Investors in Australia are increasingly looking for ways to contribute to the planet’s sustainability. One way to do this is by investing in ETFs and companies that are involved in the carbon credits industry.
In this beginner’s guide, we explore how to buy carbon credits in Australia.
We also provide some background information on how carbon credit investments work in Australia and explore the many different ways for investors to gain exposure to this emerging asset class.
How to Invest in Carbon Credits in Australia – 4 Easy Steps
For beginners, investing in carbon credits might seem like a daunting process. However, when using the right online broker – it shouldn’t take more than 10 minutes to buy carbon credits in Australia from start to finish.
Follow the steps below to learn how to buy carbon credits in Australia:
- Step 1: Create an account with a licensed broker– When selecting an online broker for purchasing carbon credits, ensure that the platform provides access to important assets like green stocks and ETFs. To begin, go to the broker’s website and set up an account by entering the necessary personal details. Users will also need to confirm their identity.
- Step 2: Deposit funds – Before buying carbon credits, investors should fund their brokerage account with the required minimum. Complete the payment via a credit/debit card, e-wallet, or bank transfer – depending on what the broker accepts.
- Step 3: Choose a carbon credit instrument – There are a variety of assets related to carbon credits offsets – such as stocks, futures, and ETFs. Choose the required asset to invest in and proceed to the trading page.
- Step 4: Buy carbon credits in Australia – Place a ‘buy order’ on the brokerage platform, specifying the amount to be invested into the chosen asset. Confirm the order and wait for it to be executed.
Assuming that the respective market is open, the broker will execute the order right away and add the carbon credit-related asset to the investor’s portfolio.
Carbon Credits Explained
Carbon credits are permits that allow a company or an individual to emit a certain amount of greenhouse gases. Typically, each carbon credit certificate represents one tonne of CO2 or another equivalent greenhouse gas.
Each and every company in Australia is awarded a certain number of carbon credits. Over the course of time, this number is reduced – which means that companies will have to come up with ways to reduce their overall carbon emission.
This can be achieved by adopting innovative production methods or by investing in green initiatives such as afforestation.
If companies exceed the cap, then they must spend capital to purchase extra Australian carbon credits. Alternatively, if they manage to reduce their emissions, the owner of the carbon credit can also sell their excess allowance.
What are Carbon Credits?
In a nutshell, the ultimate goal of carbon credits is to bring down the emission of greenhouse gases into the atmosphere. That being said, this is easier said than done.
Not every Australian company will have the resources to set up a carbon offset program and as such – firms often rely on third parties to purchase credits.
This has led to the emergence of an entirely new and innovative investment sector – carbon credit trading.
- Carbon credits are most commonly created through agricultural practices.
- Similarly, companies focused on renewable energies, such as manufacturers of solar panels or electric vehicles, can also produce carbon credits.
- These organizations or individuals can sell their carbon credits to others in the open, voluntary market.
- On the other side, companies that require extra permits can make a carbon credit purchase to offset their emissions.
This way, countries also incentivize companies or individuals that find creative ways to reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
Individuals interested in socially-responsible investing can put their money into such companies that have their own carbon offset programs.
How do Carbon Credits Work?
In the previous sections, we covered how carbon credits work in the context of sustainability. Now, let us consider the role of carbon credits in the financial market.
In Australia, carbon credits are denoted as ACCUs. This stands for the Australian carbon credit unit.
To facilitate carbon credit trading, Australia plans to launch its own exchange.
The Australian Carbon Exchange will operate like any other stock exchange; however, here, ACCUs will be the tradable asset. In the future, other types of carbon units or certificates might also be added to the exchange.

This step will ensure market transparency and accelerate the reduction of emissions while boosting Australia’s economy.
However, buying and selling Australian carbon credits directly can be difficult – as the exchange requires participants to register their business and go through other formalities.
As a result, investors in Australia that are interested in carbon credits trading will have to look for alternatives.
Fortunately, when exploring how to invest in carbon credits in Australia, traders have a few different options – which we discuss in the sections below.
Carbon Credits Tokens
These days, carbon credits can also be purchased in the form of digital tokens. Some crypto projects in the market offer tokenized versions of carbon credits, making it easy for both individuals and companies to offset their emissions.
