Employee productivity statistics reveal the meaningful contributions an employee brings to their work. In the grand theater of business, it’s the high-performing actors that steal the show and propel a company toward prosperity.
For businesses to thrive and achieve both short-term profit and long-term growth, they need more than productive employees.
They need exceptionally productive employees. So, let’s dive into our curated selection of the most eye-opening employee productivity statistics to gain a better understanding of how to make the most of your employees.
Employee Productivity Statistics Highlights
- The average American employee worked an 8.01-hour day in 2022.
- Working remotely enables 70% of employees to maintain focus easily.
- 91% of stressed employees lost productivity due to burnout.
- Low workplace engagement costs the global economy $8.8 trillion, or 9% of the global GDP.
State of Employee Productivity
Employee Engagement Levels
The average employee in America worked an 8.01-hour workday from Monday to Friday in 2022. As per data from the federal US Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), the average full-time employee dedicated an entire eight-hour workday to their job, around 8.42 hours per week, while their part-time counterparts logged about 5.54 hours weekly.
The average worker tends to be less active and make more errors during afternoons and Fridays, with Friday afternoons being the period when workplace productivity reaches its lowest point.
Researchers at Texas A&M University arrived at these conclusions based on computer usage metrics for office workers like typing speed, typing errors, and mouse activity. The team subsequently analyzed computer usage patterns, examining variations across various days of the week and different times of the day to identify the trends.
The Increase of Productivity in the Workplace
The BLS reported that in the second quarter of 2023, labor productivity in the nonfarm business sector increased by 3.5%, while in the manufacturing sector, it rose by 2.9%. These improvements may be the result of various factors, including enhanced employee performance, ultimately contributing to economic growth and competitiveness.
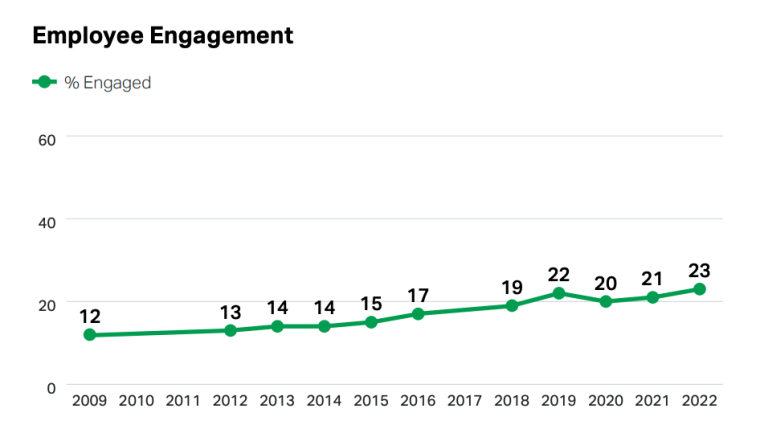
Additionally, 23% of the global workforce exhibited high levels of employee engagement in 2022. According to a study by Gallup, this marked the highest level of engagement recorded since 2009.
While there was a dip in engagement in 2020, likely attributed to the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic, it has since rebounded to follow its historically positive trend. Furthermore, the most productive countries are in South Asia, with a 33% employee efficiency rate.
The 1-3-5 rule in the workplace can enhance an employee’s average productivity levels by providing a clear and manageable structure for their daily tasks. By setting one main priority, three secondary tasks, and five smaller to-dos for each workday, employees focus on their most important goals while also ensuring they address other essential responsibilities.
While there is no empirical evidence to support this method, there is a range of anecdotal evidence to suggest it ultimately leads to better time management and increased efficiency for the average office worker.
Why You Should Measure Employee Productivity
Employee productivity measures economic performance which evaluates the ratio of produced goods and services (OUTPUT) to the effort and resources (INPUT) expended in their production.
For example, consider a scenario involving employee productivity of a customer service team in a call center. In a week, the team of 10 representatives collectively handles 1,000 customer inquiries. Here, the OUTPUT is 1,000 inquiries resolved, and the INPUT is the combined hours worked by the team during that week.
How to Calculate Employee and Workplace Productivity
To calculate net productivity levels, you’d divide the OUTPUT (1,000 inquiries) by the INPUT (total hours worked by the team). If, for instance, they worked a total of 250 hours, the average productivity rate would be 4 inquiries resolved per hour.
This measurement enables businesses to assess the efficiency of their customer service operations and make adjustments as needed to meet customer needs more effectively.

