The blockchain analytics firm Chainalysis has published its popular crypto crime report this week. This latest issue covers the first seven months of 2024 and uncovers the most recent developments and trends concerning criminal activity in the sector.
Although the report acknowledges that criminal activity is declining, certain areas of cybercrime exhibit alarming growth rates.
Overview of Crypto Crime Trends in 2024
Chainalysis emphasized that illicit activity retreated by 20% during these first seven months of the year as the ecosystem keeps maturing.
At the same time, the money moving to addresses marked as illegal dropped from $20.9 billion in the first half of 2023 to $16.7 billion in the same time frame in 2024. This decrease is credited to users being more mindful of the risks in the space and improved safety measures from entities like exchanges, DeFi protocols, and crypto wallets.
Inflows to legitimate services reportedly sit at their highest levels since the 2021 bull market as mainstream users continue to embrace crypto assets while the perceived safety of blockchain-based financial services has progressively improved.
However, the report emphasized that services like crypto mixers and dubious exchanges that do not collect any personal information from users, also known as KYC data, have grown their presence as users appear to keep looking for alternatives to stay anonymous and disguise their transactions
Hackers Have Stolen Nearly $1.6 Billion So Far in 2024
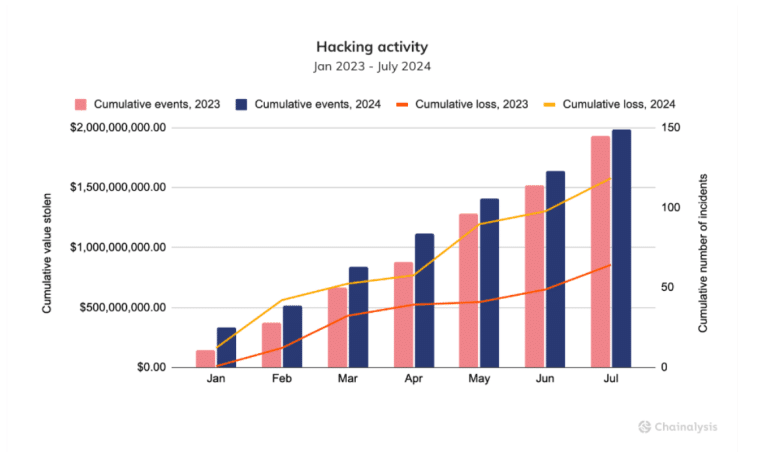
One of the most concerning trends identified in the report is the significant increase in the amount stolen through crypto heists. The value of stolen funds nearly doubled year-over-year, rising from $857 million to $1.58 billion through the end of July. This surge represents a worrying escalation in the sophistication and boldness of crypto thieves.
However, even though the total value of all stolen assets has increased dramatically, the number of incidents has risen only slightly by 2.8% during the observed period. This indicates that criminals are targeting larger organizations and executing more ambitious operations that generate bigger proceeds rather than increasing the frequency of their attacks.
Meanwhile, the average amount stolen per incident saw a 79.5% jump during this period to $10.6 million.
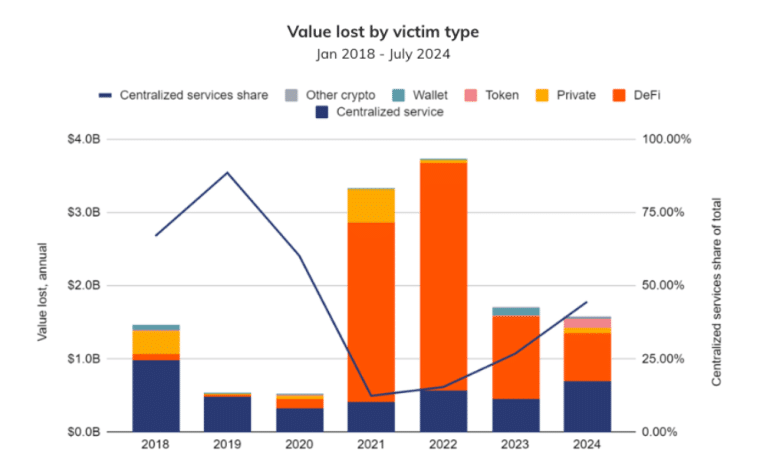
Centralized Exchanges Become Primary Targets Once Again
In the past few years, DeFi protocols became the favorite targets for crypto criminals, probably because their coding and safety protocols were weak. However, thieves appear to be returning to their roots as centralized exchanges – prime targets during the first booming years of the crypto space – have been attacked with higher frequency lately.