Alternatively, investors can also consider purchasing the most sustainable cryptocurrencies to add more green investments to their portfolios.
Carbon Credits ETFs
ETFs are pooled investment funds that track the performance of a certain group of assets – in this case, those involved in the carbon credits industry.
While some carbon credits ETFs track a selection of individual companies, others track indices or futures contracts.
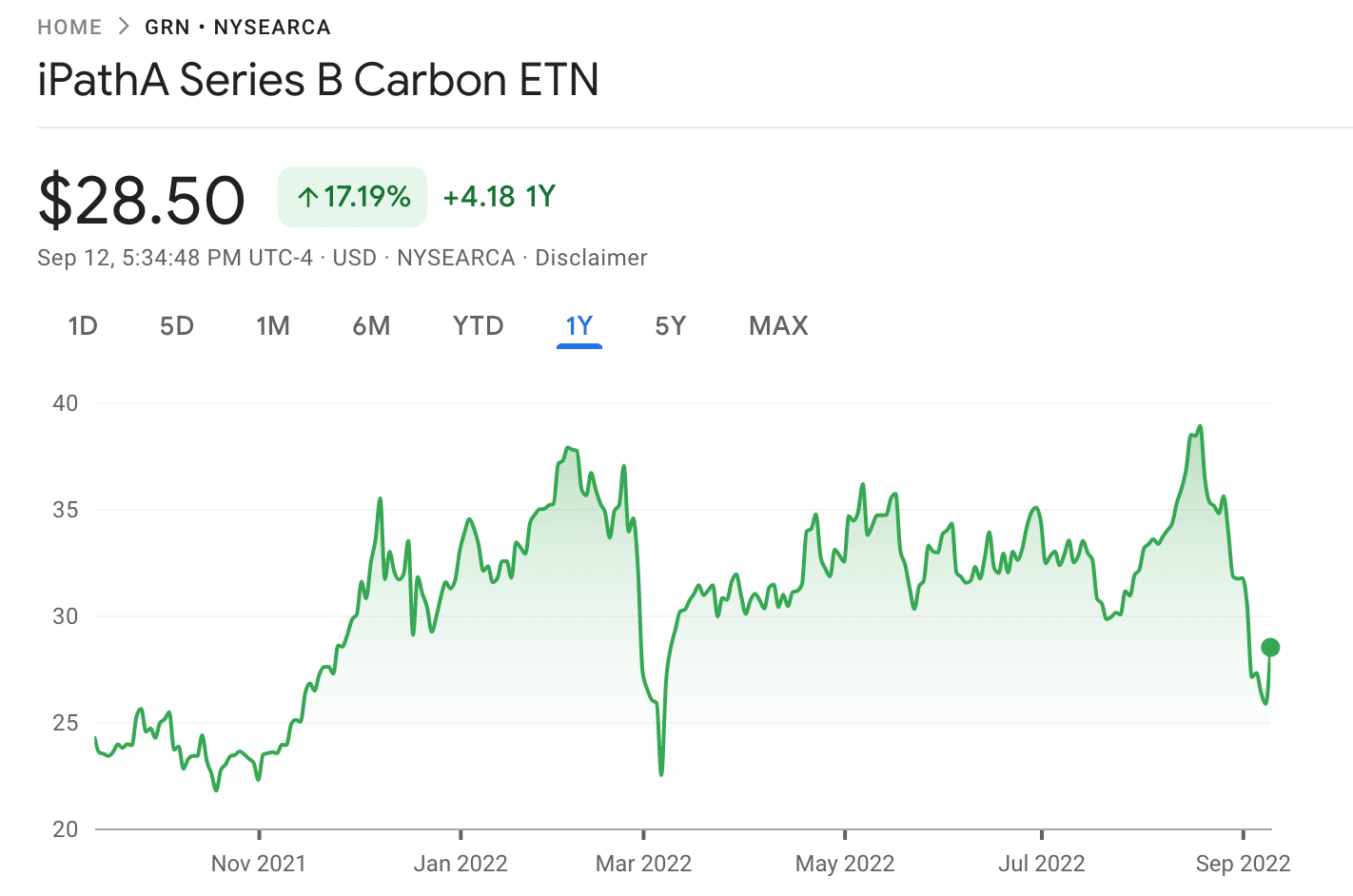
For instance, the iPath Series B carbon ETN offers exposure to the Barclays Global Carbon II TR USD Index.
