Cash App is among the most popular payment apps. It provides a quick, inexpensive way to send and receive money, save, and invest. However, users familiar with a traditional bank might wonder, “Is Cash App safe?” Here’s the scoop on the platform’s privacy policy and security features, how to steer clear of common Cash App scams, and tips for staying safe while using Cash App.
What Is Cash App?
Cash App is a digital financial services platform and mobile payment app. It is not a bank but it offers banking services, such as:
- receiving money
- sending money
- payments
- saving
- debit cards
- tax filing
- overdrafts
- investing services
Is Cash App Legit?
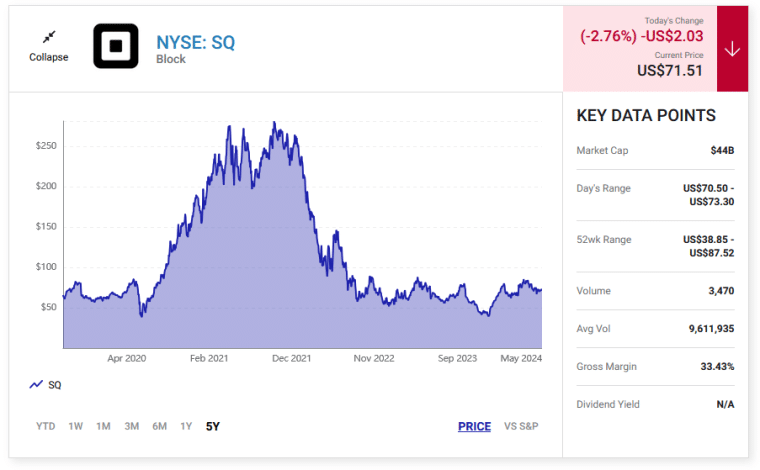
Cash App is indeed legit and safe as it is an established and popular company with extensive security features. There are more than 24m active Cash App Card users and, between January and May 2024, users deposited over $1b in Cash App Savings accounts.
The payment app made over $1B in profit in the first quarter of 2024, and Block, the company that developed Cash App, is a listed company worth $44B.
Why Use Cash App?
Many customers find that financial services apps have advantages over traditional banks – including faster transaction speeds and lower fees.
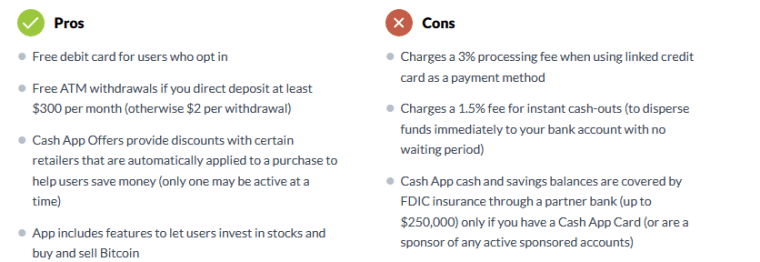
Cash App is the top-rated personal finance app on the app store. It offers free basic banking services, discounts at certain retailers, and the ability to invest in stocks and Bitcoin. Users do not need a traditional bank account to send and receive payments using the app.
CNBC named Cash App the best app for budding investors and Investopedia named it the best app for buying and selling Bitcoin.
Cash App Safety Features
Cash App is PCI-DSS Level 1 compliant meaning the app adheres to a set of practices designed to ensure the security of transactions and prevent breaches of personal information.
The features that Cash App has in place to keep your money safe and protect your information include:
- Encryption. According to their website, Cash App uses cutting-edge data encryption. This means your data is scrambled so that, even if it is intercepted by hackers, it is unreadable without an encryption key. Encryption ensures your data is safely transmitted from your device to Cash App’s servers.
- Fraud detection. Cash App’s fraud detection system keeps an eye on users’ accounts. If any payments seem suspicious, they are canceled and the money is quickly returned to the sender’s account. Cash App users are also alerted if their sign-in code or security settings change and can opt to get notifications when they send or receive a Cash App payment.
