Carbon credits are permits that authorize a business to emit a certain amount of CO2 or other greenhouse gases into the environment. They’re also recognized as tradable assets in the financial markets – allowing investors to buy and sell them for speculative purposes.
This beginner’s guide explains how to buy carbon credits in the UK via a regulated broker. We also offer some insight into how carbon credits markets operate in the UK and explore how investors can trade this asset in a risk-averse manner.
How to Buy Carbon Credits in the UK – 4 Easy Steps
In the UK, carbon credits trading is facilitated by governmental authorities under the Emissions Trading Scheme. However, for the average investor, the more seamless option is to gain exposure to carbon credits via ETFs, stocks, or other accessible trading instruments.
Irrespective of the chosen asset, investors should first have a trading account.
Follow the steps below to learn how to invest in carbon credits in the UK via a regulated broker.
- Step 1: Open an account with a regulated broker – The first step is to choose a broker that is regulated by the FCA, the financial watchdog in the UK. Next, visit the broker’s website to open a trading account. For this, investors will need to provide some personal information and complete a quick KYC procedure.
- Step 2: Deposit funds – After creating the account, investors will then need to ensure that it is sufficiently funded. Depending on the chosen broker, funding can be facilitated via a bank transfer, credit/debit card, or e-wallet.
- Step 3: Choose a carbon credit instrument – Next, search for the specific carbon credit market on the platform. Once the right asset is found, click on it to proceed.
- Step 4: Buy carbon credits in the UK – Finally, place an order to ‘buy’ the chosen carbon credits instrument. Investors will have to specify the amount they wish to invest in the chosen asset.
After confirming the order, the broker will carry out the trade on the investor’s behalf. The value of the carbon credits investment can be monitored via the brokerage account portfolio.
Carbon Credits Explained
Are carbon credits becoming the best investment in the UK in 2025? Decades ago, British economist Arthur Cecil Pigou suggested a way for companies to pay for the damage they do to the environment. He proposed that the government should fine companies in the form of taxes and fees – an idea that failed to gain traction at the time.
However, in years to come, countries came up with another way to penalize companies that emit greenhouse gases – via carbon credits. In a nutshell, carbon credits are permits that allow companies to emit a certain amount of greenhouse gases. Each carbon credit represents one tonne of carbon dioxide or other relevant greenhouse gas.
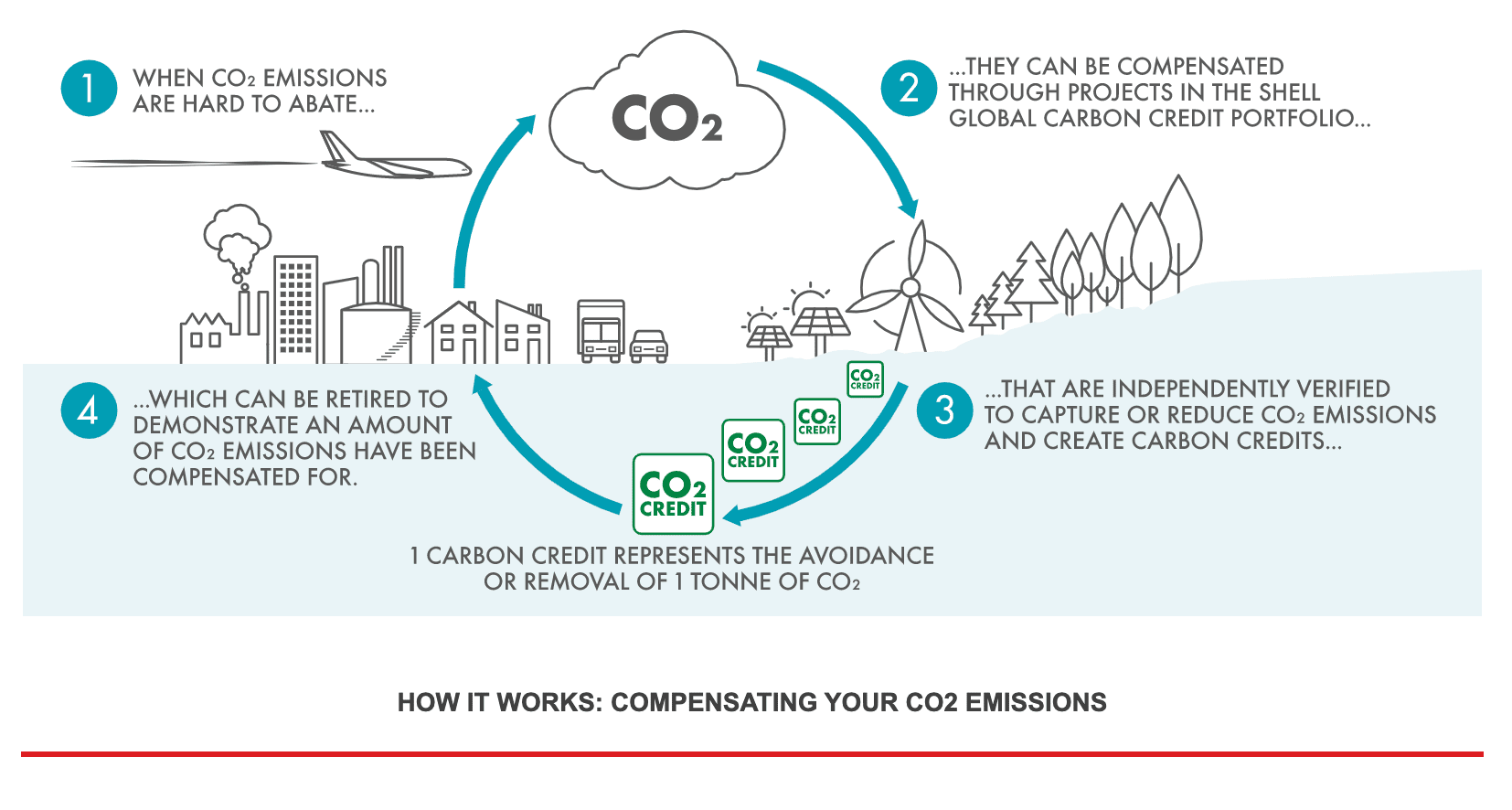
Most countries provide businesses with an allowance or credit that enables them to emit gases. In the UK, businesses can acquire this initial allocation of carbon credits free of charge. Companies that subsequently lower their emissions can sell their surplus carbon credits to other companies.