This index measures the performance of carbon credit schemes such as the European Union Emission Trading Scheme and Kyoto Protocol’s Clean Development Mechanism.
Individual Companies
A third way is for investors to invest in stocks of companies that have an active carbon offset program.
There are also companies that are eco-friendly themselves, such as electric vehicle companies, that help investors gain exposure to this sector.
Carbon Credits Futures
Another way to engage in carbon credits trading is by using derivatives such as future contracts. These are financial instruments linked to underlying assets.
For instance, the European Union Allowances and the California Carbon Allowances are available as tradable future contracts in the financial market.
However, bear in mind that trading futures can be complicated, so it is wise to first understand how carbon offset credits work before risking money.
Why Invest in Australian Carbon Credits?
Carbon credits trading is still a relatively nascent market.
Therefore, investors might have concerns about whether they should add Australian carbon credits to their portfolio.
- Profitability – It’s clear that when thinking about investing in carbon credits in Australia, investors may worry about profitability. Like any investment, putting money into carbon credits can lead to financial gains. For example, the well-known carbon credits ETF, KraneShares Global Carbon Strategy ETF, has risen in value by more than 100% since July 2020.
- Increasing demand – As years pass by and the level of pollution increases, there is a growing demand for carbon credits. And as such, companies that are producing carbon credits might see sizable growth in the upcoming years. By investing in these companies early, individuals also stand to make gains.
- Multiple investment choices – As we noted above, there is more than one way to approach carbon credits investing. Investors can choose between digital tokens, ETFs, stocks, CFDs, and futures, in addition to directly trading Australian carbon credits.
- Benefits the environment: Ultimately, by investing in the carbon credits industry, investors can find a way to help the environment in conjunction with growing wealth.
Clearly, there are certain advantages to consider when learning how to buy carbon credits in Australia. That being said, trading carbon credits futures and other assets are generally considered as an advanced strategy.
In addition to this, the carbon credit industry is still relatively nascent, and as such, there is only limited performance history to access. Therefore, investors should educate themselves about the risks involved before trading carbon credits
Best Carbon Credit Investments
Below, we discuss a number of investment options that offer exposure to the carbon credits industry.
These assets can be assessed via reputable online brokerage platforms in Australia.
1. KraneShares Global Carbon Strategy ETF – Popular Exchange Traded Fund for Carbon Credits
The KraneShares Global Carbon Strategy ETF is an exchange-traded fund (ETF) that gives exposure to some of the most traded carbon credit futures contracts.
It tracks the IHS Markit’s Global Carbon Index, which covers the major European and North American cap-and-trade programs – the European Union Allowances (EUA), the California Carbon Allowances (CCA), the Regional Greenhouse Gas Initiative (RGGI), and the United Kingdom Allowances (UKA).
In other words, this index allows investors to diversify into carbon credits easily while supporting responsible investing. This ETF was launched in July 2020, and since then, the price of the fund has increased by nearly 120%. This ETF reached its all-time high price of $56 in February 2022.
