The widespread adoption of Generative Artificial Intelligence (Generative AI) is set to revolutionize the US workforce by 2030, leading to significant changes in job roles and the nature of work. According to a groundbreaking report by consulting firm McKinsey, an estimated 12 million workers will have to switch careers, while automation will account for 30% of work hours in the economy.
While there are concerns about job displacement and income inequality, McKinsey also highlights potential opportunities for workers in emerging fields.
The Impact of Generative AI on the Rise of Automation
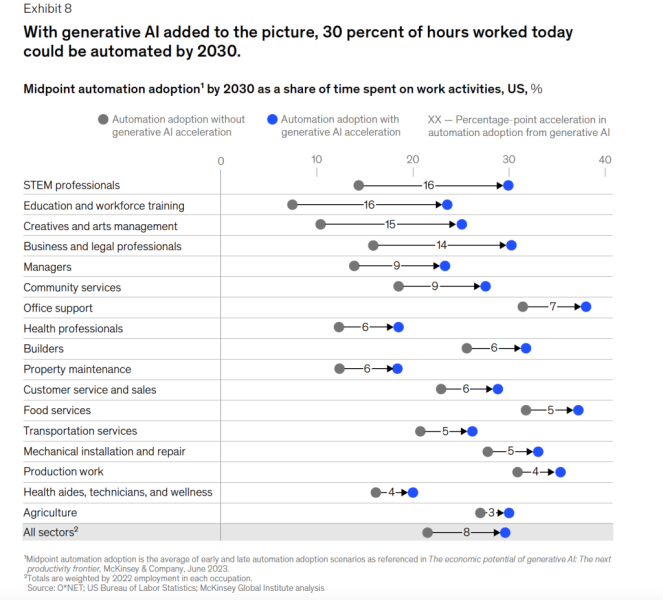
Generative AI is a branch of artificial intelligence that can create new content, such as text, images, and videos. Its increasing capabilities are expected to lead to automation in various tasks, including customer service, marketing, content creation, and fraud detection. McKinsey’s report reveals that Generative AI could automate around 30% of work hours, a significant increase from the 22% automation estimated without this technology.
Generative AI can also perform tasks requiring expertise and creativity, making it one of the first technologies to impact both knowledge, work and lower-paying jobs. For instance, natural language models could replace tasks typically performed by lawyers, and graphic designers might find tools like Midjourney and DALL-E, streamlining their work processes.
Gradual Career Shifts
The McKinsey report seeks to dispel the notion that since Generative AI brings about changes in work, it will lead to mass unemployment. Instead, there will be a shift in the job landscape, where workers will have to adapt to new roles as the nature of work changes.
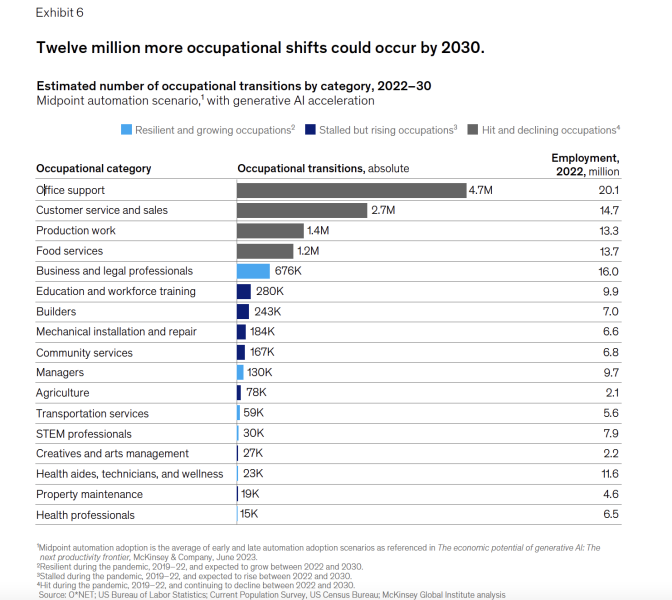
About 12 million people are expected to switch careers by 2030, which is 25% more than previously estimated.
The report acknowledges that some jobs may disappear like office support, customer service, and food services.
Office support and customer service jobs are expected to decrease by 18% and 13%, respectively, by 2030. The demand for jobs in the food service industry may also decline but at a lower rate of 2% over the same time period.
However, other industries will see growth, particularly in fields related to health care and STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics). Generative AI is likely to enhance the way STEM, creative, and business professionals work, while other job categories like office support, customer service, and food services are expected to continue declining.
Additionally, McKinsey foresees generative AI enhancing the way creative and business professionals work.
Notably, the decline in certain job roles may disproportionately affect specific demographic groups. Reduced demand in office support roles is likely to impact women more, while reduced demand in customer service and food service may pose higher risks to Black and Hispanic employees.
Impact of Generative AI on Income Inequality
While the report suggests that Generative AI will create opportunities for some workers to move into higher-paying jobs, it also highlights potential challenges. McKinsey’s analysis predicts a loss of 1.1 million jobs paying $38,200 or less, with an increase of 3.8 million jobs offering higher salaries. The lowest-paid workers are likely to be heavily affected, with those earning $38,200 or less up to 14 times more likely to need to change jobs.
Furthermore, concerns are raised about widening income inequality. In some cases, companies may opt to retain low-paying jobs instead of investing in AI systems, resulting in a potential exacerbation of income disparities.
As Generative AI continues to evolve, it is essential for policymakers, educators, and businesses to collaborate to navigate this transformative era and ensure that the benefits of generative AI are accessible to all, while mitigating potential challenges along the way.
McKinsey advises early training, starting as early as high school, particularly for STEM fields. Additionally, companies are urged to expand their applicant pools to include unemployed individuals and those without higher education.
Additionally, a focus on equitable distribution of opportunities can aid in minimizing income disparities.
The introduction of Generative AI heralds a transformative era in the workforce. While challenges and uncertainties lie ahead, McKinsey’s report provides valuable insights for navigating this technological shift. The key lies in embracing change and proactively preparing for the future of work in the age of Generative AI.
Related Articles
- 15 Best AI Copywriting Tools for 2023
- Generative AI Consulting is About to Be the Hottest Sector in the Market – Businesses Around the World Need Help Implementing It
- Netflix is Paying Top Dollar to Onboard AI Specialist while Hollywood is On Strike
What's the Best Crypto to Buy Now?
- B2C Listed the Top Rated Cryptocurrencies for 2023
- Get Early Access to Presales & Private Sales
- KYC Verified & Audited, Public Teams
- Most Voted for Tokens on CoinSniper
- Upcoming Listings on Exchanges, NFT Drops