Carbon credits are an emerging asset class particularly popular among investors looking for sustainable investment opportunities. To gain exposure to this market, investors can consider trading carbon credits ETFs.
In this guide, we explore some of the best carbon credits ETFs available in 2025. We also offer some insight into what carbon credits are and how to start investing in this marketplace via a regulated broker.
Here are the best carbon credits ETFs to watch in 2025 : New to the financial markets? Get started with the basics by reading our in-depth guide on how to invest in ETFs. You can invest in carbon credits ETFs using regular stock brokers and other leading carbon credit brokers such as Evolution Markets, Karbone, or IMPT.11 Popular Carbon Credits ETFs to Watch in 2025
A Closer Look at Carbon Credits ETFs
There are a variety of assets related to the carbon credits space – which includes stocks, futures, and exchange-traded funds.
Carbon credits ETFs, in particular, typically track a specific index, futures, or a basket of stocks related to this industry. By buying carbon ETFs, investors have the opportunity to diversify within this space without having to handpick any assets themselves.
Below, we analyze some of the best carbon offset ETFs that are accessible to retail investors and allow them to engage in green energy investing.
1. IMPT – Invest in Tokenized Carbon Credits
The main attraction of carbon credits ETFs is that this asset class provides a seamless way for retail investors to gain exposure to this market. However, ETFs aren’t the only accessible asset class in the carbon offsets industry.
On the contrary, there are new upcoming blockchain projects that enable investors to diversify into sustainable opportunities effortlessly.

IMPT is one such project that is working towards a greener future. This platform issues tokenized versions of carbon credits which can be purchased by companies in order to offset their emissions.
According to the IMPT whitepaper, individuals can also invest in carbon credits, thereby funding a green project. To get started, investors or companies can purchase IMPT digital tokens directly from the project’s website.
Then, they can choose a carbon credits program and obtain credits using their IMPT digital tokens.
The carbon credits issued will be in the form of NFTs. Companies with high emission rates can choose to burn their holdings and receive an alternative NFT in return. Investors, on the other hand, can hold their NFTs or trade them on the open marketplace.
The key takeaway here is that IMPT vets all carbon offset programs featured on its platform. Moreover, any capital invested will be accounted for using the blockchain protocol, ensuring transparency and security.
IMPT digital tokens will be offered to the general public via a presale launch that starts on October 1, 2022. The tokens can be purchased using fiat currencies, or crypto coins such as Bitcoin and Ethereum.
By investing in IMPT.io tokens, investors can be sure that their money will be used to facilitate sustainability projects. Moreover, if the demand for carbon credits increases, the value of IMPT NFTs could follow suit. As always, however, investors are advised to conduct their own research to ensure they have a firm grasp of the risks involved.
Get more information about this project by subscribing to the IMPT Telegram channel.
2. KraneShares Global Carbon Strategy ETF – Overall Best Carbon Credits ETF to Invest in Right Now
The KraneShares Global Carbon Strategy ETF (KRBN) is an index that tracks some of the most popular carbon credits markets globally. It is benchmarked to the IHS Markit Global Carbon Index – which includes futures contracts on European Union Allowances (EUA), UK Allowances (UKA), California Carbon Allowances (CCA), and the Regional Greenhouse Gas Initiative (RGGI).
This allows investors to gain exposure to the carbon credits markets in diverse locations. Launched as recently as July 2020, this ETF is relatively young. Nevertheless, the fund has over $800 million in net assets, based on the valuation at the time of writing.
In terms of performance, the KraneShares Global Carbon ETF has made gains of over 100% since its inception. When the fund was launched, it was priced at around $20. The value of this ETF climbed gradually to reach an all-time high price of around $56 in February 2022.
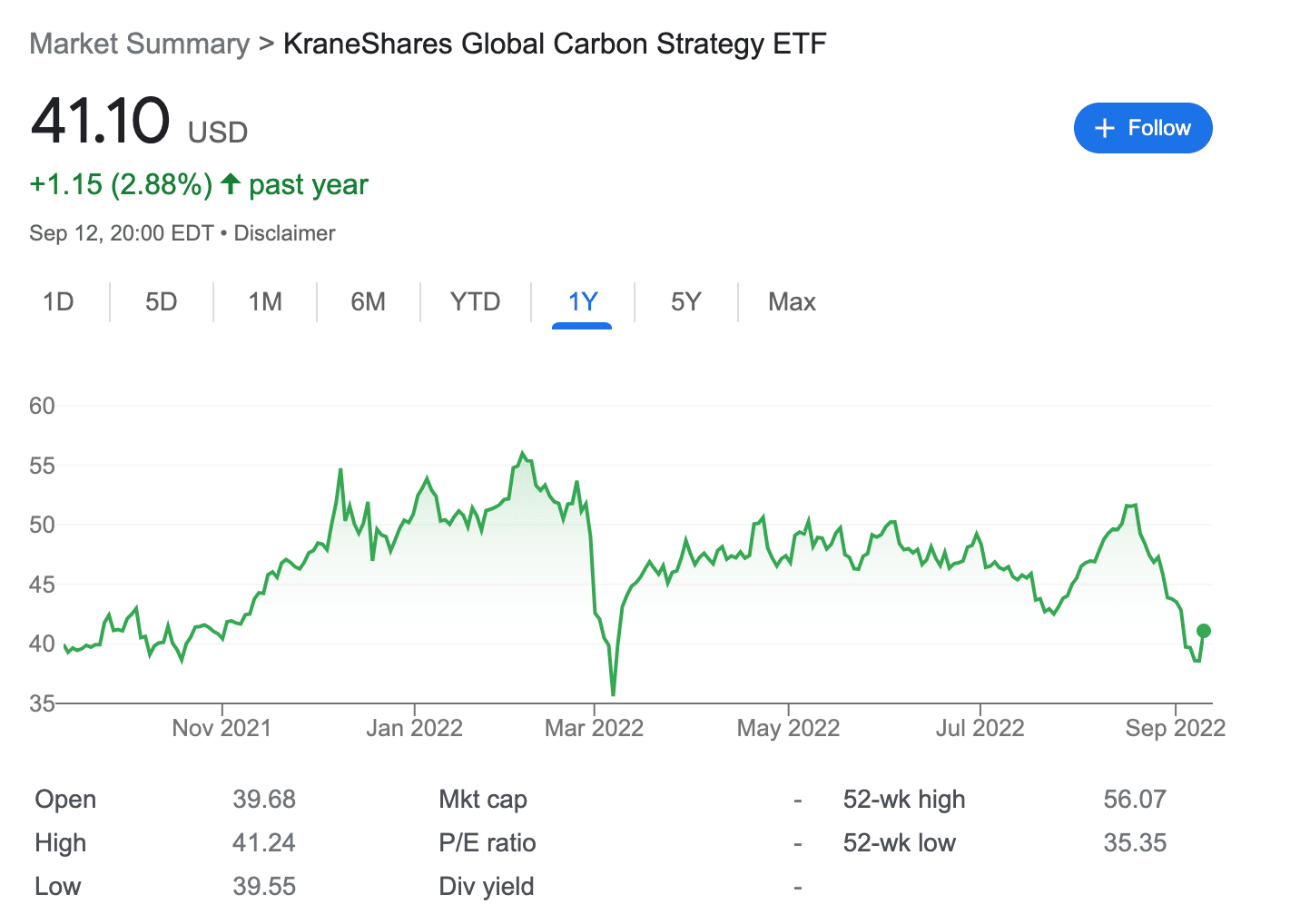
In March 2022, the price of oil increased due to the turmoil caused by Russia’s invasion of Ukraine. Following this, the carbon credits market plummeted, and so did the price of the KRBN ETF. However, since then, the carbon emission market has recovered.
