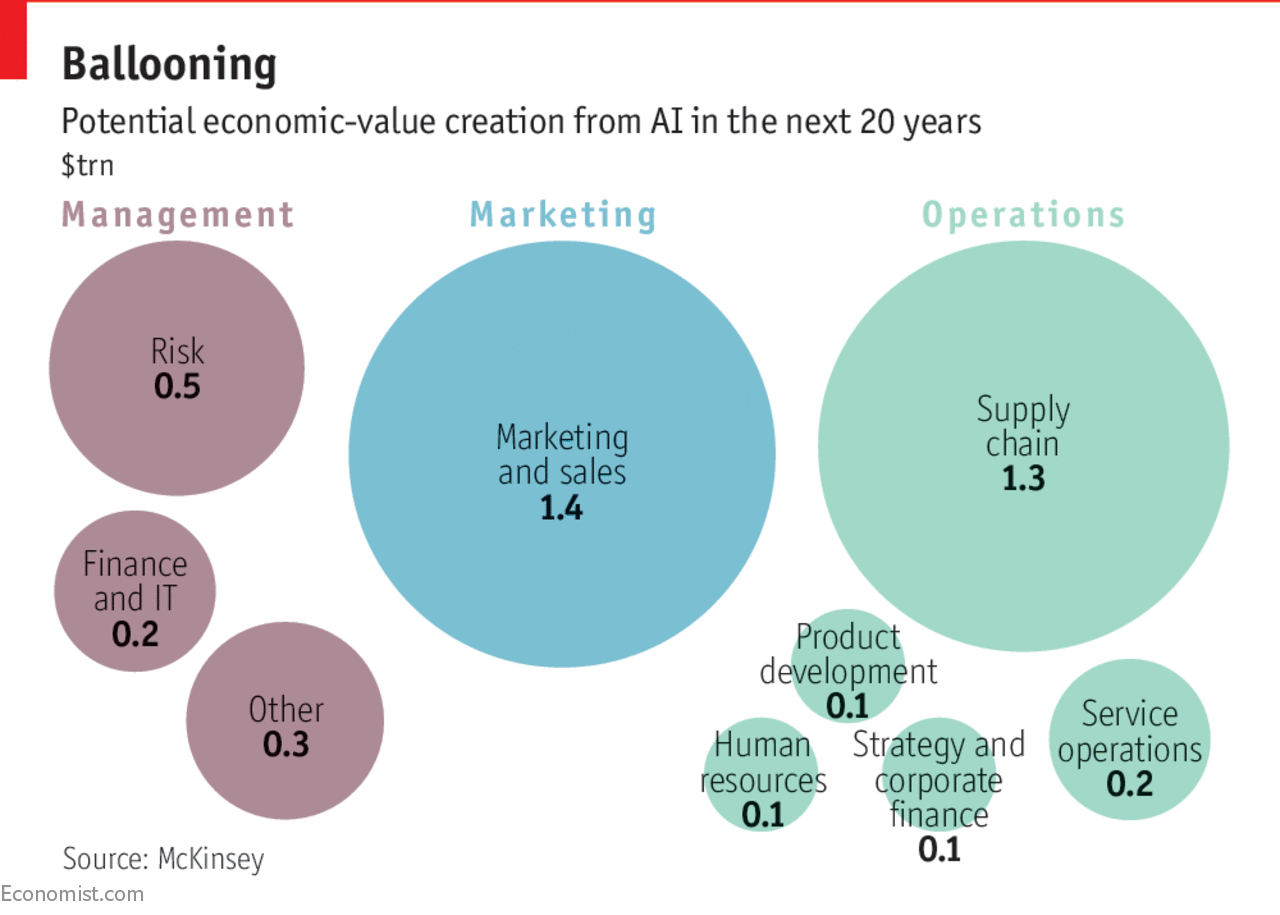
The footprints of AI in retail can be found at every stage of customer experience. Let’s take a look at the most significant areas of AI that has reshaped the way we shop, manage supply chains and set product prices.
1. Recommendation engines and personalization solutions
Today, many of us can’t already imagine shopping without Amazon’s sophisticated recommendations, but it wasn’t always like this. Recommendation engines, also called real-time product targeting, were not widely used ten years ago.
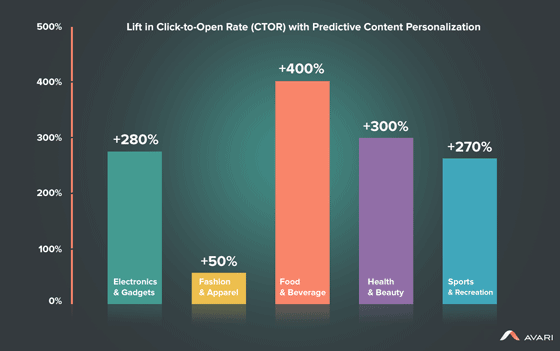
However, today most e-commerce companies are tailoring product recommendations based on each customer’s unique interests, buying propensity, and past and current buying data and customer data.
