A fixed deposit (FD) is perfect for those looking for low-risk investments.
This guide will walk you through the workings of fixed deposits, highlight their benefits, and explain how to calculate your returns using our FD calculator.
What Is a Fixed Deposit?
A fixed deposit is a savings account that fixes your money at a set interest rate for a set length of time. It is a low-risk vehicle for short to medium-term savings – usually ranging from about six months to five years.
Our fixed deposit (FD) calculator is a handy online tool that helps users calculate the maturity amount of their fixed deposits by simply inputting the principal amount, interest rate, and duration.
The FD calculator simplifies the process of determining the expected returns. You can find the calculator by scrolling down in this article.
Fixed deposits are available from some banks and other financial institutions. Their main advantages are that they usually offer a higher interest rate than other savings accounts and the interest is predictable and guaranteed.
Fun Fact: In some countries a fixed deposit is known as a term deposit, certificate of deposit (CD), time deposit, or savings bond.
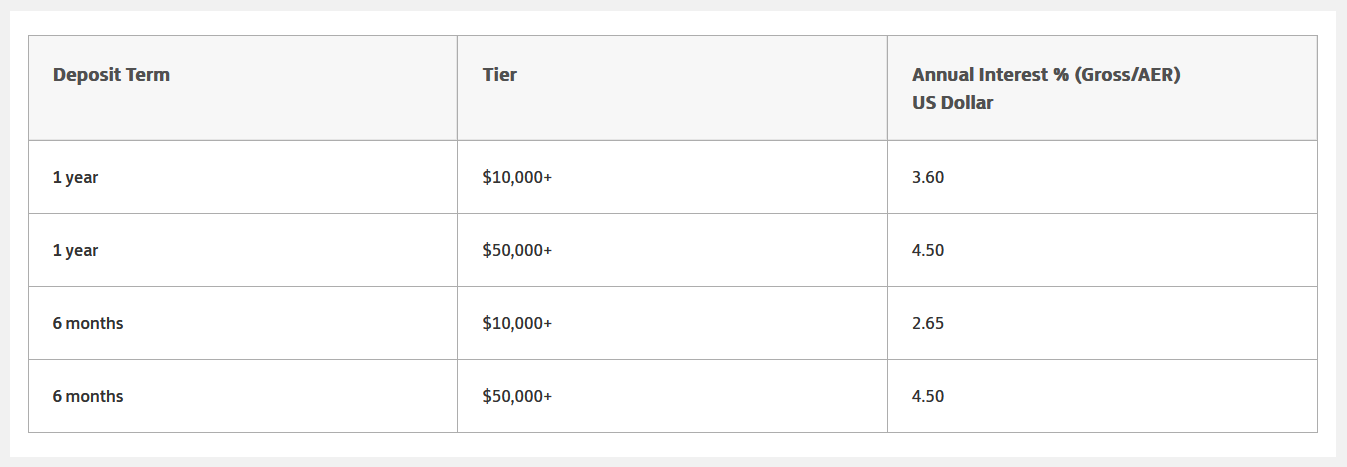
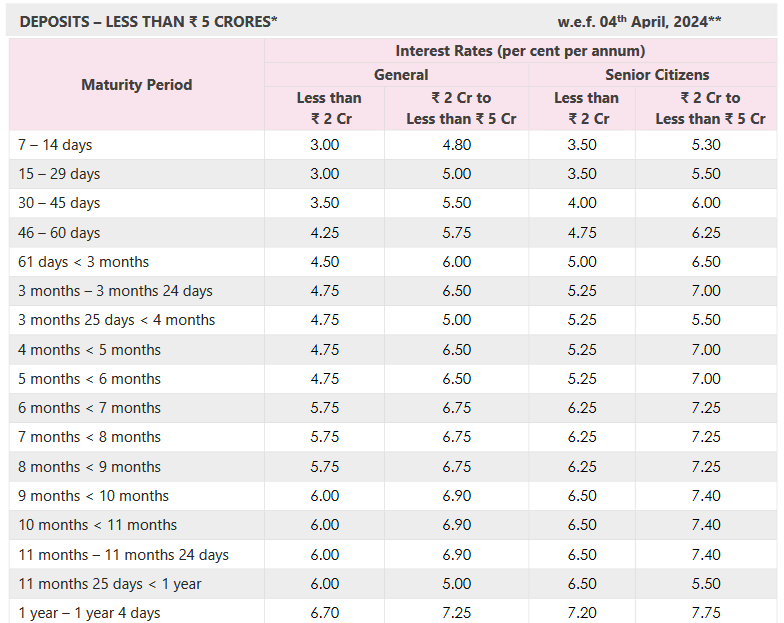
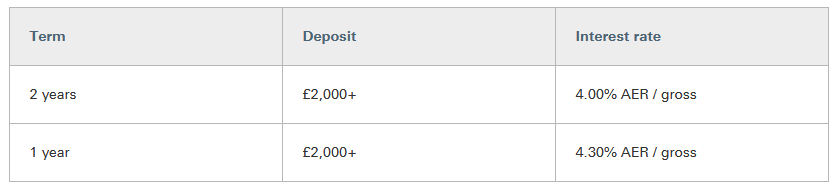
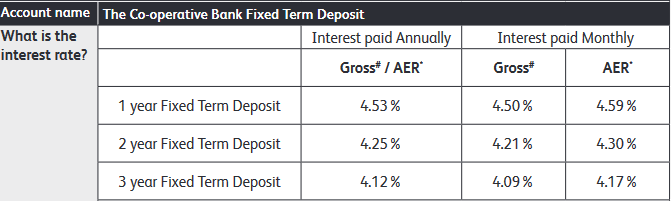
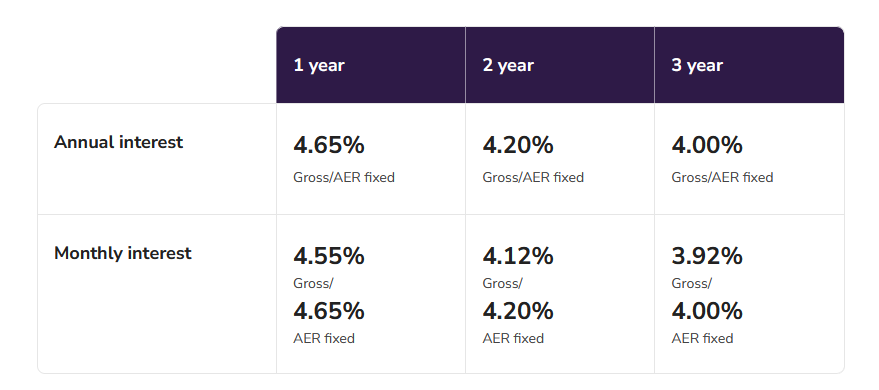
Pro Tip: Some banks offer higher interest rates on the renewal of your fixed deposit, which can be a smart way to increase your returns over time. Many financial institutions offer a selection of fixed deposit accounts with predetermined interest rates and periods. There will be a minimum deposit requirement. Once you have selected a period and deposited the capital amount, the interest rate is locked in until the end of the period. Most fixed deposits do not allow withdrawals or additional deposits until the date the deposit matures. If withdrawals are allowed, they may be subject to penalties or an enforced delay. Interest may be paid out monthly, annually, or on the date the deposit matures, depending on the terms of the fixed deposit. Use our Fixed Deposit calculator to forecast your investment’s growth and make informed financial decisions with ease. The interest rate available from your bank will be influenced by the interest rate set by the Federal Reserve, or the central bank in your country, as well as the bank’s needs and the demand for credit. The interest rates available for a specific fixed deposit account may also be impacted by the following. The more you save, the more money the bank can earn by lending that money to someone else. That’s why interest rates are typically higher for larger deposits, as illustrated in this example from Lloyds Bank. As you can see from this example from Axis Bank in India, some banks offer higher interest rates if you are willing to lock away your money for longer. However, that is not always the case. HSBC, for