As of writing, the KraneShares Global Carbon ETF is trading at around $40 – which is about 28% below its all-time-high value recorded in February.
ESG Rating: N/A
3. KraneShares California Carbon Allowance Strategy ETF – Fund Tracking the California Carbon Allowance Program
In addition to the aforementioned global ETF, KraneShares has also designed funds that track other markets. One such example is the KraneShares California Carbon Allowance ETF, which focuses exclusively on the cap and credit market in California. This ETF closely follows the price performance of the CCA futures.
The California Carbon Allowance program started in 2012 and covers almost 80% of the greenhouse gas emissions of the state. The program plans to achieve carbon neutrality in California by 2045. This offers investors the opportunity to gain exposure to this high-growth market early.
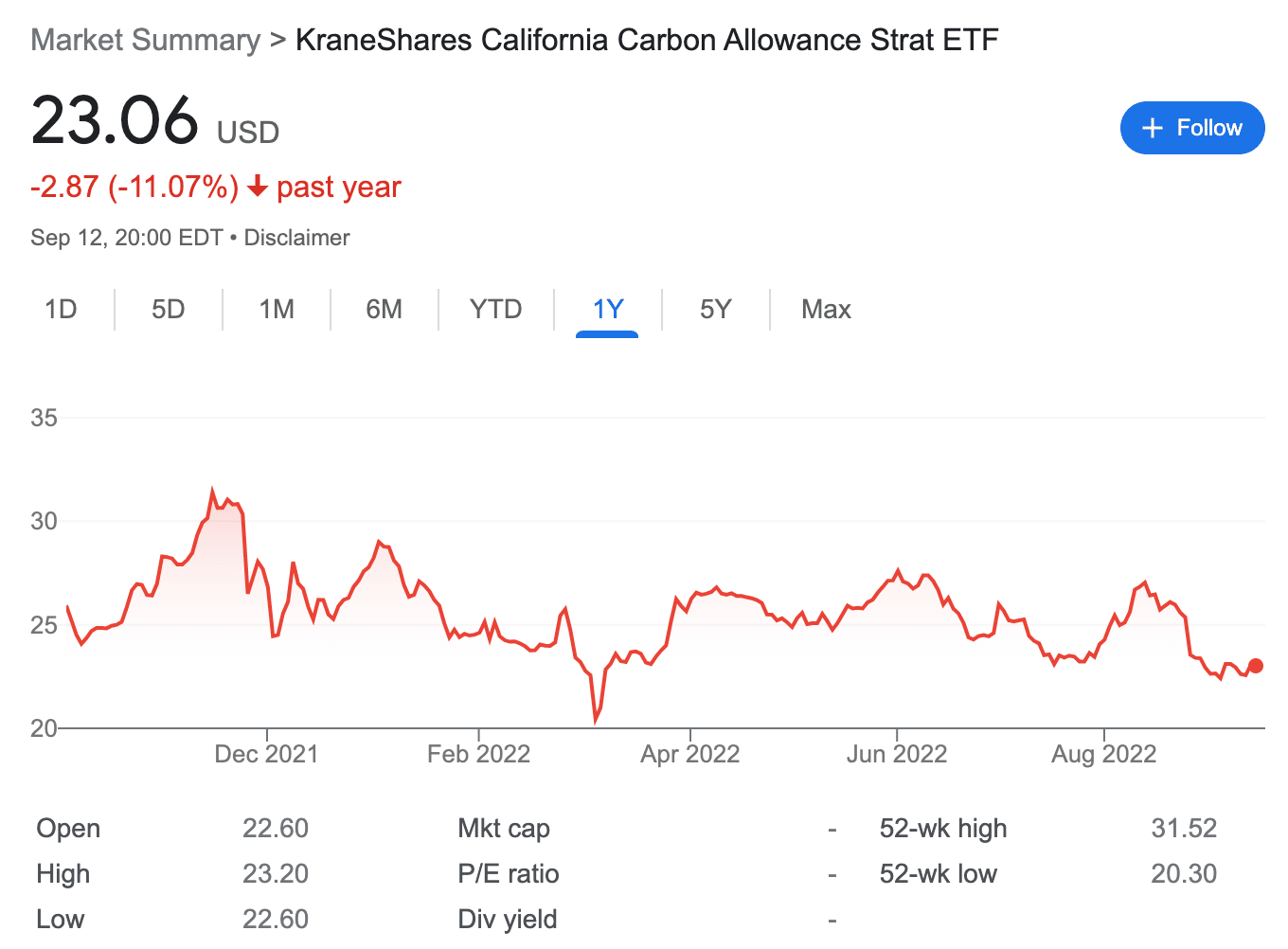
The CCA carbon allowance futures is also one of the most widely traded assets in this market. However, since this ETF follows the performance of only the Californian carbon credits market, it also comes with greater levels of risk.
After launching in October 2021, the price of this ETF has fallen by nearly 5%. Looking at its price history, the ETF has gone through extreme volatility over the past few months. As of writing, the KraneShares California Carbon Allowance ETF is traded at around $23.
ESG Rating: N/A
4. Horizons Carbon Credits ETF – Canada’s First Carbon Credits ETF
The Horizons Carbon Credits ETF is the first of its kind to be listed on the Canadian markets. In other words, this is the first carbon-credit-related investment product native to Canada. This ETF is still in its infancy, launching as recently as February 2022. The Horizons Carbon Credits ETF trades on the Toronto stock exchange.
However, this ETF does not track carbon credits issued in Canada. Instead, its underlying index is calculated depending on the daily returns of the settlement price of the EUA futures contract.
Like the KraneShares California ETF we discussed above, this fund is focused on a single market and as such, comes with greater levels of risk. This ETF can be purchased at around $8 CAD, which comes to about $6 USD based on the exchange rate at the time of writing.