Similarly, businesses that require more allowances can also purchase them from others – thereby creating a commodity market for carbon credits. Did you know that carbon credits have become one of the best ways to invest £5,000 in the UK according to traders?
What are Carbon Credits?
Countries such as the UK have specific rules about carbon offset credits. For this purpose, the UK has set up an ETS (Emissions Trading Scheme) that works on the ‘cap and trade’ principle.
This scheme has a set of compliance guidelines that govern operational functions such as issuing and ensuing carbon credits.
- To buy or sell carbon credits via this compliance market, companies and individuals must obtain a GHG emissions permit and subsequently create a UK ETS trading account.
- Through this account, operators can trade their allowances available via their Operator Holding Accounts (OHA) and Aircraft Operator Holding Accounts (AOHA).
- Companies that have excess credits can sell their excess allowance at auction or trade them with other participants.
In addition to the compliance sector, investors can also find voluntary markets for carbon credits.
- In this space, any company can sell carbon offsets they produce to others.
- Sellers are often firms that have implemented carbon reduction projects in accordance with the standard set by the UK government.
- These could be companies with strong carbon offset programs or individuals such as farmers.
- In the voluntary market, individuals can also purchase carbon credits as an investment, selling them later in the hope that a profit can be realized.
All that being said, voluntary markets are not regulated by the government. As such, retail clients looking to engage in carbon credit investing will do so via a licensed broker to ensure that the position is executed in a safe environment.
How do Carbon Credits Work?
At first glance, the process of trading carbon credits directly can be complicated, and most pertinently – this marketplace is often not accessible to retail clients.
Moreover, individuals need to register with the UK ETS service, request a trading account, and then undergo a lengthy verification process. This makes it incredibly difficult for the average investor to gain exposure to the UK carbon credits market.
As a result, investors might consider alternative ways to invest in carbon credits. Examples of asset classes that are directly or indirectly related to the carbon credits sector include everything from stocks and ETFs to CFDs and digital tokens.
Let us consider how to buy carbon credits in the UK through the aforementioned financial instruments.
Carbon Credits Tokens
In addition to carbon credits schemes run by the government, there are several other private organizations that are working towards offsetting greenhouse gas emissions.
And some of these projects have found an innovative way to sell their carbon credits to the public – via digital assets.
- This means that investors can buy or sell carbon credits in the form of tokens that operate on the blockchain.
- Similarly, companies that do not have sufficient carbon credits can also purchase these digital tokens in order to offset their emissions.
- Additionally, there are also crypto-centric projects that issue carbon credits represented as NFTs.
- Investors can hold on to these assets, and if the demand for carbon credits is to increase in the financial market, so will the value of these digital assets – at least in theory.
All in all, investing in carbon credits via digital tokens might be one of the easiest ways to gain access to this market.
However, before choosing cryptocurrencies and other digital assets for carbon credits trading, be sure to research the respective project in great detail.
It is essential to read the whitepaper of the project in order to understand how the platform is able to sell carbon credits.
For instance, find out whether the platform supports any reliable carbon offset programs or any other NGO organizations and try to verify the credibility of any claims made.
Legitimate blockchain platforms offer in-depth information about the carbon offset programs they feature.
Carbon Commodities
Just like oil and natural gas, carbon is also considered a commodity in the financial market. In the grander scheme of things, carbon is, however, a relatively new asset in this trading industry.
In the 1997 Kyoto Protocol, countries came together and set targets for reducing carbon emissions.
Under Article 17 of this protocol, countries that had extra carbon emissions units were permitted to sell their excess to other nations that have exceeded their targets. This created a new ‘carbon market’.
Investors can now participate in carbon credits investing via CFDs, which are financial instruments that track the value of carbon. This allows investors to speculate on the bullish and bearish price of carbon.
Relevant Stocks
When assessing how to buy carbon credits in the UK, investors can also consider gaining exposure to this market indirectly.
For instance, instead of buying carbon credits directly, it is possible to put money into companies that are related to this field.
For example:
- Companies such as Tesla receive emissions credits from regulatory authorities. Since Tesla is already a low-emission company, it sells its carbon credits to other firms – thus this offers an extra source of revenue.
- Similarly, companies such as Microsoft have a strong carbon credits program that it invests in, in order to offset its emissions.
- With this in mind, investors can purchase stocks of such companies, with the view of gaining indirect exposure to the ever-growing carbon credits market.