The reason behind this trend might be that exchanges typically provide custody and transact with higher volumes of Bitcoin (BTC) compared to DeFi platforms. Chainalysis indicates that around 40% of all stolen funds involved BTC tokens.
The report cites the hack of the DMM exchange as a prime example of this trend. In this single incident, attackers managed to steal approximately $305 million including around 4,500 Bitcoin. This heist alone accounted for roughly 19% of the total value stolen in 2024 through July.
Chainalysis also notes that part of the increase in stolen value can be attributed to the rise in Bitcoin’s price. In this regard, the latest increase from an average of $26,141 in early 2023 to $60,091 in 2024 has significantly inflated the dollar value of stolen funds.
Criminals Resort to More Advanced Social Engineering Tactics
The methods employed by criminals are getting more and more sophisticated every year according to Chainalysis – especially when it comes to state-sponsored attacks from North Korean groups.
They cited that criminals from this country are employing advanced social engineering tactics to infiltrate crypto companies and platforms. They may even go as far as to apply for IT jobs at Western tech firms. A recent report from the United Nations highlighted that over 4,000 North Korean operatives have been hired by these companies, which increases the risk that they can spy, sabotage, or create opportunities for hackers to penetrate their systems.
Meanwhile, when it comes to ransomware, which involves hijacking a company’s systems or databases and demanding payment to release them, the amount paid to resolve these incidents continues to rise compared to last year.
The report found that nearly $460 million were paid during the first six months of the year. Among the most notable incidents, there was a $75 million payment made to the Dark Angels group. This is the highest grossing single incident so far in 2024. It doubled the maximum amount paid by a ransomware victim in 2023.
Ransomware Payment Rates Went Down in First Half of 2024
Data from ransomware leak sites, as compiled by eCrime.ch, indicates that attacks are becoming more frequent, with at least 10% more incidents reported so far this year compared to the same period in 2023.
This increase in frequency, combined with the rise in individual payment amounts, highlights the growing threat that this type of hack poses to the ecosystem and its growth.
A ransomware incident can jeopardize an entire company’s IT infrastructure, undermine its credibility, and result in the loss or theft of valuable intellectual property that can ultimately force it out of business.
Also read: 2.9 Billion People Hit in the Biggest Data Breach: Here’s What Happened
Despite the overall growth in ransomware activity and payment sizes, the report does highlight one potentially positive trend. While posts to ransomware leak sites (a measure of ransomware incidents) have increased by 10% year-over-year, the total number of ransomware payment events has declined by 27% during this same period.
This discrepancy suggests that while the number of attacks might have gone up, payment rates are down compared to last year. Chainalysis interprets this as a positive sign for the ecosystem as it indicates that victims may be better prepared to handle ransomware incidents without paying criminals.
Andrew Davis, general counsel at Kiva Consulting, supports this view, stating: “Approximately 65% of the matters in which Kivu has been engaged in to assist victim organizations have resolved without a resulting payment of the ransom, continuing the positive trend of resiliency on the part of impacted organizations and a lack of necessity to pay the attackers.”
The Future is Bright but Not Without Spots
The Chainalysis report highlights the complexity of analyzing crypto crime. On the one hand, even though the number of incidents and the total amount stolen has been declining, criminals are getting more sophisticated and finding new methodologies to exploit the vulnerabilities of users and institutions in the space.
The return to centralized exchanges at the prime targets for cybercriminals is a notable trend that should prompt these companies to close ranks and strengthen their systems.
North Korea continues to be mentioned as one of the top countries sponsoring hacking activities and its sophistication when it comes to social engineering tactics is quite concerning.
Corsin Camichel, a researcher with eCrime.ch, emphasizes the importance of continued law enforcement efforts, stating: “I believe takedowns and law enforcement actions like Operation Cronos, Operation Duck Hunt, and Operation Endgame are essential in curbing these activities and signaling that criminal actions will have consequences.”
As the cryptocurrency industry continues to mature and gain mainstream acceptance, the battle against cybercrime remains a critical challenge. The insights provided by this mid-year report highlight the need for ongoing collaboration between industry stakeholders, cybersecurity experts, and law enforcement agencies to stay ahead of evolving threats and protect the integrity of the cryptocurrency ecosystem.