Researching how to buy carbon credits? Carbon credits are tradable assets connected with ongoing concerns over climate change. Each carbon credit acts as proof that a business has successfully removed 1,000kg of CO2 from the atmosphere – or avoided creating 1,000kg of CO2 by using clean energy.
While carbon credits can be bought for as low as $5-$20, they are mainly accessible to businesses. However, individual investors can still engage with the carbon market and offset their carbon footprint through specialized companies. Below, we explain where to purchase carbon credits and related investments like carbon credit stocks and ETFs.
How to Buy Carbon Credits – 4 Easy Steps
One of the most popular ways to buy carbon credits is by using IMPT – the groundbreaking carbon credits platform hosted on the Polygon blockchain. These carbon credits can be purchased using $IMPT tokens once the platform goes live. With that in mind, detailed below are the four steps investors must take to buy $IMPT tokens through the presale:
- Step 1 – Create a Crypto Wallet: Set up a crypto wallet that supports ERC-20 tokens. We recommend MetaMask as it can be downloaded on iOS and Android devices or installed on the user’s web browser.
- Step 2 – Buy Crypto (Optional): Investors can buy IMPT using FIAT, although they can also use crypto. If an investor wishes to take the latter approach, they must buy some crypto from a reputable crypto exchange – IMPT supports ETH, BTC, MATIC, SOL, and BNB.
- Step 3 – Link Wallet to Presale: Head to IMPT’s website and click ‘Connect Wallet’. Follow the on-screen instructions to link the wallet created in Step 1.
- Step 4 – Buy IMPT Tokens: Enter the number of IMPT tokens to be purchased in the order box (minimum ten tokens) and select the appropriate payment method. Once everything has been checked, confirm the transaction.
Where to Buy Carbon Credits
Want to clean up your carbon footprint? If so, there are plenty of popular carbon offset programs that will handle all the details in return for a monthly subscription.
So what is carbon credit trading? Some carbon products – notably carbon futures – are available with CFD (Contracts-For-Difference) trading. Unfortunately, CFD trading is not legal in the US.
Other carbon products, like ETFs, stocks and sustainable investing funds centered on renewal energy, are more freely available.
What are Carbon Credits?
Carbon credits are an investable asset accessible mostly to corporations and governments. With carbon futures and related assets, individual investors can get some exposure to the carbon credit market.
Each carbon credit is essentially a certificate. It proves that one metric ton (1,000kg) of CO2 has either been removed from the atmosphere – or that the issuer of the credit has avoided the production of the same amount of CO2 by generating energy in a clean way.
Carbon Credits: Background

Carbon credits are all about climate change.
The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change posits that as much as 5bn tons of CO2 must be removed from the atmosphere every year until 2050. Otherwise, the global temperature is predicted to rise by 4C by 2100. This will result in catastrophic weather and render large parts of the globe uninhabitable.
Carbon Credits: 3 Key Global Agreements
- Kyoto Protocol – 1997: Carbon credit trading begins.
- The Paris Agreement – 2015: Article 6 develops legislation around countries trading carbon credits in pursuit of their Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs) to global carbon removal.
- The Glasgow Climate Pact – 2021: 2% of carbon credits to be slashed from the market, and a global market is agreed upon to tackle the current fragmentary situation with accreditation.
Carbon Credits: Accreditation and Markets
The carbon credits market is actually two markets:
- The voluntary market, in which companies voluntarily offset their carbon emissions. This is largely based in Europe and North America. 2021 approx. value: $1bn.
- The regulatory market, in which companies and governments trade in carbon credits in order to meet their regulatory carbon reduction targets. 2021 value: approx. $851bn.
Regulators in the markets include:
The American Carbon Registry (ACR)

ACR was the first registry for greenhouse gas emissions and offsets. Launched in 1996, ACR is a nonprofit enterprise. It is involved in all sorts of carbon reduction projects, including forestry, smart agriculture and infrastructural initiatives.
Verra’s Verified Carbon Standard (VCS)

Gold Standard

Another key body involved in accreditation is the United Nations. Carbon reduction projects are often advertised as being aligned with specific UN Sustainable Development Goals.
How Does Buying Carbon Credits Work?
The truth of the matter is that buying carbon credits does not really work very well for individual investors. The carbon credit markets – the voluntary and regulatory – are set up for businesses.
Individuals, however, have plenty of related options, as we explore below.
How to Buy Carbon Credits For Businesses