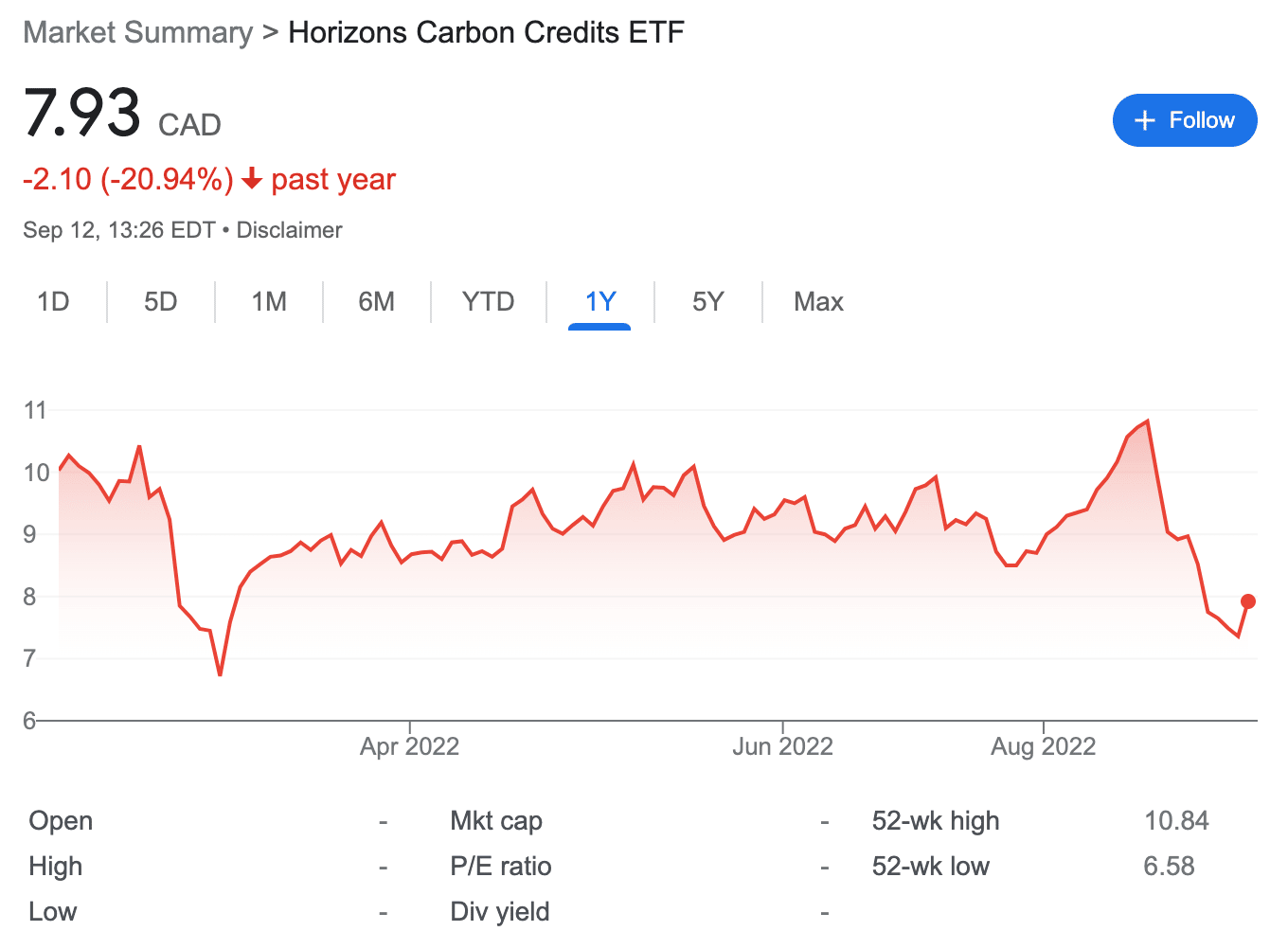
Since its launch, the price of this ETF has gone through extreme fluctuations. Over the past seven months, the value of this ETF has fallen by around 20%.
Not long after its inception, the broader carbon credits market took a hit, which was reflected in the price of this ETF. Seven months later, in the first week of September 2022, the EU announced that it was considering selling its reserves of carbon credits permits in order to lower power prices. This has pushed down the price of the Horizons Carbon Credits ETF even further.
ESG Rating: N/A
5. iShares MSCI ACWI Low Carbon Target ETF – Fund Tracking Low Carbon Companies
The ETFs discussed above track carbon credits allowances via futures. The iShares MSCI ACWI Low Carbon Target ETF, however, is composed differently. It tracks an index of the same name, which contains holdings of over 1,000 low-carbon companies around the world.
Its holdings include Apple, Amazon, Microsoft, Tesla, Verizon, Bank of America, and more. While there are stocks trading on international exchanges, its holdings are heavily weighted toward the US market. The primary benefit of this ETF is its broad diversification.
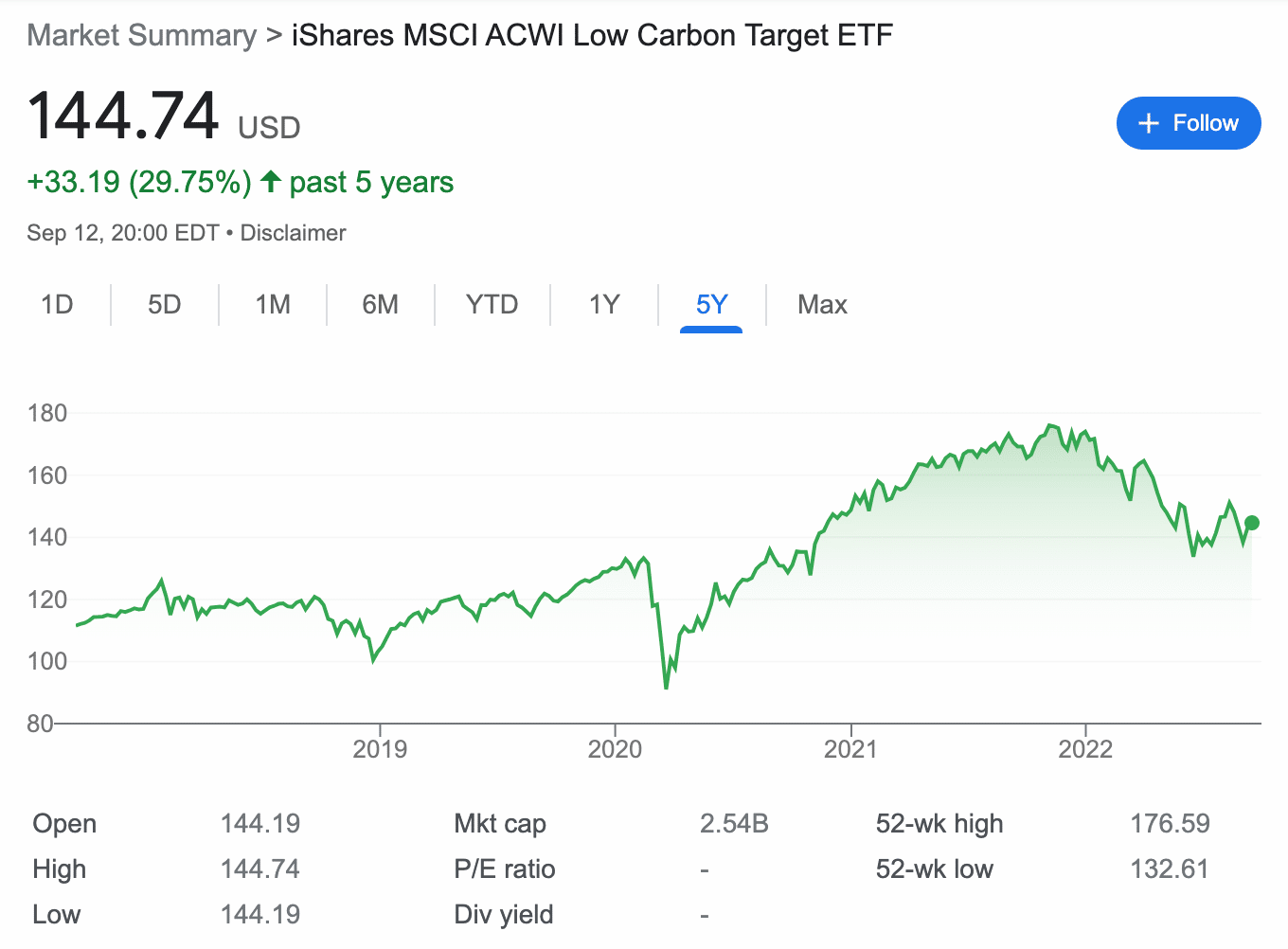
As such, the iShares MSCI ACWI Low Carbon Target ETF provides less exposure to any single carbon market. Moreover, the fund is not directly linked to carbon credits but instead to companies that have strong carbon offset programs or low fossil fuel emissions.
Over the past half-decade, the value of this ETF has increased by nearly 30%. However, the fund has not performed particularly well on a 12-month basis, with its price declining by around 15%.
