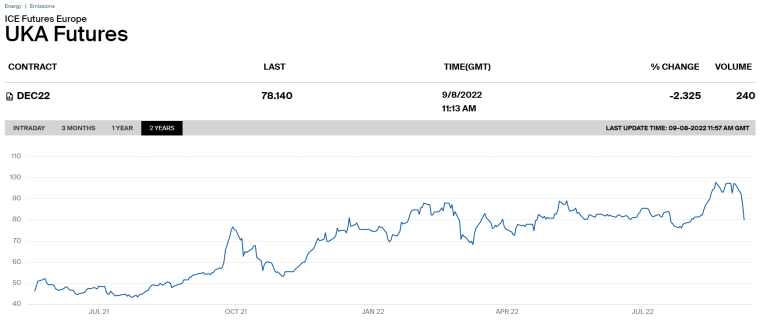
Since the UKA’s inception in May 2021, the price of the futures contract has grown well. After launching at a price of GBP 46.25, the UKA contract rose to a record high of GBP 97.75 by August 2022.
The UK government’s plan to achieve net zero forced many companies into offsetting their carbon emissions, increasing the demand for the UKA contract. While the price has retreated from its all-time high the overall uptrend is still intact.
5. California Carbon Allowance (CCA) Futures Contract
The California Carbon Allowance (CCA) cap and trade program began in 2012 and now covers 80% of the state’s green house gas emissions. Since 2014, the program also covers the emissions of Quebec.
The CCA futures contract has a volume of around $1.5 billion per month and is one of the strongest carbon performers. This is because it has – so far – had a low correlation to other traditional asset classes, providing the potential for portfolio diversification among investors.
The California Carbon Allowance futures contract has multiple trading venues which include the Intercontinental Exchange (ICE), the Chicago Mercantile Exchange (CME) and the New York Mercantile Exchange (NYMEX).
There are contracts available for most months across 2021, 2022 and 2023.
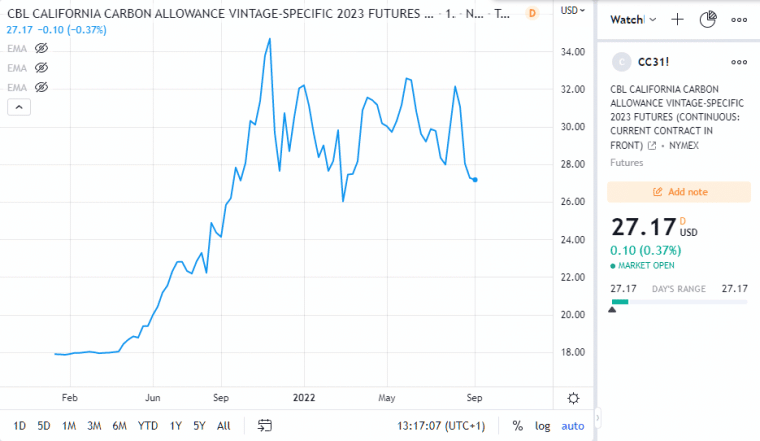
The California Carbon Allowance futures contract for 2023 trading on NYMEX under the symbol CBL, began trading in February 2021 at a price level of USD 18. Since then, the price of the futures contract rose to an all-time high of USD 34.70 in November 2021. The price of the futures contract now trades around USD 27.
6. Regional Greenhouse Gas Initiative (RGGI) Futures Contract
The Regional Greenhouse Gas Initiative (RGGI) is a cooperative of states to cap and reduce CO2 emissions from the power sector. It was one of the first market-based can and trade cooperatives in the United States.
The RGGI covers the states of Connecticut, Delaware, Maine, Maryland, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, New Jersey, New York, Pennsylvania, Rhode Island, Vermont, and Virginia. The RGGI is priced in US dollars and has contracts available to trade on via ICE, CME and NYMEX.
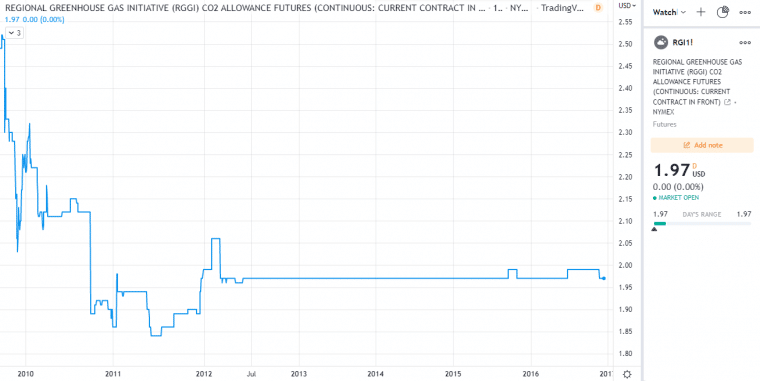
The RGGI has been one of the least effective carbon credits, compared to the EUA, UKA and CCA. The cooperative is currently undergoing a thorough review and evaluation with a report due at the end of 2022.
Are Carbon Credits a Good Investment?
There is clear evidence to suggest that – in the long term – carbon credits can be a good investment. Most carbon credit contracts such as the EUA, UK and CCA experienced strong price growth up until the energy crisis of 2022.
Once the volatility of the energy market settles, the uptrend in those carbon credits is likely to resume. Having China on board and creating its own emissions trading scheme will help other carbon credits to become more liquid and accessible.
Another consideration is that they are not as heavily traded by retail or institutional speculators so may be less liquid than other markets. This leaves the contracts open to potential big gaps from when the market closes and opens.
There is also a risk that regulations change making the contract redundant. Investors who are happy with this elevated risk may find carbon credits an interesting proposition.
Carbon Credits vs Presale Cryptos – Which is the Better Investment in 2025?

Another option investors may consider for significant price growth in a much shorter period of time and on more liquid markets are presale cryptocurrencies. This is the option of investing in cryptocurrencies before they go public, similar to investing in a company’s IPO before it becomes public.
For example, the new meme coin Tamadoge has already had its $2 million beta sale round completely sold out highlighting the demand for investing in the coin before it goes public. Currently, there are only 25% of tokens available in the limited-time presale.
Tamadoge (TAMA) is a deflationary token with a maximum supply of 2 billion tokens. 5% of all coins spent on the ecosystem are burnt to help drive its price higher by limiting supply. Tokens can be used to purchase Tamadoge pet NFTs and enter virtual competitions to earn rewards. The Tamadoge metaverse makes it one of the best utility tokens around.
TAMA is a play-to-earn cryptocurrency that will be the gateway to the Tamaverse. Unlike many other crypto projects, Tamadoge is 100% secure as its code is fully audited by Solid Proof. Coinsniper has fully verified the team to ensure project security and anti-rug pull measures.
For investors fortunate enough to invest in the presale of Tamadoge, there are many milestones that could lead to significant price increases. For example, in Q4 2022 there are plans to list the coin on some major centralized exchanges (CEX) which will likely drive demand for Tamadoge from crypto investors who didn’t invest in the presale.
Investing in crypto presales that can offer 10x growth in a shorter period of time could be something to consider for this year.
Conclusion
Carbon credit investing involves trying to capitalize on the increase in demand for carbon emissions offset by large corporations. While carbon credit contracts exhibited strong growth over the past few years, the energy crisis of 2022 has led to all of them retreating from record highs.
Those looking to invest in carbon credits today may wish to consider IMPT. As mentioned earlier, this carbon credits ecosystem allows individuals to acquire credits through everyday shopping activities. Since IMPT is still in its presale phase, investors can buy tokens for just $0.018 at the time of writing – the lowest price they’ll be made available.