CTX charges an annual fee of $1995 to corporations in return for access to a global exchange of different types of carbon credits from 4 continents:
- VERs (Voluntary Emission Reductions)
- CERs (Certified Emission Reductions)
- VCUs (Verified Carbon Units)
- EUAs (EU Allowances)
- EUAAs (EU Aviation Allowances)
CTX charges a 5% sellers fee and stipulates a minimum trade lot of 100 metric tons of C02. Only carbon credits verified by major accreditors – like Verra VCS, Gold Standard, ACR, CAR and the UN’s Clean Development Mechanism (UNFCCC) – are traded.
CTX operates under an Australian Financial Services License (AFSL).
How to Buy Carbon Credits For Individuals
The best way to buy in carbon credits for individual investors is to consider one of five routes:
1. IMPT – Digital Token to Buy Carbon Credits
As noted earlier, there are several crypto projects entering the carbon credits space. One such project is IMPT. This innovative ecosystem project facilitates the buying, selling and trading of carbon credits.

The project aims to make investing the process of investing in carbon credits in Australia accessible to all. To make this possible, IMPT has collaborated with hundreds of impactful environmental projects from across the world.
IMPT is built on blockchain technology, which ensures the security and transparency of all projects listed on the site.
Companies and individuals can get started by purchasing IMPT digital tokens. Stakeholders can then choose an environmental project to invest in, and buy carbon credits using the digital tokens. After the purchase is complete, these credits will be minted into NFTs.
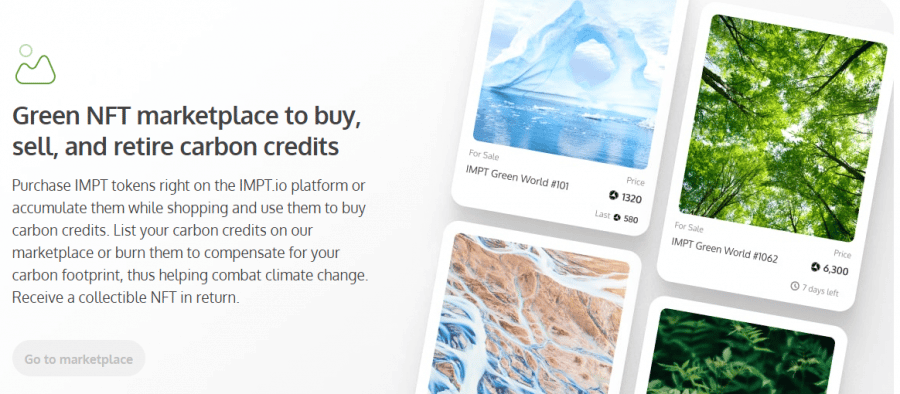
According to the IMPT whitepaper, investors then have two options. They can burn the NFT to compensate for their carbon footprint, or sell them on the IMPT marketplace. The platform also plans to reward investors who contribute to reducing carbon emissions.
IMPT has already completed the private presale of its digital asset – which resulted in more than 90 million tokens being sold. The public presale, however, is set to commence on October 1, 2022, and will last until November 25th.
IMPT tokens can be purchased using Bitcoin, Ethereum, or Visa cards. During the presale stage, this digital asset will be available at a price of $0.06.
To stay notified of the latest developments, subscribe to the IMPT Telegram channel.
2. Buy into a Carbon ETF
The KraneShares Global Carbon ETF (KRBN) is one example of a dedicated carbon ETF.
KRBN is a tracker ETF. It tracks the influential IHS Markit Global Carbon Index. This index tracks the major ‘cap-and-trade’ carbon programs in North America and Europe.
Founded in July 2020, KRBN reached over double its initial value in February 2022 with each share valued at $56. Since then its value tumbled in line with the carbon credits shock response to the turmoil wreaked on the energy markets by the Ukraine Crisis. KRBN is currently trading just below $40.
3. Buy Renewable Energy Stocks
Most full-service brokers nowadays offer access to the best ethical stocks from an environmental point of view.
Any stock involved in renewable energy is a valid environmental investment. This is because renewable energy improves the carbon dioxide situation by providing clean energy that takes away the need to use fossil fuels instead.
Individuals may invest in stocks that specialize in renewable energy across the capitalization spectrum: from well-established large-cap companies to tiny penny stocks.
What Large-Cap Green Stock Can I Invest in?
A large-cap renewable company to consider is Orsted. This Danish multinational has been operating in the renewable energy sector for 3 decades. Orsted claims a quarter of the global offshore wind sector, with installed capacity sufficient to provide power to 19m people. By 2030, the firm aims to have 50 Gigawatts of renewable energy capacity. Orsted has almost 7,000 employees, a market capitalization of $292bn and Earnings Per Share of $22.
- Other large cap renewable companies number US firm NextEra Energy and Spanish Iberdrola.
What Small-Cap Green Stock can I Invest in?