That being said, investing in stocks simply because they have a solid carbon offset program might not be the only way to approach this space. After all, there isn’t a correlation between a company’s carbon credit program and its stock price action.
Nonetheless, investors should learn about how to buy shares in the UK after analyzing the company’s growth prospects as well as its financial standing.
Carbon Credits Futures
In the context of trading, futures are a type of financial derivate that enables investors to buy or sell an asset at a set price on a specific date.
Futures can track any asset – and investors will be able to find those that are linked to carbon credits units too.

To give an example, the European Union and California carbon allowances are traded in the form of futures in the financial market.
Although investors of all shapes and sizes can trade futures, this marketplace can be complex.
Carbon Credits ETFs
Perhaps the most common way to make a carbon credits investment is via an ETF.
Today, investors can find ETFs that track various assets related to the carbon credits sector. The underlying assets could be related to index funds, stocks, or even futures.
Moreover, some ETFs track multiple assets – which facilitates diversification. However, this will ultimately come down to the chosen carbon credits market.
For instance:
- The KraneShares Global Carbon Strategy ETF tracks the price of carbon credits in several markets, including the UK, EU, and California.
- On the other hand, the KraneShares California Carbon Allowance Strategy ETF offers exposure only to Californian carbon allowances – which increases the risk.
- There are also ETFs that track low carbon companies such as Tesla, Microsoft, and others. These allow investors to diversify their funds into multiple markets and sectors. This can help reduce the portfolio’s exposure to a single market.
- In addition to this, some ETFs, such as the Horizons Carbon Credits, are linked to futures contracts.
All in all, those wondering how to find the best carbon credits ETFs will be pleased to know that there are plenty of options available in the market.
Why Invest in Carbon Credits?
Before setting out to trade carbon credits, investors should consider the advantages and potential setbacks of this market.
Needless to say, there are indeed some benefits to investing in carbon credits in the UK, such as:
- Potential to make gains – Ultimately, from an investment perspective, the purpose of carbon credits trading is to make a profit. Trading carbon credits can indeed be lucrative, especially since countries continue to find ways to reduce the supply of allowances each year. This means that the demand for carbon credits might increase in the future, creating the potential for an attractive return. Additionally, those looking for the best way to invest £20k in the UK could consider researching carbon credits as the climate crisis continues to make headlines.
- Low correlation to equity markets – It is observed that carbon credits futures have a low correlation with the border equity market. This could provide a hedge and allow investors to diversify their portfolio.
- Plenty of investment choices – Investors in the UK have access to many different financial instruments that track the value of carbon credits. As we discussed above, investors can secure direct exposure to this market via futures or carbon commodities. Alternatively, it is also possible to invest in low-emission companies that generate revenue by selling carbon credits.
- Sustainable investment: At its core, carbon credit investments offer a direct approach to capitalize on the shift to a low emission economy. In this sense, investors buying carbon credits are helping to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and keep the planet in a stable climate.
Crucially, carbon credits trading offers an alternative way to invest capital in the financial markets. And as such, this marketplace enables investors to make a positive impact on the world while targeting monetary returns in the process.
Risks of Investing in Carbon Credits
When assessing how to buy carbon credits in the UK – investors should also be aware of the risks.
The carbon credits market is often impacted by governmental policies such as allowance allocation, compliance guidelines, and approval rules for emission reductions. These factors can influence the price of carbon credits in the market.
- Similarly, factors such as the economic landscape, the development curve of low-carbon industries, and the degree of air pollution can also affect how carbon credits are priced.
- In simple terms, there are several aspects an investor should consider when speculating on the price of carbon credits.
Additionally, since carbon credits trading in the UK is still a niche market, there is no abundant data available to track the performance history.
Therefore, investors in the UK should make sure they understand how this market works before risking any money.
Most Popular Carbon Credit Investments in the UK
Wondering how to buy carbon credits in the UK?
In this section, we consider a selection of carbon credit markets that investors can access via an online broker.
1. KraneShares Global Carbon Strategy ETF – Popular Fund That Tracks Carbon Credits Futures
One of the most popular ways to gain direct exposure to the carbon credits market is via allowance futures. For instance, countries across the world have their own carbon credits units – such as the United Kingdom Allowances (UKA), the European Union Allowances (EUA), and the California Carbon Allowances (CCA).
These are traded in the compliance market in the form of futures. The KraneShares Global Carbon Strategy ETF is a fund that tracks the prices of such futures. This ETF is linked to the IHS Markit’s Global Carbon Index – which follows carbon credits futures issued by the UK, EU, and North America.
In other words, this ETF allows investors to gain access to multiple carbon credits markets across different countries. This brings down the overall risk for the investors in diversification terms. Moreover, the KraneShares Global Carbon Strategy ETF has also performed well since its inception. The fund was first launched in July 2020 and at that time – its price was around $20.