Remote Work and Employee Productivity Stats
34% of employed individuals engaged in some or all of their work remotely from home. Meanwhile, 69% performed their work primarily at their workplace.
On an average workday, remote employees dedicated 5.4 hours to their work, while those working on-site typically put in 7.9 hours. These statistics shed light on the evolving landscape of work, where flexibility and productivity are redefining the way we approach our jobs and workplaces.
Out of 39% of individuals who engage in remote work several times a month, 77% of them noted increased productivity while working remotely.
Whether it’s the enhanced efficiency that remote work allows or the increased motivation to showcase their effectiveness outside the office, 30% of remote workers achieve more tasks in less time. Another 24% find themselves accomplishing the same workload within the regular timeframe.
In addition, 23% are willing to extend their work hours beyond the usual on-site schedule to achieve greater productivity, and 52% are less inclined to take time off, even when they are sick, resulting in fewer sick days while working remotely.
Habits of Work from Home Employees
Remote workers tend to extend their hours beyond the conventional office schedule.
According to an employee productivity statistics survey by Buffer, 48% of remote workers find themselves working frequently outside of the traditional nine-to-five schedule. Further:
- 81% admit to regularly checking work emails outside of their designated work hours.
- 63% check emails on weekends.
- 34% check their emails during their vacations.
22% of remote workers struggle to disconnect from work and achieve a work-life balance. This challenge can impact the productivity of remote employees, potentially leading to burnout and reduced effectiveness in their tasks due to the lack of clear boundaries between work and personal life.
Working remotely makes it easier for 70% of individuals to maintain focus.
- 65% of remote workers find it more manageable to handle workplace stress.
- 50% of WFH employees can avoid distractions such as other employees more effectively while working remotely.
- 58% are either very or somewhat engaged in their job.

In terms of workplace stress, whether an employee is engaged in their work is 3.8 times more important of a factor than where they work – so where a person works has much less of an effect on stress levels than how much they care about what they do, according to a 2023 Gallup report.
Factors Affecting Employee Engagement
Interruptions Influence Employee Productivity
The average employee in the US experiences 56 interruptions each day.
80% of interruptions are categorized as trivial in the workplace, which means that the majority of interruptions employees face are minor and often do not contribute significantly to their tasks or goals.
Interruptions can impede productivity and require employees to divert their attention from more important and valuable work. On average, employees work for only 3 minutes before they switch tasks. This frequent task-switching results in employees spending approximately 2 hours per day recovering from distractions.
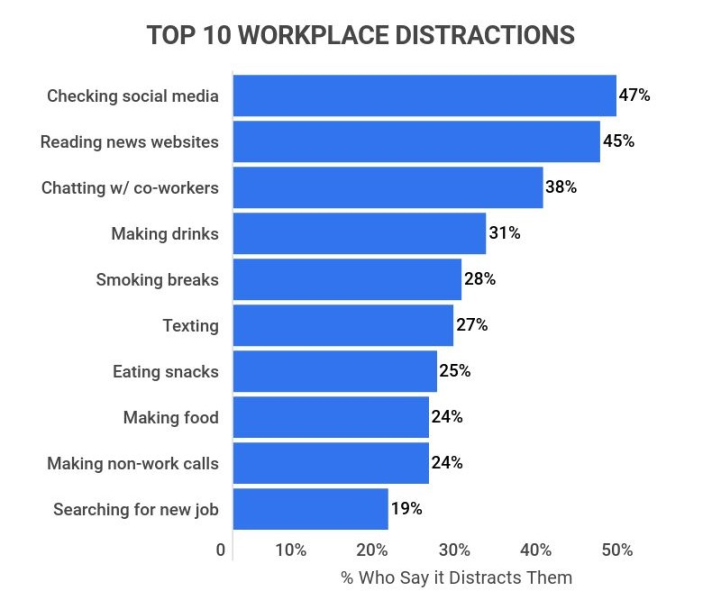
According to employee productivity statistics from Zippia, 47% of employees are distracted from their workplace tasks due to social media.
Unnecessary Meetings and Redundant Tasks Cause Reduced Productivity
Employees spend 31 hours each month in unproductive meetings, according to data from Atlassian.
US employees have 62 meetings per month on average, which reflects the significant portion of their work hours allocated to these gatherings. Unfortunately, up to half of these meetings are perceived as unproductive or time-wasting, contributing to challenges in time management and overall productivity.
62% of employees lose part of their workday to repetitive tasks. Worker productivity is wasted on tasks that are monotonous, routine, and lack variety or intellectual challenge.