ESG Rating: AAA
6. BlackRock US Carbon Transition Readiness ETF – Collection of US Companies With Carbon Offset Programs
Like the iShares fund that we discussed above, the BlackRock US Carbon Transition Readiness ETF is another asset that offers indirect exposure to the low emission economy. This ETF is made up of mid-to-large-cap US companies that are considered to be one of the most popular sustainable investing funds.
There are over 300 holdings in the portfolio, which includes Amazon, Tesla, Johnson & Johnson, Coca-Cola, United Health Group, and more. In other words, the ETF is well diversified, which can help mitigate risk.
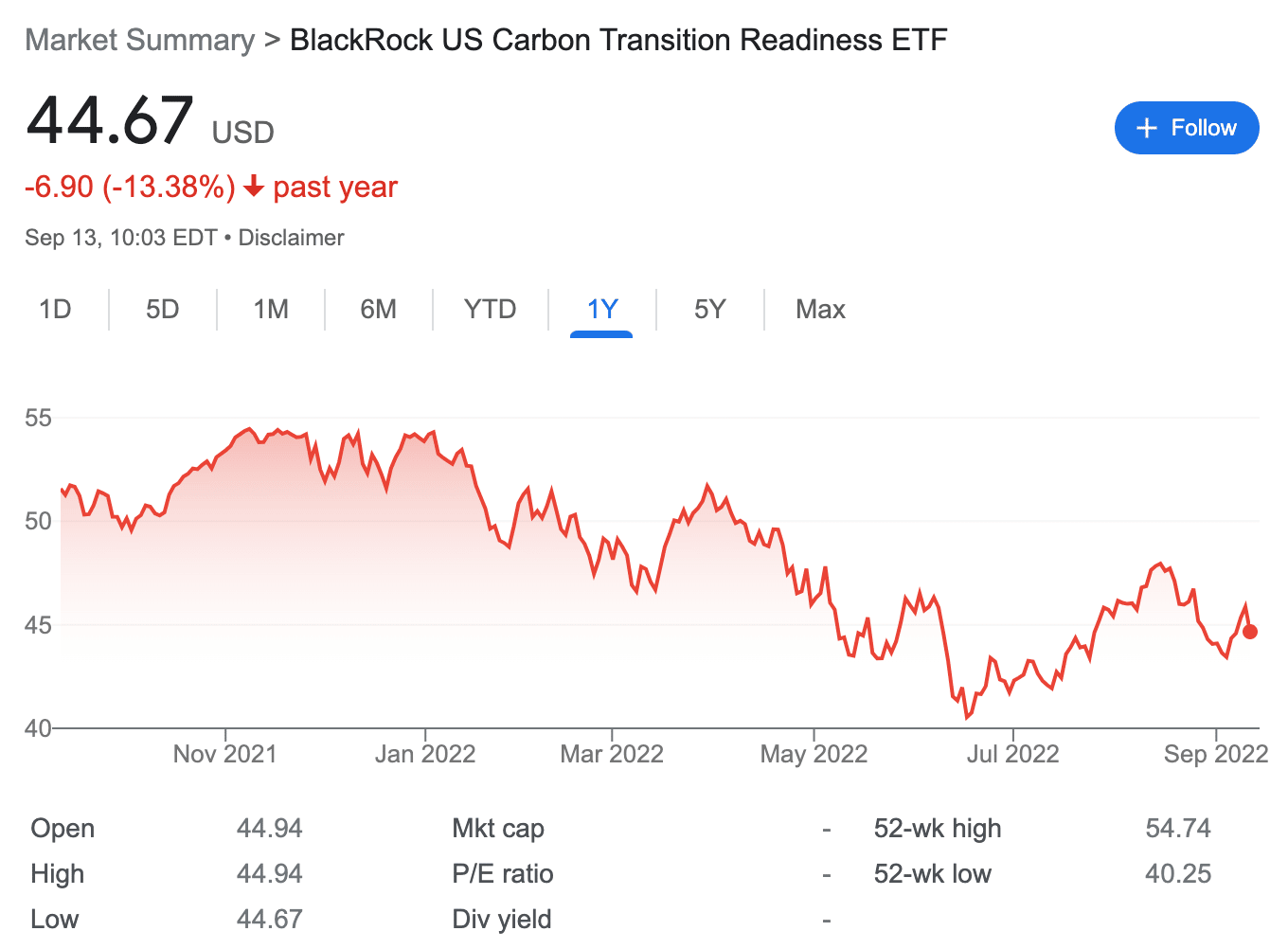
However, the performance of this low carbon ETF to date has been somewhat lackluster. Moreover, since launching in April 2021, the BlackRock US Carbon Transition Readiness ETF has witnessed moderate volatility. Over the past 12 months, for instance, the fund has lost around 13% of its value.
Nevertheless, given that the companies within the fund could benefit from their low carbon strategy over the long term, the value of this ETF has every potential based on prices as of writing.
ESG Rating: AAA
7. SPDR MSCI ACWI Climate Paris Aligned ETF – Carbon Credit ETF With Exposure to 60 Markets
The SPDR MSCI ACWI Climate Paris Aligned ETF is one of the most diversified funds available in this category. This fund tracks the MSCI ACWI Index, which holds large and mid-cap securities across 60 markets. This includes 23 developed markets, such as the US and the UK, and 27 emerging countries, like Taiwan.
The ETF aims to support those looking to reduce their exposure to climate transition risks. At the same time, the ETF also allows investors to benefit from the shift to a low carbon economy by supporting companies that have aligned themselves with the requirements of the Paris Agreement.
This fund is not only diversified in terms of markets but also sectors. For instance, nearly 25% of the portfolio is focused on tech stocks, whereas 15% is on financial companies. There are also constituents operating in the healthcare industry, consumer discretionary, telecommunication, real estate, and more.