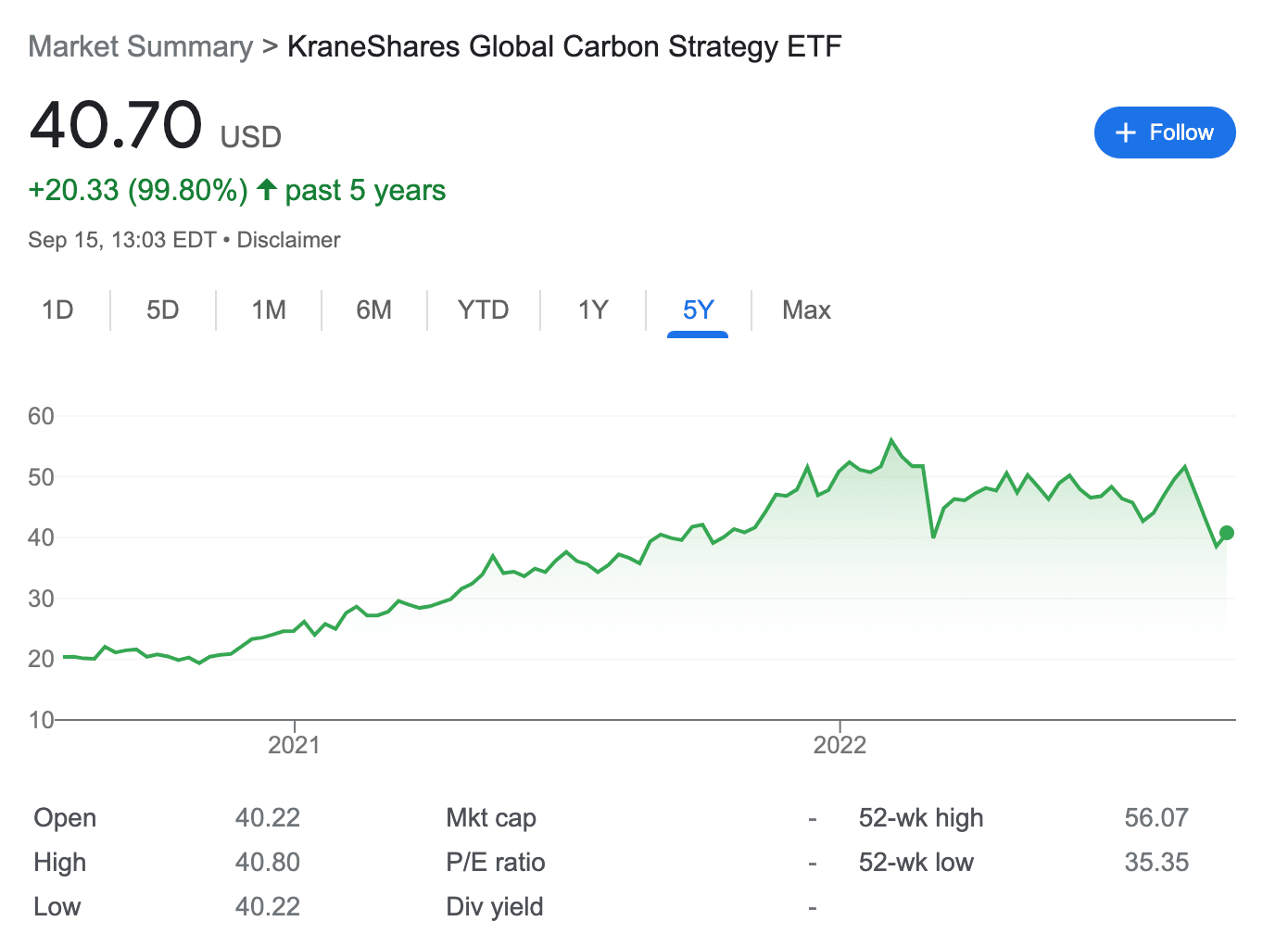
After reaching an all-time high of $56 in January 2022, the fund experienced extreme volatility in the market. Nevertheless, the price has since managed to bounce back. As of writing, this fund is up over 100% since its inception.
Those interested in socially responsible investing might wish to consider going long on this ETF. Since this fund tracks only futures, the ETF has historically demonstrated a low correlation to the equity market. This means that the performance of the broader stock market should not have a significant impact on the value of this ETF.
As such, if investors are worried about their portfolio’s exposure to companies with large carbon footprints, this ETF might help to mitigate this risk. Moreover, the KraneShares Global Carbon Strategy ETF is also well positioned to benefit from the tightening of carbon emissions regulation worldwide.
2. Tesla – Leading Seller of Carbon Credits
Tesla is one of the most popular tech stocks among socially responsible investors. This company sells eclectic cars, and as such, it is a key player in the world’s transition to sustainable energy. Moreover, this means that the carbon credits allowance received by Tesla is of no use to the company.