These repetitive tasks often do not contribute to productivity or the accomplishment of more important and meaningful work goals. Furthermore, repetitive tasks can be detrimental to overall workplace efficiency and job satisfaction.
Multitasking Productivity Stats
Brief interruptions caused by switching between tasks can potentially consume up to 40% of an individual’s productive time. According to a productivity study conducted by researchers at the University of Southern California, employee productivity statistics demonstrate that multitasking reduces productivity.
Multitasking consumes additional time when individuals switch between tasks, necessitating mental gear shifts. For example, if a worker transitions from analyzing financial data in a spreadsheet to composing emails, their brain must shift focus and determine that it’s now moving from a numerical task to a linguistic one.
The Effect of Emails on Employee Productivity
Employees receive 304 business emails per week, reflecting the high volume of digital communication in the modern workplace.
Excessive emails are a top contributor to poor employee productivity. This constant influx of messages leads employees to check their email approximately 36 times in a single hour, highlighting the pervasive nature of email interruptions throughout the workday.
Furthermore, the time spent refocusing after handling incoming emails amounts to an average of 16 minutes, emphasizing the disruptive impact of email on employee productivity levels.
These employee productivity statistics underscore the need for effective email management strategies to mitigate the negative effects of email-related distractions on work efficiency.

Employee Wellbeing and Productivity Stats
Stress Negatively Affects Productivity
Approximately 1 million Americans miss work each day because of stress. The American Institute of Stress reported in 2020 that job stress costs the US industry over $300 billion due to:
- Absenteeism
- Decreased productivity
- Accidents
Each week, an employee will lose an average of more than five hours working time when they think about their personal stressors.
91% of stressed employees report that burnout caused a decrease in productivity. Burnout is a major challenge for both institutional and individual productivity in the workplace. That’s because major productivity losses related to burnout can dramatically affect the quality as well as the quantity of any employee’s work.
Future Forum research has shown that a who lack of work-life balance and schedule flexibility are 43% more likely to report feeling burned out compared to those who are happy with their flexible working options.
The US and Canada have the highest regional percentage of daily stress in the work environment. Furthermore, Canada and the United States exhibit the highest regional percentage of female workers dealing with daily high-stress levels at work, with 33% of women in these regions reporting daily stress experiences.
Sleep Deprivation and Employee Productivity
Sleep deprivation can negatively impact worker productivity, quality, and interpersonal working relationships.
A 2007 study found that nearly 38% of workers in the US had experienced fatigue at work.
According to a survey by Glassdoor, 66% of US adults agree they could improve productivity at work if they got more sleep, particularly among individuals aged 18-44.
How to Boost Employee Productivity
Workplace Productivity Statistics: Involving Team Members in Decision-Making
In a Lithuanian study in 2022, it was found that when a worker found meaning, enthusiasm, and competency along with information, resources, and opportunities, they felt psychologically and structurally empowered.
Highly engaged employees are generally more productive and also exhibit higher retention rates and lower instances of burnout within their organizations.
In 2022, employee engagement rates in the US were 32% according to a Gallup survey. Collaboration, employee wellbeing, and performance were all key to engagement, with the best companies in the survey reaching 70% employee engagement.
Employee Satisfaction with Financial Compensation
When employees are in a state of active disengagement, 61% of them are either actively looking for a new job or keeping an eye out for new opportunities.
Engaged employees typically need a 31% salary increase as an incentive to contemplate switching to another organization, while their counterparts who are not engaged or actively disengaged, on average, desire a 22% pay raise to consider changing jobs.
Increased Productivity with Positive Workplace Interactions
Positive interactions in the workplace create a conducive environment that promotes more productive employees. These factors collectively lead to improving productivity as employees are more motivated, focused, and satisfied in their roles.
A study published in the Harvard Business Review found that teams with higher levels of positive interactions and mutual support tend to perform better and are more productive.