- Identity verification. Cash App uses one-time-use login codes, touch ID, and facial recognition to ensure no one else can gain access to your account. You will be asked to verify your identity if you send or receive a large amount, order a debit card, or make an investment.
- Card locking. You can temporarily lock your Cash App debit card if is lost or stolen to prevent unauthorized transactions.
What Happens If Cash App Goes Out of Business?
The Consumer Financial Protection Bureau has issued a warning that, in the unlikely event that a financial services app goes out of business, your money may be at risk. This is because apps don’t always carry the same FDIC protection as traditional bank accounts.
The Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC) is an independent agency of the US government. FDIC protects the money in your bank account by insuring it to the value of $250k or more, so that is is safe if the bank fails.
Cash App is not a bank (and thus it isn’t FDIC-insured), but it does work with Wells Fargo, its partner bank, to secure some user funds. Your Cash App balance is only FDIC-insured if:
- You have a Cash App Card
- You are an adult who sponsors an account for a minor
- You are a minor with an active sponsored account
FDIC is there to cover you when a financial institution fails so it’s worth noting that your Cash App investing and Bitcoin balances are not protected if your investments lose value. FDIC also doesn’t cover individual Cash App payments including fraudulent transactions.
What About Outside the US?
Check local policy to find out whether your Cash App account is protected by your government.
In the UK, for example, bank deposits are protected by the Financial Services Compensation Scheme (FSCS), which does not cover Cash App deposits. Instead, UK users are protected by a policy called “safeguarding” which ensures their deposits are covered if Cash App goes out of business.
Safeguarding means Cash App has a legal obligation to keep your money safe by putting it in a protected bank account, investing it in low-risk assets, or taking out insurance.
Safety Tip:
If you’re a US user, consider getting a Cash App Card so you’ll be covered by FDIC. Alternatively, consider limiting your Cash App balance so you’ll lose less if the platform goes bust. Store your cash in a linked bank account and only move cash to Cash App when you need to make a transaction. Similarly, when you receive money, make a habit of moving it to your bank account.
Are My Investments SIPC-insured?
The Securities Investor Protection Corporation (SIPC) protects customers if their brokerage firm goes out of business. It insures customers’ securities and cash up to $500k.
Cash App is a member of SIPC and securities in your Cash App account are SIPC-insured. However, cash from sales of investments is not SIPC-insured.
Is Your Privacy Protected By Cash App?
Like other financial services apps, Cash App collects lots of user information, including (according to their privacy policy):
- identifying information e.g. zip code
- financial information e.g. bank account information
- contact details of people you send money to
- transaction history
- geolocation i.e. where you are
- device information e.g. IP address
Users can opt to share additional sensitive information, like a driver’s license, in order to become a verified user, as well as their phone contact list, a photograph, and survey responses.
Some of this data is necessary to provide users with Cash App’s services while some is used for marketing purposes.
Cash App shares user data with third parties including partner companies, service providers and government agencies.
What Are My Privacy Options?
Users’ options are limited when it comes to data collection, but there are a few things you can do if you’re concerned about privacy.
- Opt out of sharing your precise location by changing the settings on your device – although this may limit the functionality of your account.
- Use a virtual private network (VPN) to hide your IP address.
- Some locations have additional laws that give you more control over your data. In California, for example, you have the right to opt out of sharing your information for certain kinds of advertising.
What About The Cash App Data Breach?
In 2022, Cash App announced that a former employee had downloaded reports containing personal information about US users – including names and brokerage account numbers. This is concerning, but it’s not clear whether any users lost money because of this breach. This problem is not unique to Cash App – nearly 70% of companies are worried about insider cybersecurity threats and these kinds of breaches are unfortunately common in tech.