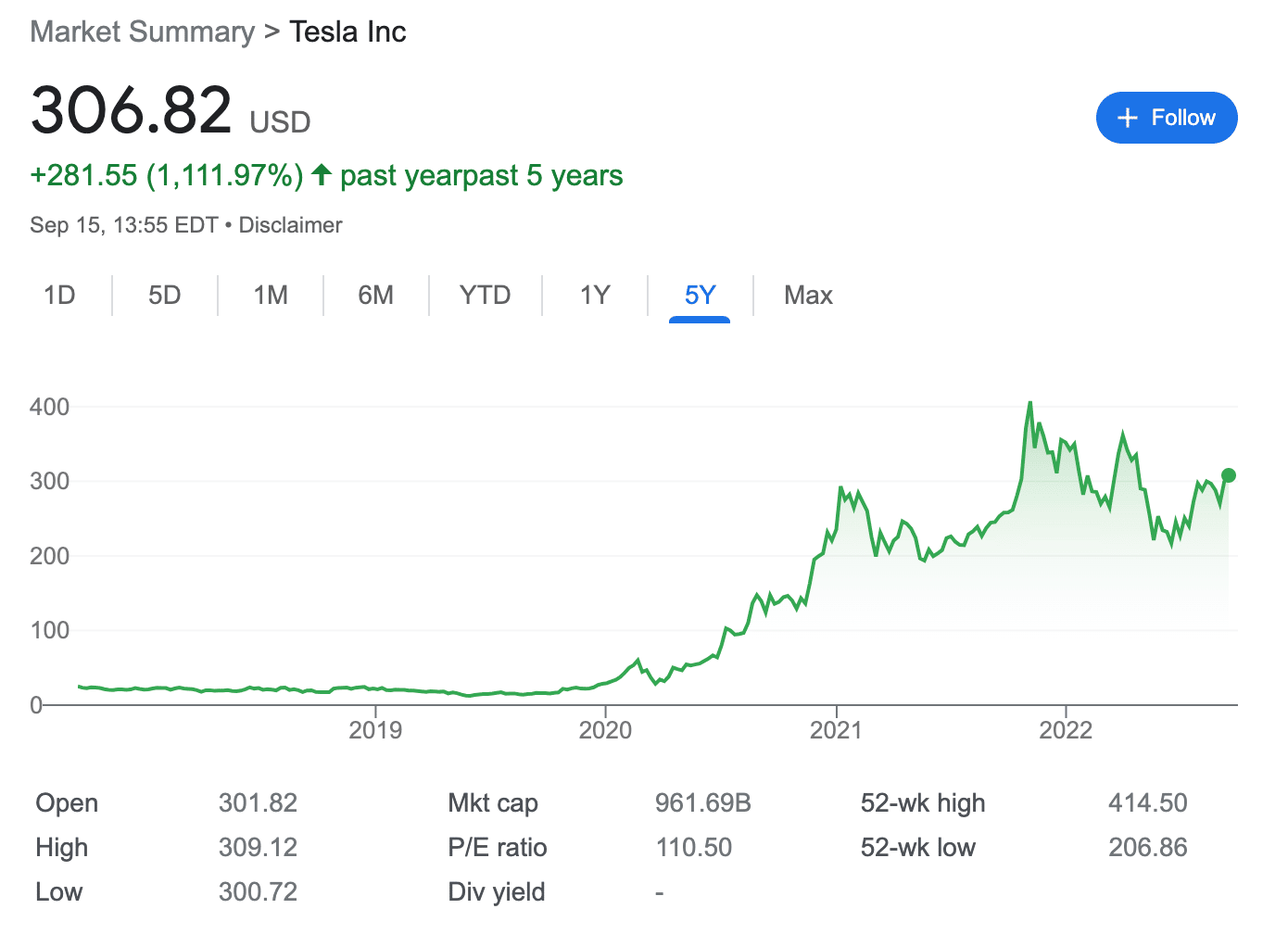
Instead, Tesla sells them at a profit to other companies that can’t meet their regulatory requirements. In the second quarter of 2022, Tesla raked in $344 million by selling regulatory carbon credits. The company primarily sells its carbon credits to other popular automakers – such as General Motors and Fiat Chrysler Automobiles.
With governments tightening up legislation to decarbonize the automotive industry, Tesla is well-positioned to continue generating revenue in this marketplace. In fact, as per current trends, this can help amplify Tesla carbon credits sales even further in the coming years.
However, it is also important to remember that many traditional automakers have already launched their own zero-emission vehicle programs. This means that other automakers might rely less on Tesla for their carbon credits. When it comes to popular stocks such as Tesla, the leading brokers also offer stock trading apps UK which allow users to buy and sell stocks via their mobile devices at any time.
Nevertheless, Tesla remains one of the top-performing stocks on Wall Street since its 2010 IPO. In the last five years alone, the value of Tesla stock has increased by over 1,100%. And early investors who bought Tesla shares at the time of its IPO in 2010 are now looking at gains of over 23,000%.
3. Carbon Emissions – Trade Carbon as a Commodity
As we noted above, it is also possible to trade carbon emissions as a commodity in the UK. Some brokers allow their users to gain access to carbon emissions via derivative trading instruments such as CFDs. To elaborate, CFDs are financial instruments that track the price of an underlying asset, which is carbon emissions in this case.
Since CFDs only represent the value of the commodity, investors can speculate on both the rising and falling prices of carbon emissions.