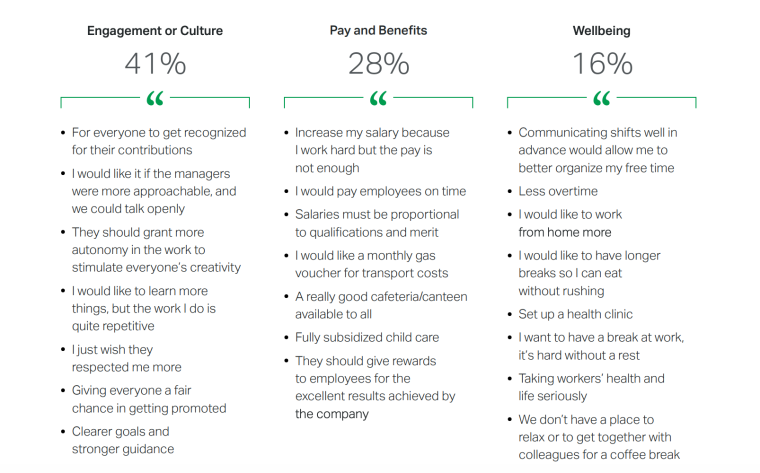
What’s more, according to survey results from Gallup, 41% of employees would prefer for their workplace to improve in the engagement and culture sector. This would include:
- Recognizing everyone for what they contribute.
- Granting autonomy to increase productivity.
- Allowing employees to learn more skills at work.
Time Management and Employee Productivity
To boost productivity in the workplace, organizations are increasingly exploring strategies to streamline meetings and make them more purposeful.
For example, setting clear agendas and objectives and utilizing productivity software and collaboration tools.
Productivity and Technology
Digital productivity tools have revolutionized the way employees work, offering a multitude of benefits to increase productivity. These tools streamline tasks, automate processes, and provide efficient ways to collaborate, ultimately saving time and reducing manual labor. Some notable software for employee collaborations include:
A 2020 Asana survey found that 87% of respondents saw an increase in productivity levels while using the tool. Meanwhile, Slack’s internal data in 2021 showed that it reduced email use by 32% and meetings by 23%. In a case study of a Zoho client, an uplift of 30% in productivity was observed after implementing the tool.
The power of implementing leading technology to increase workplace productivity is clear.
Music for Workplace Productivity
Music can help employees concentrate better, reduce stress levels, and create a more pleasant work environment, all of which contribute to enhanced productivity, says an analysis of studies from Harvard Business Review.
However, it’s important to note that the effectiveness of music in the workplace can vary among individuals, the effects of music on performance can depend on various factors, for example:
- the choice of music genre
- task complexity
- individual personality and taste
The Importance of Work-Life Balance
Taking regular breaks and adopting shorter workdays seems to increase productivity. While it may feel counter-intuitive, studies have demonstrated that when a work week is shortened and work-life balance improved, productivity often increases.
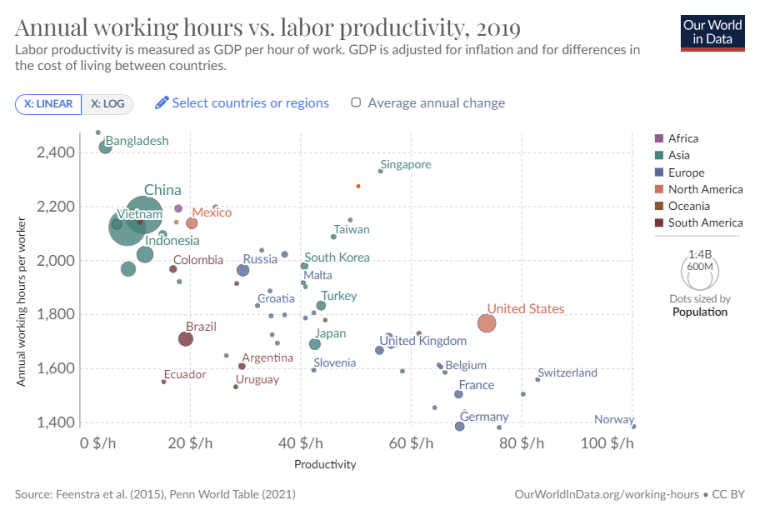
Nations that have shorter average annual working hours tend to have a higher dollar value productivity per hour, based on national GDP. Singapore is a notable outlier to the trend, with a high annual working hour average and a relatively high productivity rate.
The Most Productive Countries
Luxembourg was the world’s most productive country (per capita) in 2022. According to data collected from the OECD and World Bank, Luxembourg’s strong financial sector is the main reason for this, but cross-border workers also play a big part.
Global Average Hourly Work Productivity Statistics
The size or complexity of a country’s economy does not guarantee unusually high employee productivity though these factors are often correlated. For example, despite having the world’s largest economy and longer working hours than many nations, the United States does not rank among the top ten countries in terms of productivity per person. The US still has relatively impressive GDP and productivity figures nonetheless.
- GDP per capita($): 69,288
- Hours worked: 1,791
- Productivity per person per hour ($): 38.69
The Cost of Employees’ Productivity
Useless meetings stand as a primary driver of employee productivity expenses. Unnecessary meetings cost US businesses an estimated $37 billion in salary expenses.