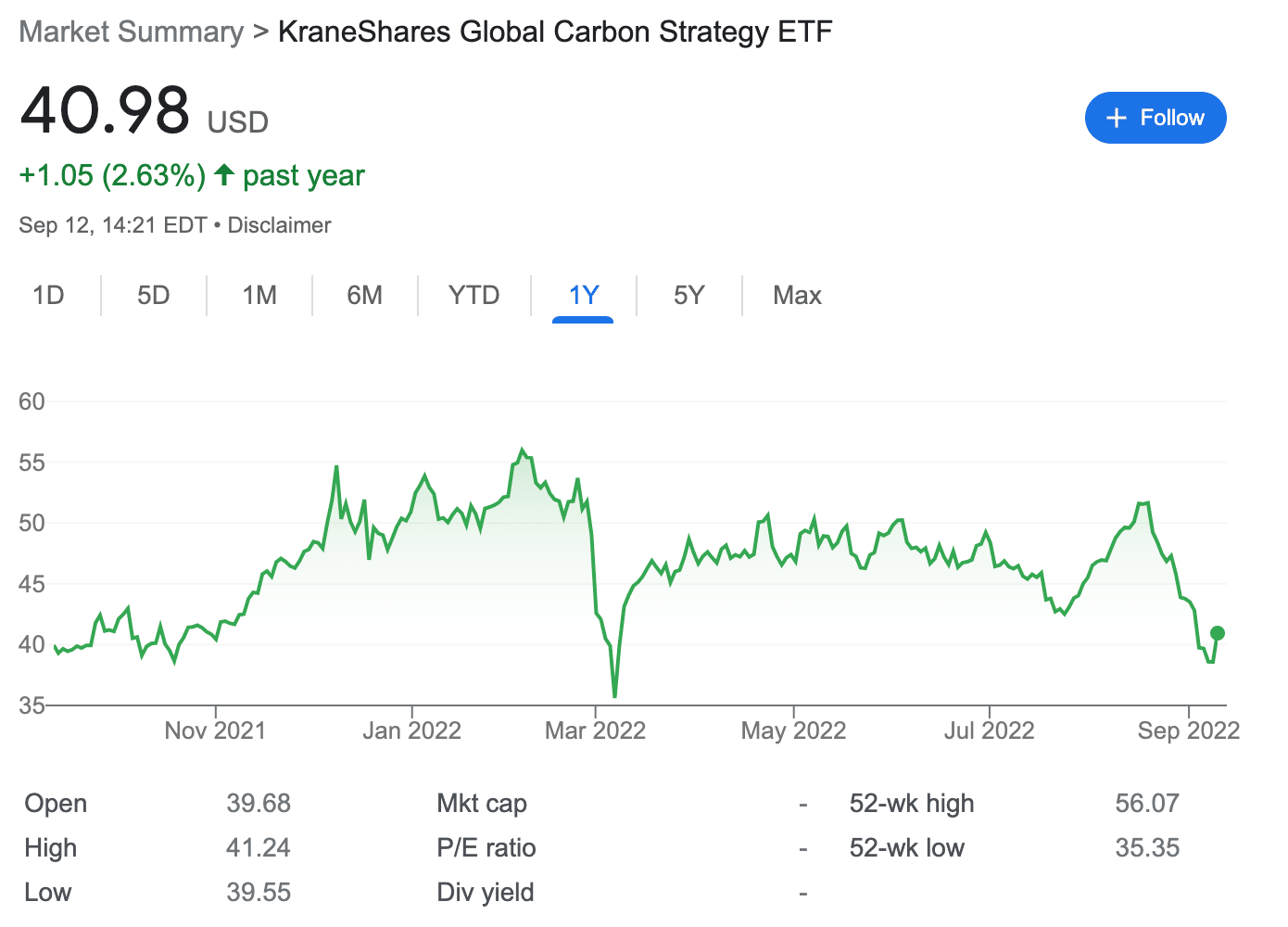
However, over the past 12 months, the ETF has experienced significant volatility and has gained only around 2.5% in value. The KRBN ETF might be appropriate for investors whose portfolios have exposure to companies with heavy carbon footprints. As the cost of carbon emissions goes up, this ETF generally benefits – thus offering a way to hedge portfolios.
2. Carbon Emissions – CFD Tracking Commodity
Trading carbon emissions as a commodity is a very new concept in the financial market. For those unaware, carbon emissions are a type of greenhouse gas that is formed due to the burning of fossil fuels. Carbon emissions came to be a commodity as an effort by countries to reduce greenhouse gas levels.
In 1997, at the UNFCCC conference in Japan, 30 countries voluntarily adopted greenhouse gas emission reduction schedules – resulting in what’s known as the Kyoto Protocol. Soon after this protocol was instated, greenhouse emissions became a liability, and since then, the carbon credits trading market came into being.