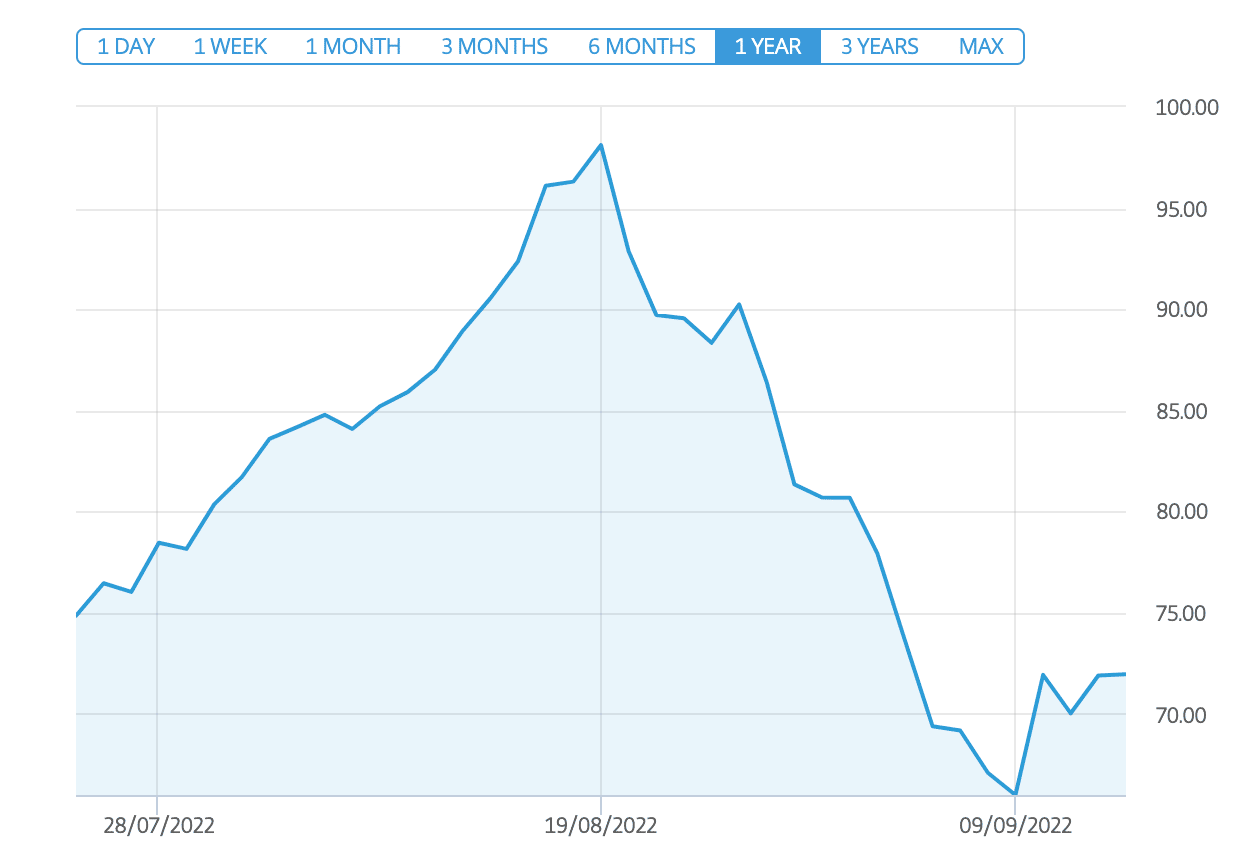
This point is particularly important because the price of carbon emission is tied not only to climate change but also to economic factors. For instance, if global warming gets worse, there will likely be increased demand for carbon credits, which can drive up the price of this commodity.
On the other hand, economic factors such as war can lead to carbon credits declining in value. The Russian-Ukraine war and its economic impact on the EU is a prime example of this. Investors are selling their EUAs to limit their exposure to the European market – which has led to the price of EU carbon permits falling significantly.
This is a crucial point that investors should consider before trading carbon emissions as a commodity. With that said, this is why CFDs are used to speculate on both rising and falling carbon credits prices. Moreover, as noted earlier, UK traders can access carbon emission CFDs with leverage of up 1:5.
4. Shell – Conventional Oil Company With a Strong Carbon Offset Program
Shell began its business in oil transportation in the 1880s. However, as per global shifts, Shell has since shifted its focus toward greener energy.
In 2021, the company declared that it would begin cutting its oil production by 2% every year. It aims to slash its petrol and diesel production by 55% by 2030. It also has plans to expand its business into the clean energy sector by investing in different carbon capture technologies.
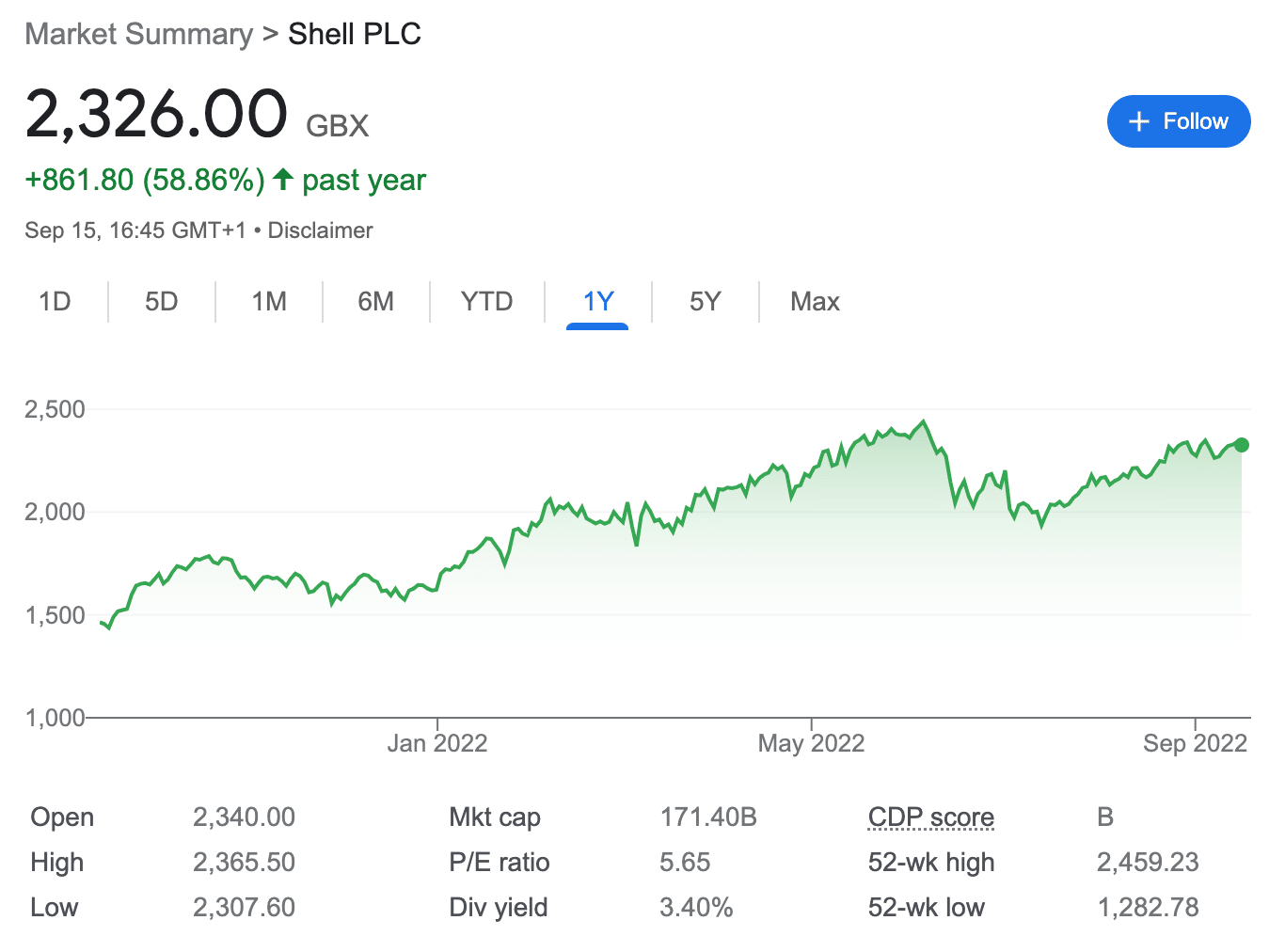
According to Shell, this includes investment into projects aimed at restoring ecosystems such as forests. This allows the company to offset its emissions. In this regard, Shell is one of the largest companies globally to be working towards a low-carbon structure – which might make it an attractive choice for sustainable investors.
On top of this, Shell stock has performed well in recent years. In fact, the stock has gained nearly 60% in value in the past twelve months alone. Shell is also one of the few dividend stocks in this market with a strong carbon offset program. It offers a running dividend yield of just over 3.5% at the time of writing.
5. iPath Series B Carbon – Invest in Carbon Credits via Exchange Traded Notes
Another carbon credits investment option to consider is the iPath Series B Carbon ETN. This is an exchange-traded note, which is slightly different from an ETF. While ETFs represent a stake in an underlying commodity, ETNs are issued as senior debt notes by a financial institution.