example, offers a higher interest rate for a one-year fixed deposit than a two-year fixed deposit. Monthly interest payments allow you to earn more regularly but annual payouts tend to offer a better rate because of compounding. However, that is not always the case. As you can see from this information from the Co-operative Bank, if your interest is paid monthly rather annually you may earn a higher AER interest rate. If you take out a fixed deposit account with the Post Office in the UK, you earn at the same AER whether you receive payouts monthly or annually. To fully understand the potential returns from a fixed deposit, it’s important to know how to calculate the maturity amount. This calculation can help you predict how much your investment will be worth at the end of its term. There are two main types of calculations depending on the interest calculation method used: simple interest and compound interest. The formula for calculating the maturity amount with simple interest is straightforward: M=P+(P×r×t/100) Where: Example: If you deposit $10,000 at an interest rate of 5% per annum for 3 years, the calculation would be: M=10,000+(10,000×5×3/100)=10,000+1,500=$11,500 For compound interest, the formula is a bit more complex as it accounts for the interest being added to the principal at each compounding period and then earning further interest: M=P×(1+i/100)^t Where: Example: If the same $10,000 is compounded annually at a rate of 5% for 3 years, the calculation would be: M=10,000×(1+5/100)^3=10,000×1.157625=$11,576.25 A fixed deposit is a fitting solution for many savers for the following reasons. There are some occasions when a fixed deposit is not the right tool. Here’s why. The best way to compare different fixed deposit accounts is to look at the AER or Annual Equivalent Rate. This is a percentage that indicates what you could earn from an account over a year. Unlike the gross interest rate, AER accounts for compound interest i.e. interest earned not just on your lump sum but on the interest you’ve already accumulated. This makes it a more realistic measure than gross interest. However, AER does not account for any fees or bank charges. When comparing fixed deposit accounts, you should also look at minimum deposit requirements, the periods available, withdrawal rules, and the reputation of the financial institution. A fixed deposit might be a good choice if: There are lots of different ways to save or invest money. If a fixed deposit isn’t quite right for you, here are some other ideas. Some banks (especially online-only banks) offer savings accounts that earn higher yields than a normal savings account. For example, Barclays advertises an account with an average annual percentage yield (APY) of 4.25% at the time of writing. These accounts usually offer a variable rate which means high returns are not guaranteed. You will lose out if interest rates fall and benefit if interest rates rise. However, as