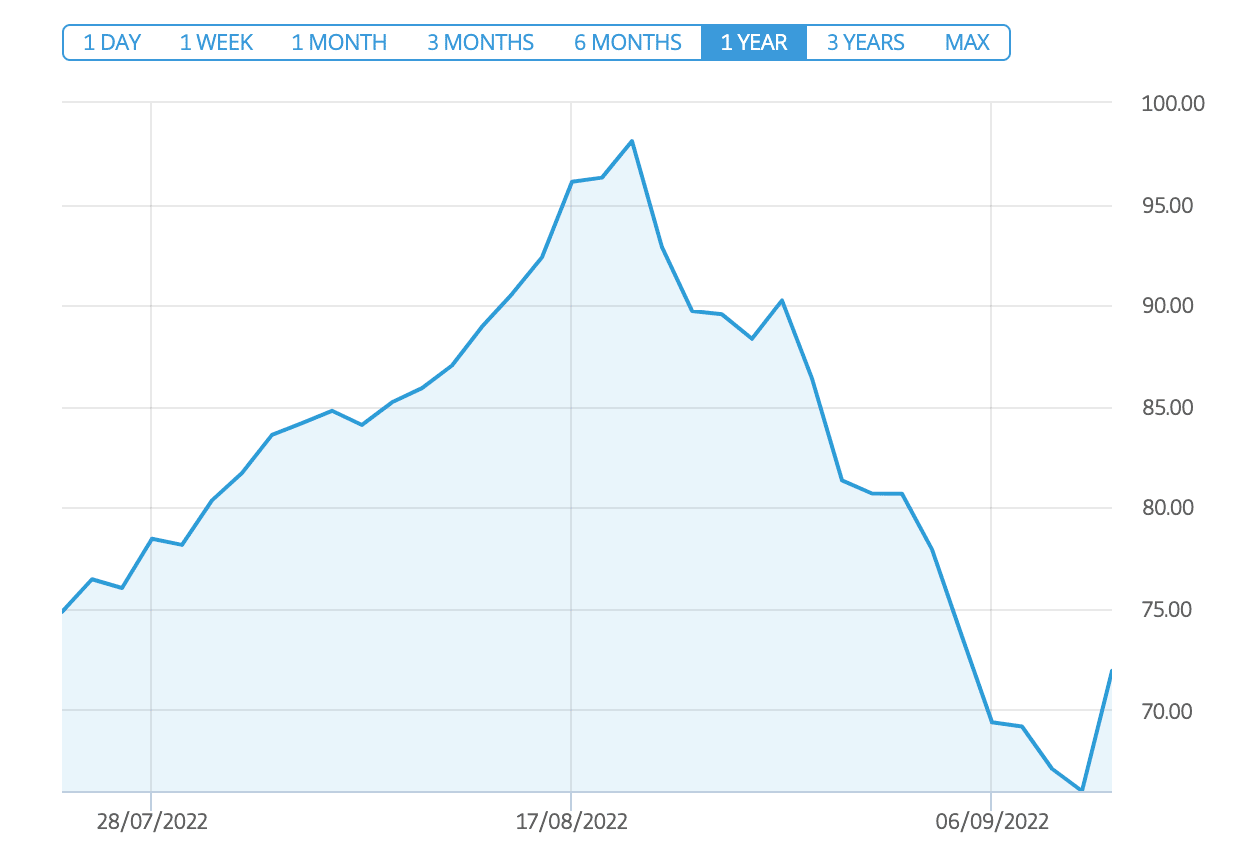
Today, some brokers in Australia allow their users to trade carbon emissions via CFDs. This means that traders will not be directly buying or selling carbon emissions. Instead, they go long or short on the price of this commodity via CFD instruments – which are financial assets that track the price of carbon emissions.
The main factor that affects the price of carbon emissions is climate change. As the rate of climate change goes up, the price of carbon emissions also increases in tandem.
3. Tesla – EV Company Selling Carbon Credits
Tesla is primarily known for its range of electric vehicles, making it one of the most popular tech stocks available today. However, due to its eco-friendly nature, Tesla is also a major player in the carbon credit market. The company is already making billions of dollars from its Tesla carbon credits sales.
Tesla receives emissions credits via regulatory sources, such as California’s ZEV program. The company then sells its credits to other organizations, which is an additional revenue flow for the firm in addition to its core EV sales. For Q1 and Q2 2022, Tesla recorded earnings of $679 million and $344 million, respectively, by selling regulatory carbon credits alone.