- A 7-year agreement with Delta Airlines to provide 75m gallons of Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF).
- A deal with Oneworld Alliance (a network of airline firms including American Airlines) to supply 200m gallons per year of SAF.
4. Buy into a Carbon Future
Select platforms offer a carbon future for sale in the form of one European Union Allowance (EUA). Investors can go long or short on the price.
5. Offset Your Carbon Footprint with a Consumer Provider
There are numerous companies online which specialize in offsetting carbon footprints.
These outfits do not offer investable assets, though. Rather, they agree to offset an individual’s carbon footprint by investing in accredited carbon projects or carbon credits generated by them.
Popular carbon offset programs available to individuals include Direct Air Capture specialists Climeworks, afforestation experts Ecologi, travel offsetters Sustainable Travel International and Myclimate, which offers expertise in precise carbon footprint calculation and offset.
Why Buy Carbon Credits?
Why buy carbon credits? It is a good question because, for individual investors, it is very difficult to purchase carbon credits. The closest we can get as retail investors is to invest in carbon futures.
Arguably, buying carbon credits is unnecessary for individual investors – given the breadth of options to buy into the carbon/green market easily.
How to Buy Carbon Credits – Tutorial
As we have discussed above, buying actual carbon credits is generally the preserve of businesses. Retail investors exploring how to buy carbon credits can get a piece of the market by investing in carbon futures. Variants of these are available with popular brokers.
To buy into the carbon credits market with a broker, the process is straightforward. Investors need only take four steps:
- Sign up With the Broker of Your Choice.
- Get Validated.
- Deposit Funds.
- Execute a Trade.
1. Sign Up
Whichever broker you choose, our advice is to select one with as much regulation as possible..
To sign up, the investor will need to head to the broker’s online platform and enter a few details.
2. Get Validated
Regulated brokers will insist that the investor provides proof of who they are – as well as proof of where they live.
This process is handled by either scanning ID and uploading it, or using the investor’s webcam to photograph the ID.
3. Deposit Funds
Unsurprisingly, popular investment apps make it easy to deposit. Without investors making deposits, the brokers could not generate any revenues from fees.
As examples of the spread of deposit options on offer:
- Most brokers accept bank transfer, credit/debit cards. PayPal, Skrill and other payment wallets.
4. Execute a Trade
Again, brokers make opening a trade very easy.
Generally, the process is to pinpoint the homepage of an asset. And here there will be a button to press which initiates the trade process.
For example, one carbon-related stock on offer is Canadian Solar (CSIQ). This firm manufactures solar PV modules and runs large solar projects.
Investing in CSIQ is one way consumers can invest in the carbon sector – as backing a firm like this is backing the renewable energy that means less CO2 is released into the environment.
Investors can press ‘Buy’ to go long on CSIQ, and ‘Sell’ to go short. Once the trade is complete, funds will be deducted from the investor’s account, and the asset will be displayed in their portfolio.
- Watch out for overnight fees with CFDs! We note on the right of the CSIQ profile above that an overnight fee of -0.0516% applies to Buys, and a fee of -0.03624% applies to Sells. Overnight fees can add up. So CFDs are not suitable for long-term investment positions.
- We note also that a spread percentage fee of 0.99% applies to CSIQ.
Conclusion
Above we have outlined how to buy carbon credits for businesses as well as individuals. Carbon credits in their original format are generally available only to businesses via brokers like CTXglobal.com.
But if an individual were looking how to invest $1,000, for example, there are plenty of options to invest in carbon-related assets. Sustainable energy stocks and ETFs, popular green investment funds, and commodity futures contracts are all options.
Another excellent option for those looking to buy carbon credits is IMPT. This innovative ecosystem allows individuals to acquire carbon credit NFTs through their everyday shopping activities, which can be freely traded on the built-in marketplace. IMPT’s presale is ongoing, allowing investors to buy tokens at a discounted rate of $0.018 – the lowest they’ll be made available.