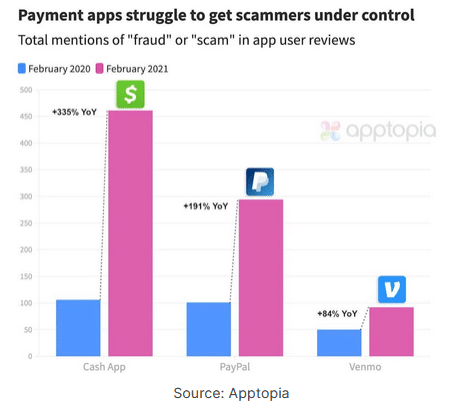
Common Cash App Scams
Unfortunately, many users fall victim to Cash App scams, and many complain that they received limited assistance from Cash App’s support team. It’s important to dodge any Cash App scams you encounter as you may never recover lost money or data.
Here are some 6 common Cash App scams and how to avoid them.
1. Send-Cash-To-Get-More-Cash Scams
In this Cash App scam, the scammers promise to increase your money if you send them some funds first, but they never send you anything in return. This kind of promise is called “cash flipping.”
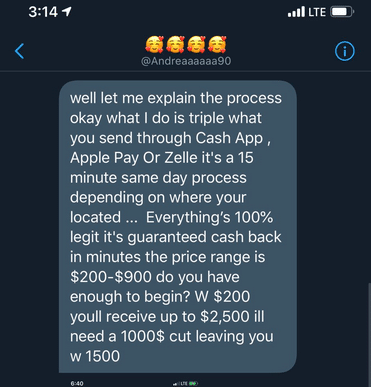
Cash flipping scammers may request funds as a deposit, clearance fee, or administrative charge in order to release money to you. They might request that you complete a “test transaction.” They may also claim that they will invest your money, promising guaranteed returns.
Safety Tip:
To avoid scams, never trust anyone who promises you free money and don’t send money to strangers unless you can verify their identity.
2. Deposit Scams
Scammers may ask for a deposit for a product or service that turns out not to exist, such as a rental apartment or a puppy or kitten – especially pets of an expensive breed at an unusually low price. Once they receive the funds, they disappear.
Safety Tip:
If you’re buying something from a stranger (especially something high-value), verify their identity or meet in person (ideally in a public, secure place) and view the product before making a deposit. Ideally, only make transactions with reputable organizations or someone you know.
3. Accidental Payment Scams
The “accidental payment” scam is a form of money laundering. Scammers hack into an account and steal money. They then set up a fake Cash App account and send the stolen money to you. They send you a message telling you they made the payment by mistake and ask you to send the money back to them. In the meantime, the bank finds out about the stolen money and reverses the original payment.
Alternatively, the scammer may simply send you money, ask for a refund, and then dispute the original payment to get a refund from their bank.
Safety Tip:
If you receive money from someone you don’t know and they tell you it was a mistake, you can either use the refund function to return the money (do not set up a new payment!) or decline their request and report and block them.
4. Fake Giveaway Scams
Scammers create a social media account that looks like the official Cash App account. They set up a fake cash giveaway or prize draw with hashtags like #cashappgiveaway or #cashappfriday and ask participants to download an app, send sensitive information, buy a product, or complete a “test transaction” to enter.
Cash App does hold sweepstakes on its official X (formerly Twitter) account (https://twitter.com/CashApp) where customers can win money but they never ask participants to share their Cash App pin or sign in code, send money, or download an app. Winners will always be paid from a verified Cash App account.
Safety Tip:
Only enter competitions if they come from an official Cash App account. Here is a list of legitimate accounts from the Cash App website.

5. Phishing Scams
Phishing is the most common type of cyber crime and Cash App is not exempt from this kind of scam. Phishing scammers pretend to be a legitimate company. They may communicate with their victims by phone, email, text message, or social media acting as a Cash App representative or Cash App support.
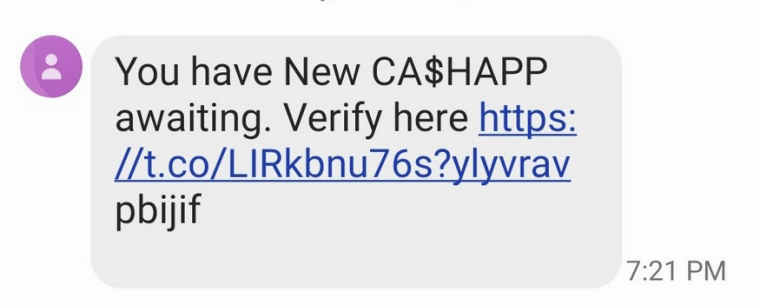
Phishing scammers usually ask the recipient to reply or follow a link to update their account information, confirm a purchase, or change their password. This allows the scammers to steal sensitive information such as bank account details, sign in code, or social security number.