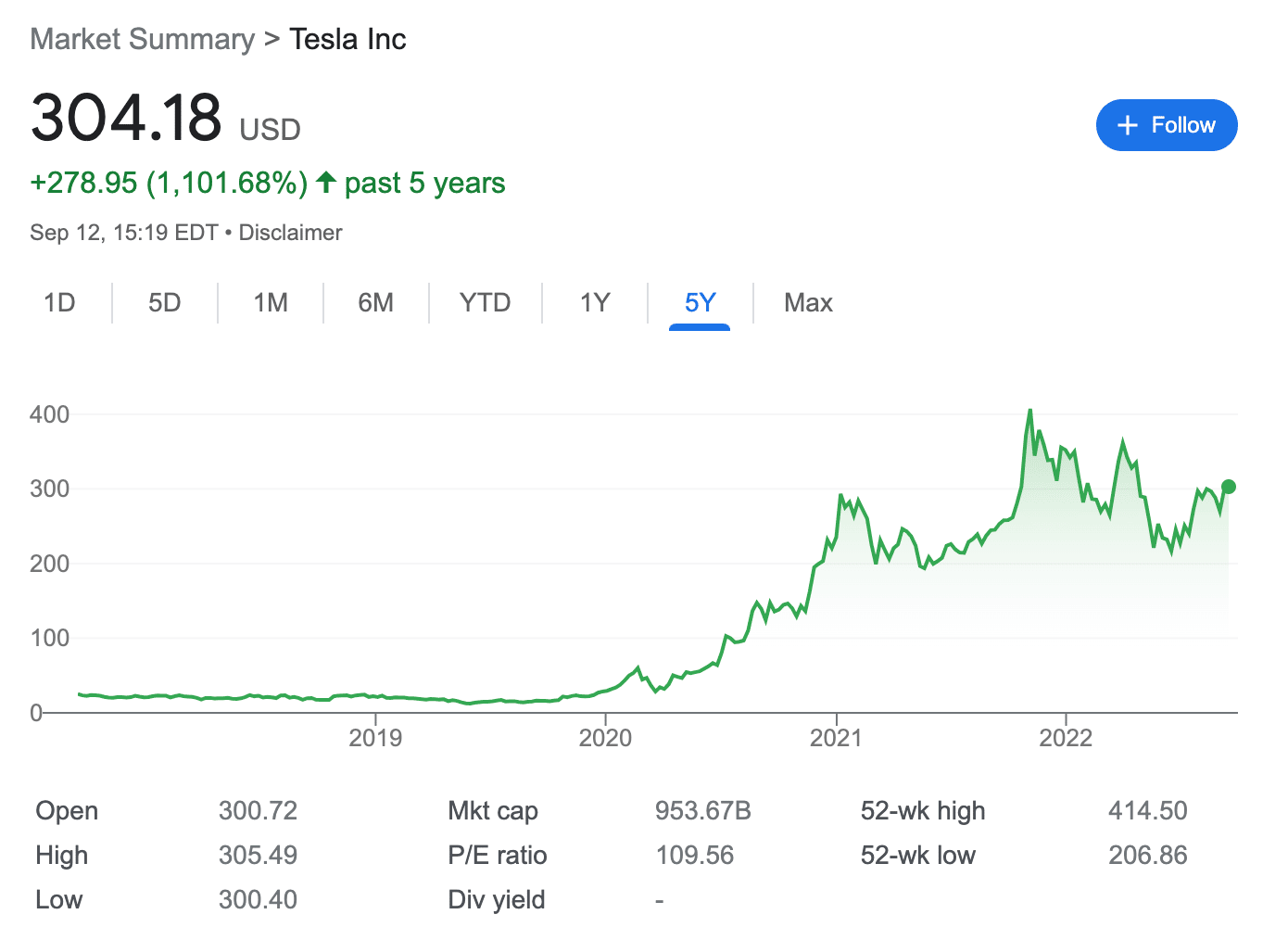
In addition to this, Tesla stock has performed extremely well since it became a public company in 2010. Since its IPO, the price of Tesla stock has increased by over 23,000%.