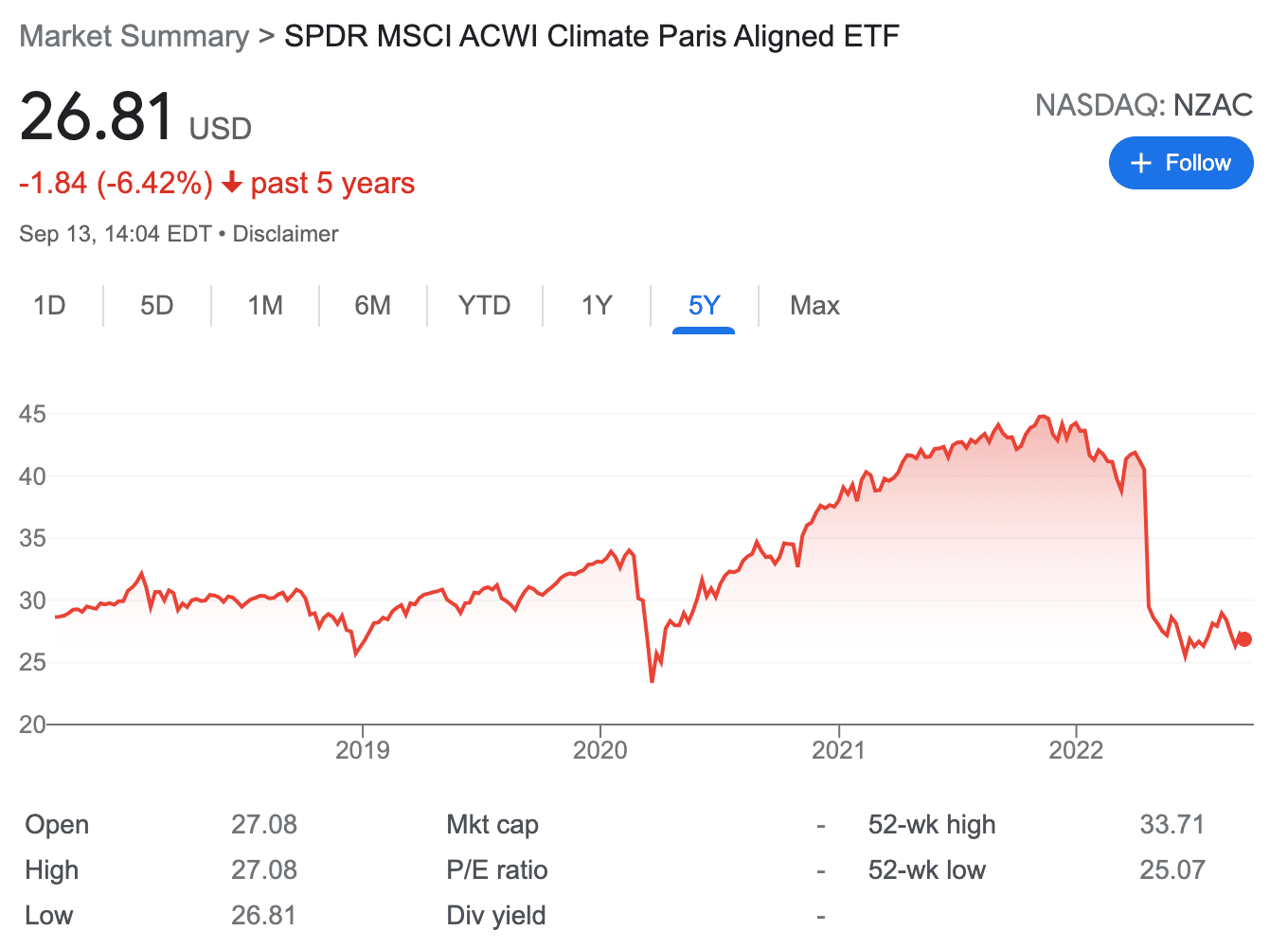
With that said, over 50% of its holdings are focused on the US market, so this is something to bear in mind. For instance, in April 2022, the broader US stock market fell sharply, mainly due to concerns over rising interest rates and high inflation.
This also led to the SPDR MSCI ACWI Climate Paris Aligned ETF declining from $40 to $27 in a matter of days. In other words, this carbon ETF has a high correlation to the US stock market – which is something to consider before investing.
ESG Rating: AAA
8. Wisdomtree Carbon ETC – Exchange-Traded Commodity Tracking Carbon Emissions
WisdomTree is an exchange-traded commodity that is designed to enable investors to gain exposure to the European Union’s carbon emissions allowances. It is linked to the performance of the Solactive Carbon Emission Allowances Rolling Futures Index.
By investing in this asset, investors can track the index indirectly, using fully funded swaps. These swaps are contracts with the financial institution that delivers the return of the index.
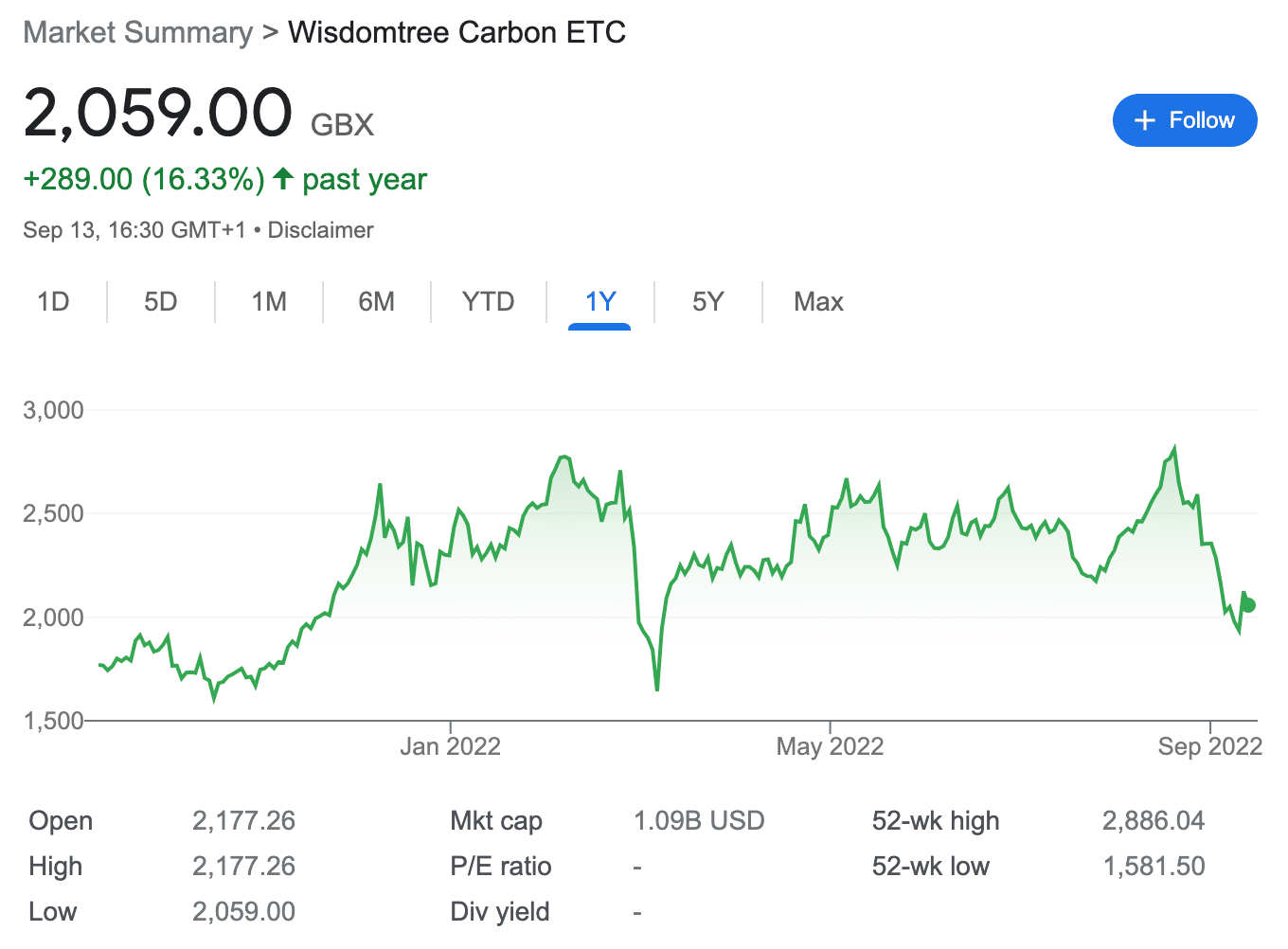
WisdomTree was introduced to the market in September 2021. Although this is technically an ETC, it is traded on exchanges just like ETFs. This security is packed by swaps and, as of writing, managers over $300 million worth of assets.
WisdomTree Carbon is listed on the London Stock Exchange. Over the past year, the value of WisdomTree Carbon has increased by over 15%. However, it is worth noting that this asset offers exposure only to the European carbon credits market and is, therefore volatile, as is evident from its price history.
ESG Rating: N/A
9. SparkChange Physical Carbon EUA ETC – World’s First Physically-Backed Carbon ETC
Another ETC for the purpose of investing in carbon credits is the SparkChange Physical Carbon EUA. This asset differentiates itself from the other funds we discussed today – as it is backed by physical carbon, as opposed to futures or stocks. Typically, investing in physical carbon is not possible due to the operational challenges involved.