Poor workplace engagement costs the world economy $8.8 trillion, which is 9% of the global GDP. Research by Gallup has suggested that effective leadership and management play a crucial role in boosting workplace engagement, and organizations can take significant steps to help their employees thrive at work.
The Need for Increased Employee Productivity
The pursuit of increased worker productivity has become a paramount objective for organizations worldwide.
Heightened productivity not only translates into greater profitability but also fosters an environment of operational excellence.
By improving employee productivity, companies can accomplish more with existing resources, reduce operational costs, and optimize their workforce’s potential. Moreover, in an era characterized by global competitiveness and technological advancements, organizations that help employees increase productivity gain a distinct edge in the market.
The Impact of Diversity and Inclusion on Productivity
Diversity and inclusion (D&I) are no longer just buzzwords; they are key drivers of workplace productivity and innovation.
Research consistently shows that diverse teams outperform homogeneous ones, offering fresh perspectives, creative problem-solving, and improved decision-making. A McKinsey report revealed that companies in the top quartile for gender and ethnic diversity were 25% more likely to have above-average profitability than their less diverse counterparts.
Inclusivity plays a pivotal role in fostering a sense of belonging, which directly impacts employee engagement and satisfaction.
Employees who feel included are 3.5 times more likely to contribute to their full innovative potential, according to Deloitte’s 2020 Inclusion Pulse Survey. Moreover, inclusive teams make better business decisions up to 87% of the time.
However, achieving diversity and inclusion is not just about filling quotas.
It requires intentional hiring practices, ongoing training, and leadership commitment. Companies like Microsoft and Accenture have set benchmarks by embedding D&I in their cultures, leading to higher retention rates and greater employee productivity.
In today’s competitive world, businesses that prioritize D&I not only create a more equitable work environment but also position themselves for sustained success.
The Role of AI and Automation in Enhancing Productivity
Artificial intelligence (AI) and automation are transforming workplaces, revolutionizing how tasks are completed, and boosting productivity. From chatbots handling customer inquiries to AI-driven analytics providing actionable insights, these technologies are enabling organizations to achieve more with less.
A report by McKinsey estimates that AI can increase global productivity by 1.2% annually over the next decade.
Tools like robotic process automation (RPA) streamline repetitive tasks, such as data entry and payroll processing, freeing employees to focus on strategic and creative work. For instance, Deloitte implemented AI in its audit processes, reducing review time by 50% while improving accuracy.
However, the integration of AI is not without challenges. Concerns about job displacement and ethical implications remain top of mind for employees and policymakers alike. To mitigate these concerns, companies must invest in upskilling and reskilling their workforce, ensuring employees can collaborate effectively with these advanced tools.
AI and automation are not replacing human ingenuity but amplifying it. Businesses that embrace this symbiotic relationship will unlock new levels of efficiency and innovation.
Mental Health and Its Effect on Productivity
Mental health is a cornerstone of workplace productivity, yet it remains an often overlooked factor.
The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that anxiety and depression cost the global economy $1 trillion annually in lost productivity. Stressed or burned-out employees are more likely to disengage, leading to decreased performance and higher turnover rates.
A 2022 Gallup report found that 23% of employees worldwide feel burned out very often or always, with burnout being linked to absenteeism, reduced output, and a decline in workplace morale.
Conversely, organizations that prioritize mental well-being see tangible benefits. For example, companies that implement Employee Assistance Programs (EAPs) report a 24% reduction in absenteeism and a 14% increase in productivity, according to research by the American Psychological Association.
Workplace initiatives, such as flexible hours, mental health days, and access to counseling services, can alleviate stress and promote a healthier work-life balance. Tech giants like Google and Salesforce lead by example, offering mindfulness programs and onsite wellness facilities to support employee well-being.
Investing in mental health is not just a moral imperative; it is a strategic business decision.
A mentally healthy workforce is more engaged, resilient, and productive, creating a win-win scenario for employees and employers alike.
Wrapping Up
Boosting employee productivity requires a comprehensive strategy that includes effective leadership, a focus on mental health, and the integration of technology.
By understanding and addressing key productivity challenges – such as distractions, burnout, and ineffective processes – organizations can create a work environment that fosters engagement and operational excellence.
In a competitive global economy, businesses that prioritize productivity through innovative practices and supportive cultures will remain agile and successful. By implementing the insights and strategies discussed, companies can unlock their workforce’s full potential and drive sustainable growth.