Phishing communications may contain a link or an attachment that triggers the installation of spyware – software that gives scammers remote access to your device.
Safety Tips:
- Never share sensitive information via email or social media or over the phone. Cash App will not ask for full bank account information or personal info via these channels.
- Get good at spotting phishing messages. Check that communications come from an official account or a legitimate Cash App phone number. Grammatical errors, out-of-date logos, demands to act quickly, and generic greetings (e.g. Dear user) are major red flags (but not all phishing emails have them).
- Avoid links. Instead of clicking on a link in a message, open the Cash App app or go to the official website and log in to check for new messages.
- Enable two-factor authentication so that anyone who steals your login credentials will not be able to access your account.
- Report phishing attempts by contacting Cash App support.
- Use antivirus software to keep your device safe from spyware.
- Update your password if you think you’ve fallen victim to phishing.
6. Catfishing Scams
Some scammers pose as someone looking for love online. They earn their victims’ trust, making them believe they have a genuine romantic connection, but offer excuses about meeting in person. Then they ask for money, perhaps claiming an emergency or saying they’ll use it to cover travel expenses to visit their victim.
Safety Tips:
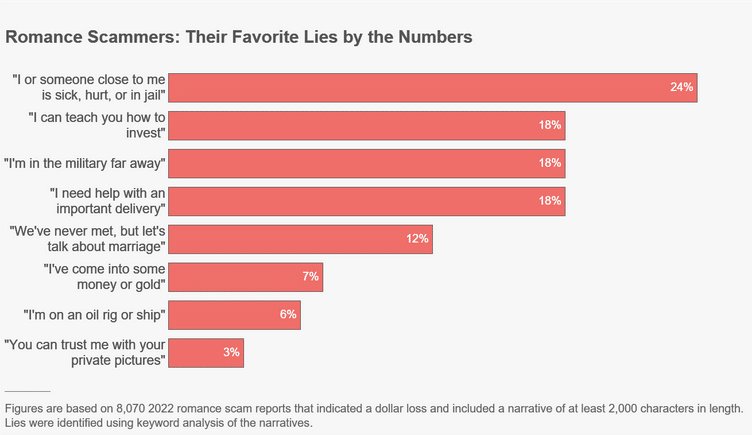
Once again, never send money to anyone unless you can verify their identity. Look out for these common lies which have been identified by the Federal Trade Commission.
Tips For Staying Safe on Cash App
Here are some of the best ways to stay safe while using Cash App.
- If a deal seems too good to be true, it probably isn’t true.
- Keep your Cash App balance low.
- Get a Cash App debit card to ensure you are covered by FDIC.
- Turn on notifications so you are aware of transactions on your account.
- Turn on Security Lock to require a PIN, Touch ID or Face ID for payments from your account.
- Contact Cash App support if there is strange activity on your account.
- Don’t send money to someone you haven’t met if you cannot verify their identity.
- Double-check details before sending money to ensure you send it to the correct person.
- Enable privacy settings so you only receive payment requests from your existing contacts.
- Use antivirus software and set strong passwords.
So Is Cash App Safe?
Security features like encryption, fraud detection, two-factor authentication, and payment notifications help to keep Cash App users safe. Like PayPal and Venmo, Cash App shares user information with third parties. Unfortunately, this is now a common practice but isn’t necessarily a major security risk.
Users’ money will be at risk if Cash App goes bankrupt, but customers can access FDIC insurance for this eventuality by taking out a Cash App card.
The biggest risk to Cash App customers is scams. If you look out for phishing, keep your balance low, and never send money to strangers, you should be able to use Cash App safely like many people around the world.