The advantage of investing in the SparkChange ETC is multifold. Since SpartChange holds physical EUAs, industries cannot use them as a permit to pollute. This means that there will be a reduced supply of EUAs over time, which might positively impact the price of this ETC. Moreover, unlike funds that follow futures-based products, this ETC manages to avoid performance drag.
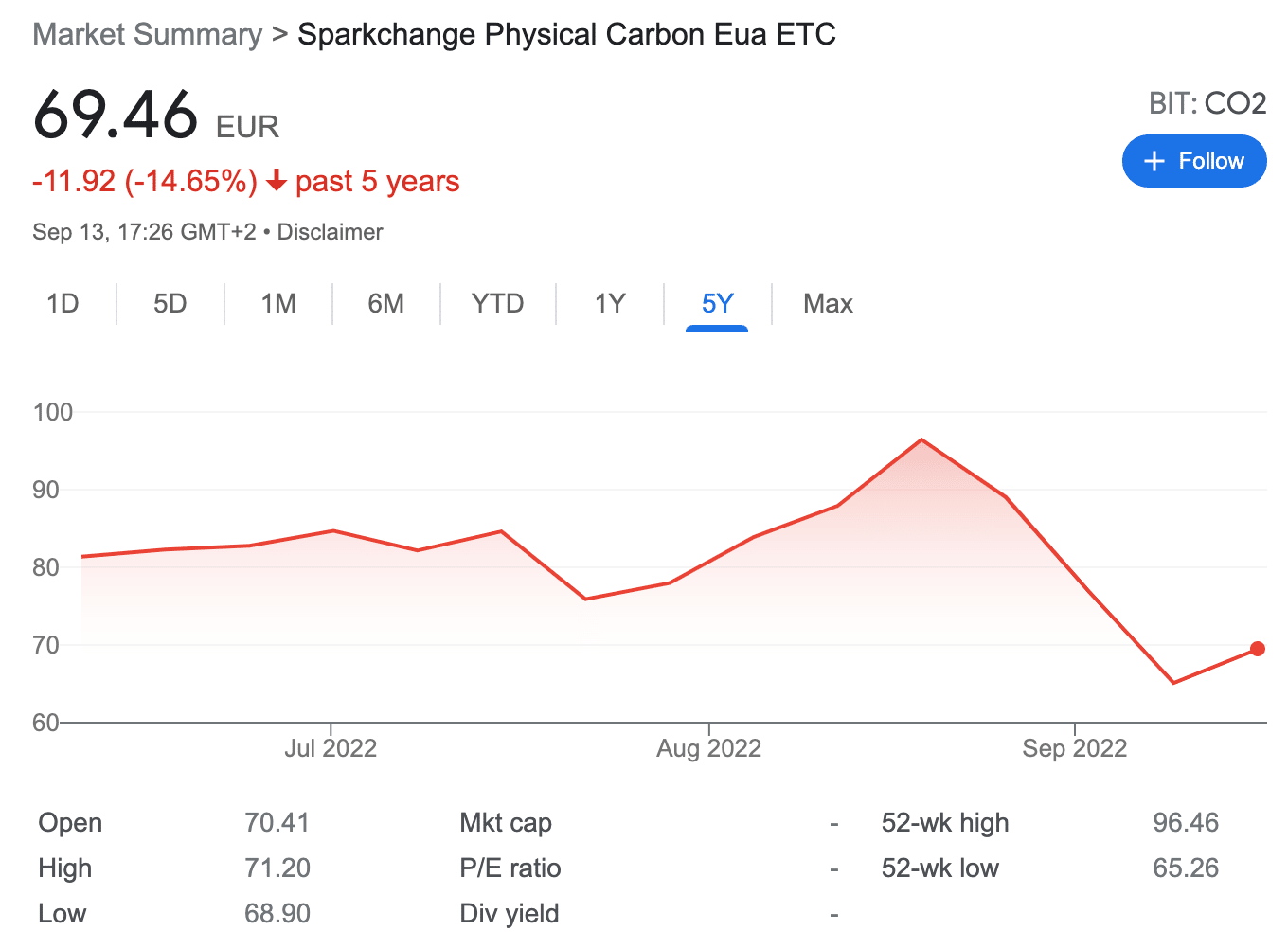
Crucially, by investing in the SparkChange ETC, investors can directly purchase carbon credits, not a derivative. This way, they can be sure that their investment will have a direct and positive environmental impact.
SparkChange’s CO2 ETC is one of the latest financial instruments to hit the carbon credits market, as it was launched only in June 2022. However, since then, due to the rising price of oil, the fund is trading below its inception valuation.
ESG Rating: N/A
10. KraneShares Global Carbon Offset Strategy ETF – ETF Tracking Carbon Credit Futures on the Voluntary Market
The last two KraneShares carbon capture ETFs we discussed track regulated emissions allowances. The KraneShares Global Carbon Offset Strategy ETF, on the other hand, targets the voluntary carbon market instead. It does so by tracking carbon offset futures contracts from the likes of Nature-Based Global Emission Offsets (N-GEOs) and Global Emission Offsets (GEOs).
Before proceeding, let us explain how a cap and trade or compliance market differs from its voluntary counterpart. Cap and trade carbon markets are regulated, meaning, authorities set a limit on carbon emissions. Those who have excess credits are allowed to trade their allowances.
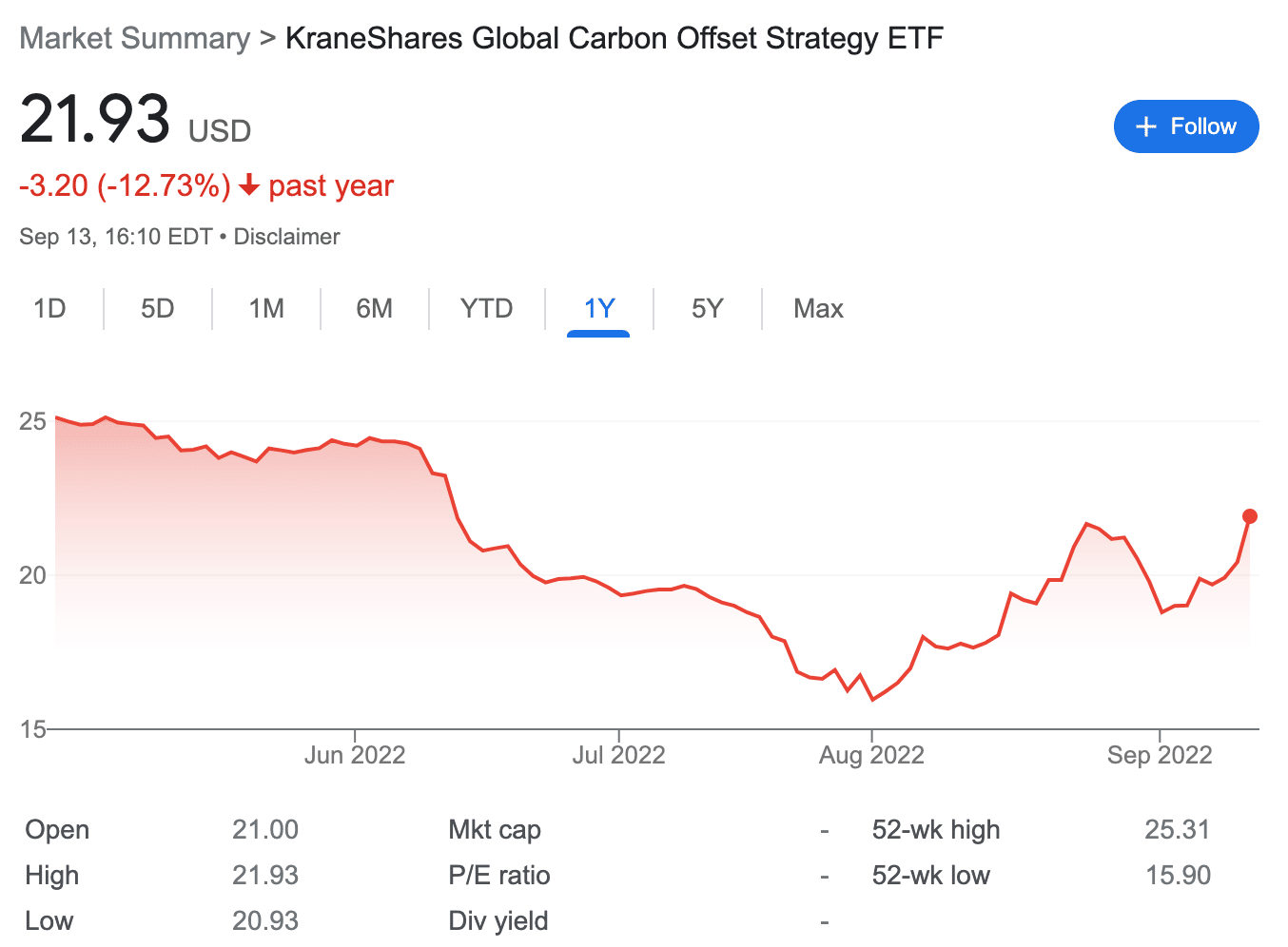
In comparison, voluntary carbon markets are not regulated; instead, they are self-governed. Any organizations or individuals that generate carbon offsets can sell them to others who are willing to purchase them. The KraneShares Global Carbon Offset Strategy ETF only tracks futures that are traded through the CME Group.