This particular ETN is a structured product offered by Barclays Bank. Its performance is linked to that of the Barclays Global Carbon II TR USD Index. This index is comprised of allocations in carbon credit futures contracts that trade on the ICE Futures Europe exchange.
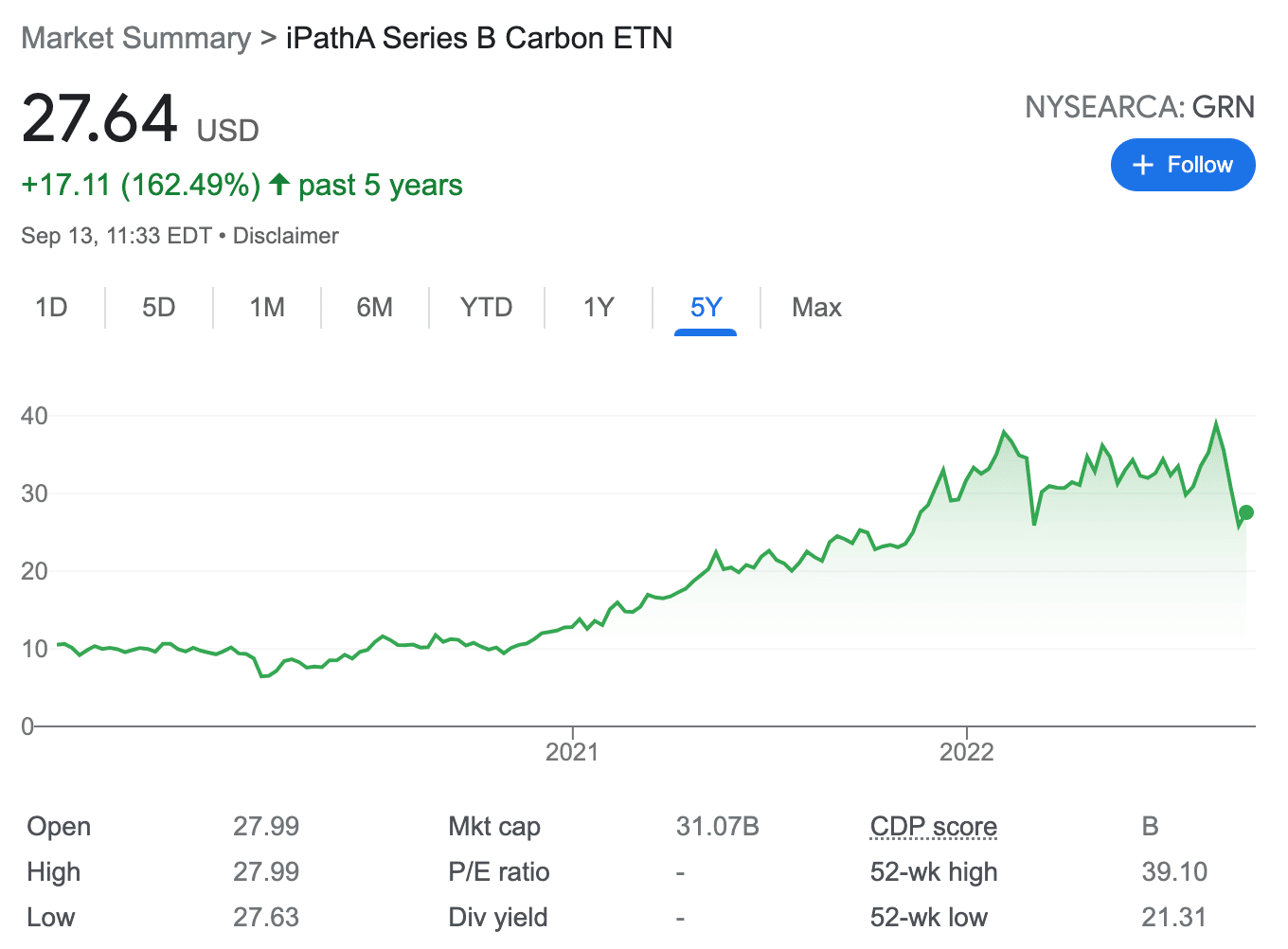
At the time of writing, this only includes the European carbon allowance. As such, when buying this ETN, investors will be over-exposed to a single carbon credits market, which can increase the risk. This ETN was launched in September 2019. Over the past two years, it has increased by more than 160% in value.
How to Invest in Carbon Credits in the UK – Tutorial
After deciding which carbon credits marketplace to invest in, the next step is to complete the investment with a regulated broker.
Below, we break down the process of how to buy carbon credits in the UK into just four simple steps.
Step 1: Open a Brokerage Account
Investors will first need to set up a trading account with an online broker. When choosing a broker, look for one that supports different carbon credit asset classes – such as stocks, ETFs, futures, and commodities.
- This way, investors will have multiple options for investing in carbon credits in the UK.
- Moreover, the chosen broker should be FCA-regulated and facilitate cost-effective trading.
- After deciding on a broker, head over to the provider’s website and open an account.
- This entails providing some personal information such as a full name, address, and contact details.
Investors will also be required to provide documentation – such as a passport/driver’s license and a utility bill to verify the information they have provided. Nonetheless, on most platforms, the end-to-end registration process takes only a few minutes.
Step 2: Deposit Funds
Investors should make sure that their brokerage account is funded sufficiently. Each broker will have its own minimum deposit requirements.
Depending on the broker, funding can be done via a debit/credit card, bank transfer, and oftentimes – an e-wallet like PayPal.
Step 3: Find Carbon Credits Instrument
Assuming that the investor knows which carbon credit asset to invest in, they can make use of the search feature to find the respective market.
Alternatively, the asset might also be listed under the specific market. For instance, those looking to buy the KraneShares Global Carbon Strategy will find the fund under the ÉTF section.
Step 4: Buy Carbon Credits Instrument
The last step is to place a ‘buy order’ for the chosen asset. This requires the user to specify the amount they wish to invest in the chosen carbon credit market.