The use of recommendation engines drives traffic, delivering relevant content at the right time to the right consumer. This increases customer engagement, converts sales, and increases average basket value, etc.
Apart from tailoring the customer experience, AI is also helping sales and marketing teams do their job better. Tools like Salesforce Einstein are helping sales teams to identify leads that are most likely to convert based on an array of data points across its database and the internet. For marketing teams, Salesforce Einstein is helping tailor content or products as well as the timing of when they are offered.
2. Computer Vision
Computer vision already has a lot of applications across different industries; however, in retail, this technology is entirely changing customer experience, both in-stores and online.
Amazon amazed the world when they opened an Amazon Go store where checkout stations and cashiers did not exist. In these stores customers can grab the items of their choice and exit the store without ever fetching their credit cards. Items are scanned, and customers are charged through their Amazon account with the use of computer vision, deep learning, and sensor fusion.
Computer vision is also making its way into traditional retail stores more and more. Via in-store cameras and artificial intelligence, companies can monitor how their products perform on the shelves and conduct analysis using machine learning to optimize product placement and promotion. A startup called Eversight that delivers similar services reports that promotions deployed based on their data analysis outperform traditional promotion by 10-25%.
In-store cameras and AI can also help retail stores better understand customer experience in physical stores.
Is this floor plan optimized? Do customers spend more time in one zone of the store than others? Where do they spend the most of time? Do these patterns correlate with the sales conversion data we gather from our POS system? All these questions can be answered with the usage of a camera and AI that analyses facial expressions and connects them to different human facial expressions and emotions.
The shopping experience will be revolutionized as well. Some predict that the camera will become a much bigger part of the buying process within the next 5-10 years. For example, customers will be able to buy shoes by photographing their feet to be 3D mapped for a custom fit, and goods in stores will be paid for with little more than selfies thanks to facial recognition.
3. Supply chain optimization
AI has been implemented across many stages of a supply chain. It includes efficient inventory management, autonomous replenishment systems, determining optimal distribution routes and allocations, etc.
AI has especially been useful for omnichannel retail where inventory management can be particularly hard. One leading footwear retailer implemented a system that links inventory across all sales points and determines where the order should be shipped from – a store or a central warehouse.
The system works the following way. When an order is placed, the system identifies a store that has the product in stock and has the lowest chances of selling it at full price before the end of the season. The extra cost of shipping the order from the store is compared against the average markdown. The product is shipped from the location that results in biggest profit.
AI also helps with manufacturing of products. A new industrial revolution has created smart factories where robotics together with AI are driving the majority of the manufacturing. Workers no longer need to operate the machines. Everything is done through computer software that can initiate production based on forecasting data, detect a malfunction before it happens, and optimize the settings on the machines to use the least amount of raw material to get the best quality products.
By far the biggest task in supply chain management is supply chain planning. The game of forecasting customer demand is the driving force of profit in all supply chains. Customer preferences and thereby demand for products depends on an array of factors that are represented in big data sets that only machine learning algorithms can interpret.
For example, Otto, a German e-commerce startup, uses a deep-learning algorithm to process an incredible amount of data to predict what and when customers are going to buy. By analyzing factors like price, shipping times, number of shipments per order, and many others, Otto has had a 90% accuracy about sales made within 30 days after the initial analysis.
4. Dynamic pricing
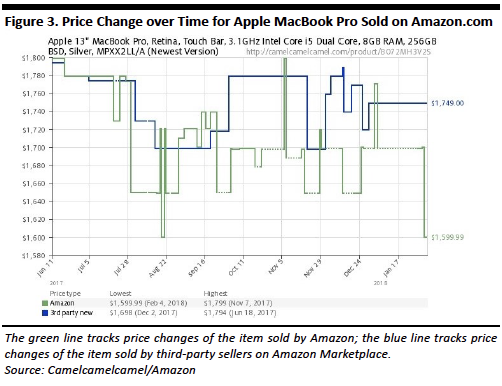
Pricing in many industries (airlines, rental car companies, hotels etc.) can be complicated because multiple factors can affect the price. Still, many companies have been relying on an age-old formula involving only cost of acquisition and a static profit margin.
Dynamic pricing is arguably a better pricing model because it is based on an analysis of factors that truly influence prices. Factors that are typically taken into consideration with dynamic pricing: competitors’ prices, consumer behavior, shopping periods (both long term and short term), customer information and customer price perception (big impact on the profit margin). Furthermore, with the help of machine learning, prices are systematically updated to reflect any change in the conditions.
The main benefit of adopting dynamic pricing, is the ability to offer the optimal price at the right time to the right customer, with the objective of maximizing sales conversion and margins. However, in order to get valuable results from dynamic pricing it is important to take into account the following factors: (1) enough quality data, and (2) a custom algorithm that suits your particular business model.