The chosen offset projects are also thoroughly vetted by top carbon offset registries. Furthermore, this ETF is designed to add extra offset markets as they reach the pre-determined scale.
The KraneShares Global Carbon Offset Strategy ETF started trading on April 2022. The price of the ETF has decreased by nearly 12% since its inception.
ESG Rating: N/A
11. iPath Series B Carbon ETN – Most Popular Carbon Credits ETN
The iPath Series B Carbon ETN is one of the most popular exchange-traded notes belonging to the carbon credits category. This ETN links its returns to the performance of the Barclays Global Carbon II TR USD Index. Its tracks the price of carbon as measured by the returns of EUA futures contracts.
At the time of writing, the ETN tracks futures contracts that trade on the ICE Futures Europe exchange. The note was first introduced in September 2019 and has grown by over 150% in value since then.
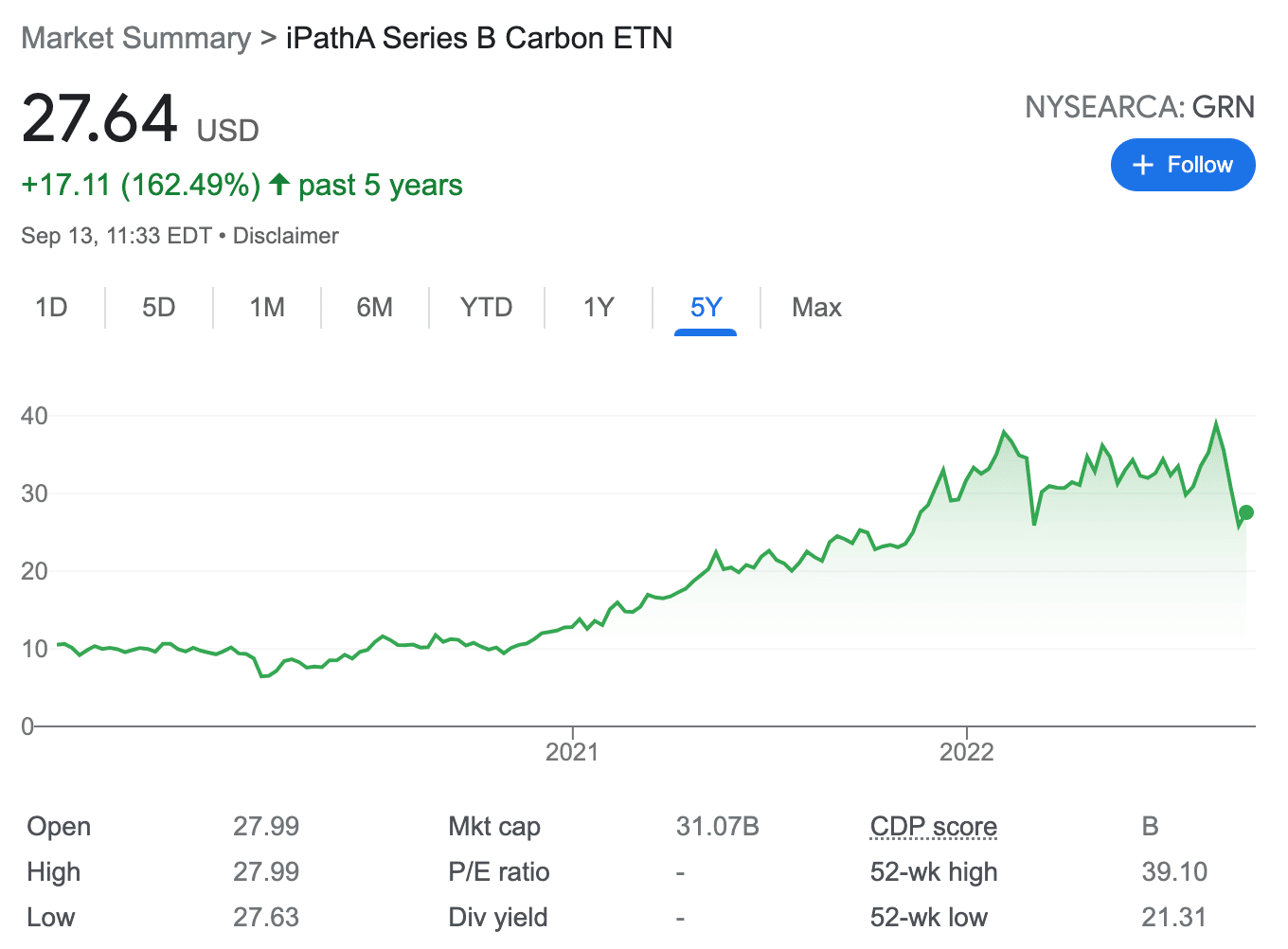
Bear in mind that this is an ETN. As such, while it tracks an underlying asset, investors will not have the capacity to inject capital into the fund directly. Instead, ETNs are issued by an institution – such as a bank, and they function more or less like a bond. In this case, the iPath Series B Carbon ETN is issued by Barclays Bank.
This ETN has posted almost the same returns as that of the Barclays index. It has increased in value by just over 64% in the past year, while the Barclays index returned about 66%.
ESG Rating: B
What are Carbon Credits ETFs?
To appreciate how a carbon credits ETF works, it is important to first gain an understanding of this emerging asset class.
In a nutshell, carbon credits are permits issued by regulatory organizations which allow companies and/or individuals to emit a certain amount of greenhouse gases.
Companies and businesses that pollute the environment are offered a certain number of carbon credits – which indicates how much they are allowed to pollute.
- Over time, this cap is reduced. Meaning, the participants of the regulatory program must emit less greenhouse gases into the environment.
- Alternatively, they will have to purchase additional carbon credits. To meet this demand, regulators then issue or sell additional carbon credits allowances.