Then, confirm the order for the broker to execute it. Once the trade is entered, the carbon credit asset can be found in the investor’s brokerage portfolio.
How to Sell Carbon Credits in the UK
After purchasing carbon credit instruments in the UK, investors can monitor the performance of the asset via their brokerage account.
The value of the investment might meet the price target after a while – and if this happens, individuals can sell the asset to lock in a profit.
That being said, bear in mind that the value of the carbon credit investment can also go down, which will lead to a financial loss if the investor cashes out.
- Regardless, investors in the UK can cash out their carbon credits investment via the same FCA-regulated broker they used to make the initial purchase.
- To do this, sign in to the brokerage account and locate the specific carbon credits investment.
- Next, place a ‘sell order’ to close the position.
The broker will execute the order, and the proceeds will be added to the user’s account balance.
How are Carbon Credits Taxed in the UK?
In the UK, there are no specific tax rules that pertain specifically to carbon credits trading.
Therefore, the tax on carbon credits investments is determined by applying general rules.
For instance:
- The purchase of carbon credits under mandatory rules is deductible.
- To get a deduction on a carbon credit purchase made via the voluntary market, investors will need to demonstrate and document the business reasoning for this expenditure.
- Otherwise, income derived from trading carbon credits is subject to capital gains tax in the usual way.
- In the UK, investors will have to pay between 10% to 20% tax on any capital gains made from trading carbon offset credits.
- With that said, all UK residents get an annual capital gains tax allowance of £12,300.
Ultimately, investors that are considering buying or selling carbon credits in the UK should consult a professional that can offer advice about any tax implications that the process might invite.
Conclusion
As climate change continues to make headlines, interest in carbon credits trading continues to surge. This has subsequently resulted in new investment opportunities to acquire exposure to this market.
In this guide, we have identified a number of ways to invest in carbon credits in the UK. Based on the risk appetite, investors can choose which carbon credits asset to buy and how much capital to stake. Nevertheless, it is important to choose an FCA-regulated broker when conducting a carbon credits investment in the UK.
FAQs
How do I buy carbon credits in the UK?
How much is a carbon credit worth in the UK?
Can an individual buy and sell carbon credits?