4. Microsoft – Tech Company With Strong Carbon Offset Program
Microsoft achieved carbon neutrality in 2012. However, this was not accomplished by reducing its carbon emissions. Instead, Microsoft invested heavily into carbon offset programs and continues to do so.
This means that Microsoft is an ideal match for investors looking for responsible investing options. In addition to this, Microsoft aims to become carbon negative by 2030 by cutting down its carbon footprint.
With this in mind, investors can buy Microsoft stock as a way to gain exposure to the carbon credit marketplace. This is perhaps more suited for newbies that do not have the required experience to trade carbon emission CFDs. Miscorost is also one of the few tech stocks that offer a dividend to shareholders – albeit, the running yield as of writing amounts to just under 1%.
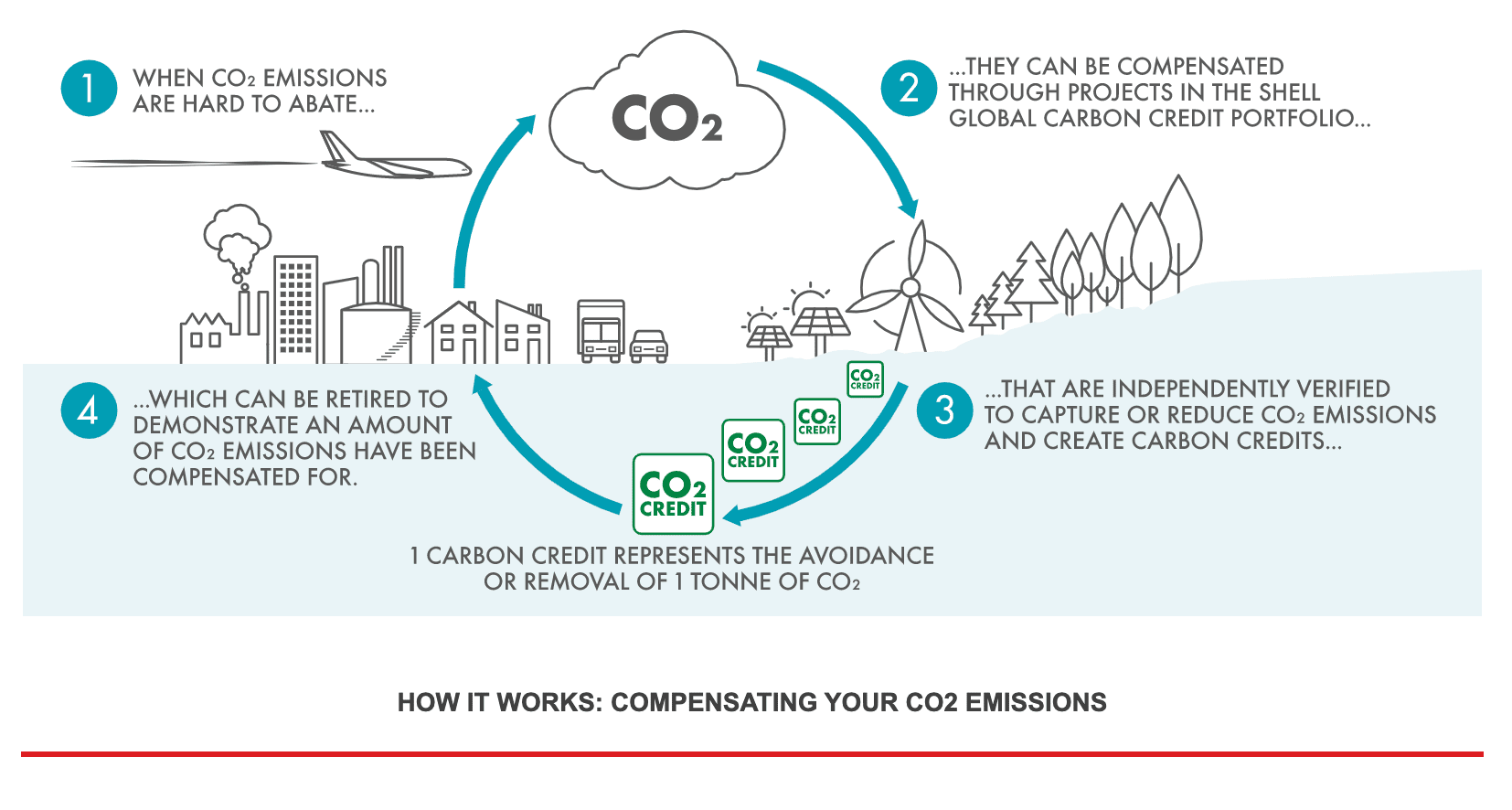
5. Shell – Energy Company Focusing on Renewables
Shell is a multinational oil and gas company headquartered in the UK and trading on the London Stock Exchange. At first glance, it might seem counterproductive to choose an oil and gas company to invest in carbon credits. However, Shell is redirecting its focus towards renewable energy and plans to achieve net zero emissions by 2050.