- Companies can buy these allowances via the carbon credits market.
- On the other hand, if the company manages to reduce its emission, it can hold on to its allowances to cover future needs or sell them to participants.
There are several regulatory bodies that sell carbon credits – each offering its own version of allowances. For instance, the EUAs are tradable units of carbon credits issued under the European Union Emissions Trading Scheme.
Similarly, there are others, such as the Australian Carbon Credits Units (ACCU) and the California Carbon Allowances (CCA). As the demand for carbon credits continues to rise, the price of these allowances follows suit.
Conversely, as companies become greener, there will be less demand for carbon credits, which will likely result in allowances declining in value. Buying and selling carbon credits directly can be a complicated process, especially since this marketplace might not always be accessible to retail clients. For this reason, some investors are also looking for the best green investment funds in 2025.
To circumvent this barrier to entry, investors can buy and sell ETFs that track the price of the carbon credits allowances issued by various authorities. As we covered above, ETFs in this market track the price of carbon credits futures, or other funds – thus making them more accessible to retail investors.
Why do People Invest in Carbon Credits ETFs?
When assessing how to invest in carbon credits, it is crucial to consider the advantages as well as any identified downsides.
As with other asset classes, carbon credits ETFs offer both risks and rewards.
Below, we discuss some of the core reasons why investors are increasingly exploring the carbon credits industry, and ETFs in particular.
Diversification
Carbon credits offer an alternative investing solution to global investors, presenting them with another way to diversify their portfolios. Moreover, carbon credits and related futures contracts have shown a low correlation with the broader financial market.
This means that funds such as the KraneShares Global Carbon Strategy ETF could potentially provide resilience against climate transition risk. However, bear in mind that not all low carbon ETFs can be used for hedging.
For instance, ETFs that track carbon offset stocks – such as the BlackRock US Carbon Transition Readiness, will not offer the same advantage.
Profit Potential
When considering the current climate crisis, it is not unreasonable to assume that the carbon credits markets are poised to grow. Moreover, there is a limited supply of carbon credits issued by regulatory authorities.
If demand continues to increase, the price of carbon credits could follow suit.
Low Barrier to Entry
There are several ways to trade carbon credits, however, buying and selling allowances directly might not be a feasible approach for retail investors.
Instead, investing in a carbon credit ETF is much simpler. This way, investors only need to find a regulated broker that supports their chosen carbon capture ETF.

This way, investors can gain exposure to this market without having to trade carbon allowance futures directly.
Moreover, ETFs such as the iShares MSCI ACWI Low Carbon Target offer indirect exposure to this space via stocks with less environmental impact.
Environmental and Social Benefits
The main goal of carbon credits is to decrease greenhouse gas emissions. As the price of carbon credits goes up, it gets more expensive for companies to purchase additional allowances.
By investing in carbon credits and related assets, investors can contribute to an emissions-reduction strategy and help make progress toward a net-zero future.
Risks of Carbon Credits ETFs
All that being said, carbon credits ETFs present clear risk considerations, especially if the investor does not have a full understanding of how this market operates.
- Moreover, as we pointed out above, some ETFs in this space are not well diversified.
- This means the exposure is limited to a single market – which can increase the overall risk.
- Therefore, it might be wise to allocate only a small portion of the portfolio to carbon credits ETFs.
It is equally important for investors to make sure that they have a firm grasp of the factors that affect the price of carbon credits, and how their chosen ETF would react to market variations.
Regulated Stock Brokers Offering Carbon Credits ETFs
As carbon credits are still an emerging asset class, it can be challenging to find brokers that offer access to this market. Nevertheless, there are a small number of regulated brokers that offer access to some of the best carbon credits ETFs discussed on this page.
How to Invest in Carbon Credits ETFs
Before rounding off this guide on how to buy carbon credits ETFs, let’s take a look at the investment process. One of the most popular ways to gain exposure to the price of carbon credits is by using IMPT – a blockchain-powered ecosystem that pairs buyers and sellers together with increased transparency.
Although IMPT users won’t be investing in ETFs, they’ll be able to purchase carbon credits directly – providing exposure to their price fluctuations. With that in mind, detailed below are the four simple steps investors can take to buy IMPT tokens, which they can then exchange into carbon credits once the platform goes live.
Step 1 – Set Up a Crypto Wallet
Since IMPT is an ERC-20 token, investors must set up a crypto wallet compatible with this token standard. Many of the best crypto wallets have this functionality, although we recommend MetaMask since it’s free to use.
Head over to MetaMask’s website and click ‘Download’. Choose the appropriate operating system on the following page and follow the on-screen instructions to install the wallet.

Step 2 – Acquire Crypto (Optional)
IMPT allows investors to buy IMPT tokens using FIAT currency. However, some investors may prefer to use crypto. If this is the case, investors must purchase some crypto using an established exchange beforehand. At the time of writing, IMPT supports the following:
- BTC
- ETH
- MATIC
- SOL
- BNB
Step 3 – Connect Wallet to Presale
Go to IMPT’s website and click ‘Connect Wallet’. Choose the appropriate wallet provider and follow the instructions to link the wallet created in Step 1.

Step 4 – Buy IMPT
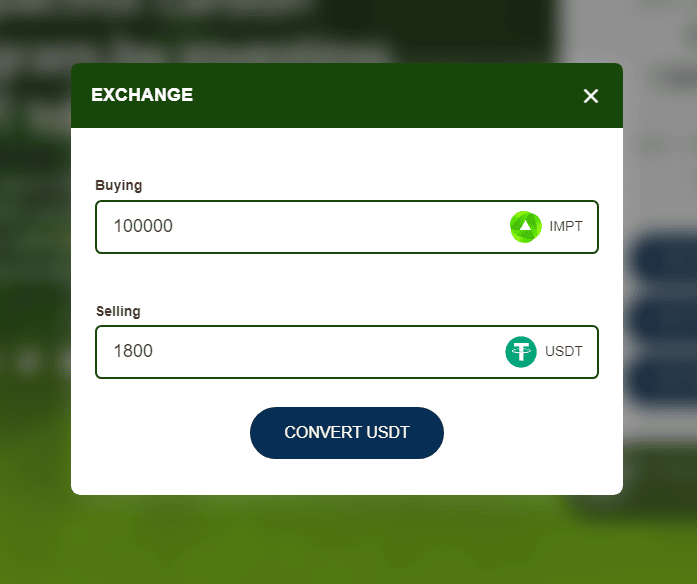
An order box will appear, much like the one below, in which investors can enter the number of IMPT tokens they’d like to purchase (minimum 10). Investors can also choose how they’d like to fund the purchase, whether that be through crypto or FIAT.
Either way, once everything has been double-checked, the transaction can be confirmed. Investors can claim tokens once the contract address is released following the conclusion of the presale phase.
Conclusion
Investing in carbon credits can be an appropriate choice for those looking to inject capital into energy transition. By choosing carbon credits ETFs, investors can diversify their funds into multiple sustainability markets.
This guide has reviewed some of the best carbon credits ETFs to consider right now. We have also discussed why investors might consider this asset class and what advantages carbon credits ETFs present for an investment portfolio.
Those seeking exposure to carbon credits pricing may wish to consider IMPT. This blockchain-powered ecosystem looks to revolutionize how carbon credits are traded – even allowing individuals to acquire them through their everyday shopping activities. IMPT’s presale is ongoing, allowing investors to buy tokens at a significantly discounted rate.

FAQs
What is a carbon ETF?
What are the most popular carbon credits ETFs?
How do I invest in carbon credits ETFs?