with a fixed deposit account, your original deposit will be safe. High-yield accounts are also generally more flexible than fixed-deposit accounts and will allow withdrawals. A mutual fund is an investment that pools the money of multiple investors and invests it in a diversified portfolio of stocks, bonds, equities, and other assets. The portfolio is managed by a professional fund manager who aims to maximize the yield and a fee is charged for this service. Investing as a group gives investors access to portfolios that are difficult to access as an individual. There are many types of mutual funds with different yields and risk levels that invest in different assets. Money market funds are a type of mutual fund that could be an alternative to a fixed deposit. A money market fund is the lowest risk category of mutual fund with the lowest returns and is suited to short-term investing. Unlike a fixed deposit, a money market fund does not offer guaranteed returns. The value of your investment will depend on the performance of the fund manager and the market, so look the past performance of the fund manager and market trends before investing. According to the Wall Street Journal, the median money market fund returned 4.2% over the past year, while Time notes that some certificates of deposit pay as high as 5%. A crypto savings account works like a normal savings account except that, instead of storing cash, you store cryptocurrency, such as Bitcoin, Ethereum, or Tether. Crypto savings accounts are available from providers like Coinbase and Binance. There are even some fixed deposit crypto accounts that lock funds for a set period and offer higher yields. The benefits of a crypto savings account include: Downsides include: There is a much debate about whether cryptocurrencies are a good investments but you should do your own extensive research either way. There are so many options available to individuals and businesses when it comes to saving or investing money. It can be difficult to know which product to choose. If you have a lump sum that you’d like to set aside for the short to medium-term and a low risk appetite, a fixed deposit is a good choice, especially when interest rates are high. However, there are alternatives available that promise a higher yield. Consider your investment goals, use the fixed deposit calculator and do your homework before you decide.Key Takeaways: Fixed Deposit Calculator
How Does a Fixed Deposit Work?
Fixed Deposit (FD) Calculator
What Impacts The Interest Rate?
Deposit Amount
Length of Term
Regularity of Interest Payouts
The Formula to Determine FD Maturity Amount
Simple Interest Formula:
Compound Interest Formula:
Benefits of a Fixed Deposit
Disadvantages of a Fixed Deposit
What Is Annual Equivalent Rate or AER?
When Are Fixed Deposits Generally Best?
Alternatives to a Fixed Deposit
High-Yield Savings Accounts
Mutual Funds
Money Market Mutual Funds
Crypto Savings Accounts
Bottom Line