The company already has a strong carbon offset program and has invested millions of dollars into carbon credit projects across the world. Moving forward, Shell might redesign its entire business structure to add more renewable energy projects, which may be a positive indicator for carbon credits investors.
Shell may also be an appropriate choice for income investors in the market for dividend stocks related to the carbon credits sector. As of writing, this company offers a running dividend yield of just under 3.5%.
How to Invest in Carbon Credits in Australia – Tutorial
Curious about how to invest carbon credits in Australia?
in this section, we offer some clarity with a step-by-step explanation of the process when it comes to buying a carbon credits ETF.
Step 1: Open a Brokerage Account
The first port of call is to choose a broker that supports stocks, ETFs, or commodities related to carbon credits. Make sure that the broker is regulated by ASIC.
Investors can visit the brokerage website of their chosen provider to open an account.
This will require the investor to enter some personal details, such as a full name, date of birth, and address. New users will also need to verify the information submitted by providing a copy of a government-issued ID.
Step 2: Deposit Funds
Next, add funds to the brokerage account. The minimum amount required will vary from one broker to another.
Funding can often be facilitated with a credit/debit card, e-wallet, or bank transfer – depending on the payment methods supported by the broker.
Step 3: Find Carbon Credits ETF
Next, use the search function on the brokerage platform to locate the specific carbon credits asset to invest in.
For example, if the investor wishes to buy KraneShares Global Carbon Strategy ETF, simply search for KRBN on the respective platform.
When the result appears, click on it to proceed.
Step 4: Buy Carbon Credits ETF
Finally, it is time to place a ‘buy order’. To do this, specify the amount of money to allocate to this ETF, and confirm the order.
The broker will execute it, and once completed, the investor’s portfolio will reflect the new purchase.
How to Sell Carbon Credits in Australia
Learning how to buy carbon credits in Australia is only one part of the investment journey.
In order to make gains from carbon credits, investors should also think about how to cash out.
Selling carbon credits in Australia can also be completed within a few minutes via a suitable ASIC broker.
- After purchasing the carbon credit ETF or stock, wait and see how it performs.
- Investors can track the performance of their investment via their portfolios.
- Over time, the carbon credit investment might increase in value – albeit, there are no guarantees.
- Moreover, there will likely be some volatility in between.
- When the price reaches the profit target, locate the asset in the brokerage portfolio.
- Next, proceed to close the trade.
After the order is executed, the proceeds will be added to the investor’s account balance.
How are Carbon Credits Taxed in Australia?
As we have discussed in great detail, there are several ways to invest in carbon credits in Australia.
This means that taxation on the carbon credits investment will likely come into play:
- The cost of acquiring ACCUs is tax deductible.
- However, any proceeds from selling ACCUs are assessed as income on the revenue account.
- Similarly, if investing carbon credits via stocks, ETFs, or other financial instruments, taxes are calculated differently.
- Profits made on such investments will be applicable to capital gains tax of up to 15%.
Regardless of which approach is adopted, we suggest that investors seek the help of a tax professional to understand how to correctly file taxes on carbon credits in Australia.
Conclusion
Carbon credits are used for offsetting greenhouse gases through a market-based system. Due to the urgency in reducing greenhouse gas emissions, there is a growing demand for carbon credits across the world.
This beginner’s guide has discussed how to buy carbon credits in Australia and what asset classes are available when investing in this sector.
Nevertheless, buying and selling carbon credits can be risky, and as such, investors should conduct sufficient research before proceeding with any purchase.