Duplicate content is an SEO problem that many SEOs or content marketers have likely faced in their daily work. Content marketers who invest time in crafting quality content strategies want to avoid penalties for duplication or similar content. In 2013, Matt Cutts mentioned that 25% of the web was made up of duplicate content, and you can find this figure in the video at the end of the article.
Duplication refer to blocks of content that appear more than one time inside or outside a website or which are pretty similar. Duplicate content or near duplicates can lead to SEO penalties.
Crawlers struggle to index the correct content across different versions. Bots must then select the content they think is the best, which can cause a loss of relevance since choosing the right version isn’t always easy. Additionally, bots find it hard to provide the link metrics to the correct page or to share them among the various versions. As a result, duplicate content prevents the right version from ranking for a specific query. Ultimately, this will lead to a decrease in traffic.
The thing is, Google gives a lot of credits to user experience and focuses on delivering the best content possible to its audience. This is also why duplicate content is penalized.
While not all types of duplicate content can hurt your SEO, some of them need to be on the look out to avoid SEO penalties.
This article will cover:
- types of duplicate content
- how to deal with duplicate content
- tools to get rid of duplicate content
Types of Duplicate Content Leading to SEO Penalties
There are different types of duplicate content you should avoid.
Duplicate product forms
E-commerce websites often use manufacturer’s item descriptions to describe the products they sell. The problem is that those products are often sold to different e-commerce websites. Then, the same description appears on different websites and creates duplicate content.
Syndicated or copied content
Many bloggers use content, quotes or comments from other websites to illustrate their articles. There is nothing wrong with that if you link back to the original one. However, Google can still consider this as a duplication and will poorly value those pieces of content.
Sorting and multi-pages lists
Large e-commerce websites have filter and category options that generate unique URLs. Product pages can appear in different categories and be ordered differently depending on how the list is sorted. For instance, if you range 45 products by price or by alphabetical order, you will end up with two pages containing the same content, but with different URLs.
URL issues
Google considers URLs in www, http, https, .com and .com/index.html as different ones even if they point to identical pages and will evaluate them as duplicate content.
Session IDs
Session IDs issues refer to different session IDs stored in the same URL that are assigned to a visitor when he or she comes to the website.
Printer-friendly
Printable versions of content can lead to duplicate content issues when different versions of a page are indexed.
How to Avoid Duplicate Content?
There are different best practices to avoid duplicate content issues. The main solution with content located in different URLs is to canonicalize the original one. You can use a 301 redirect, a rel=canonical or parameters handling tool from Google Webmaster Central.
301 redirect
The 301 redirect is great for URL issues leading to duplications. It informs search engines which version of a page is the original and it links the duplications to that original one. Plus, when different well-ranked pages are linked to a single one, they are not in competition anymore and they create an overall stronger and more popular signal.
Rel=canonical
It works quite the same as 301 redirects, but it is easier to set up. That tag is located in the HTML head section of your web page and looks like this:
Then search engines know the above URL is a copy of the original one.
You can use it for content you integrated from other websites. It will inform search engines that you know the content is not from you and that the link metrics of that content should pass to the original one.
NoIndex, NoFollow
Use the noindex, nofollow tag to tell search engines not to index the content. Bots will be able to crawl the page, but won’t index it. Thus, you won’t be penalized for duplicate content.
Preferred domain
A quite simple operation is to set a preferred domain for search engines. It will inform whether a site must be displayed under ‘www’ or not in the SERPs.
Unique product description
As we said, product information on e-commerce websites can lead to duplicate content issues. Take the time to write unique ones or enrich your descriptions as it will help you rank above sites whose descriptions are duplicated.
What tools can help me to detect duplicate content?
In order to save time, you can use different qualitative tools to help you eradicate duplicate content. Here are three different ones, with some being totally free.
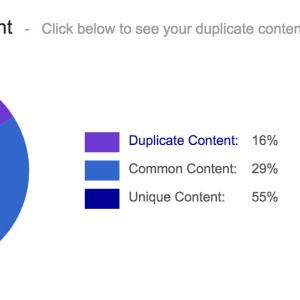
This tool detects any duplicate content on your website. You just need to add your website’s URL and it will draw a full report with your content performances.
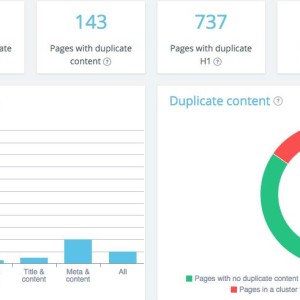
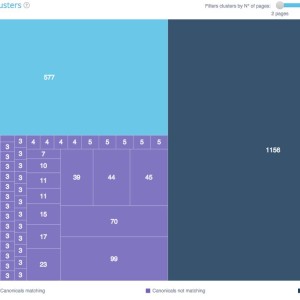
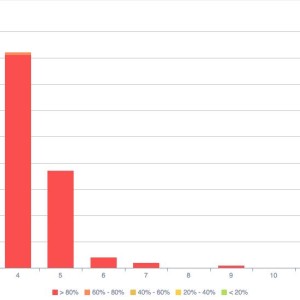
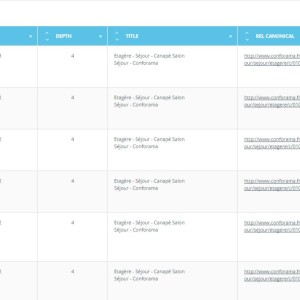
This onsite SEO semantic crawler also offers a duplicate and near duplicate detection feature. It shows you clusters of duplicates and near duplicates, types of duplication and clearly indicates which URLs are concerned.
The tool offer a 30 days-trial. If you want to enjoy all the functionalities, you just need to pick a plan and cancel your subscription before the end of the trial and you won’t pay anything.
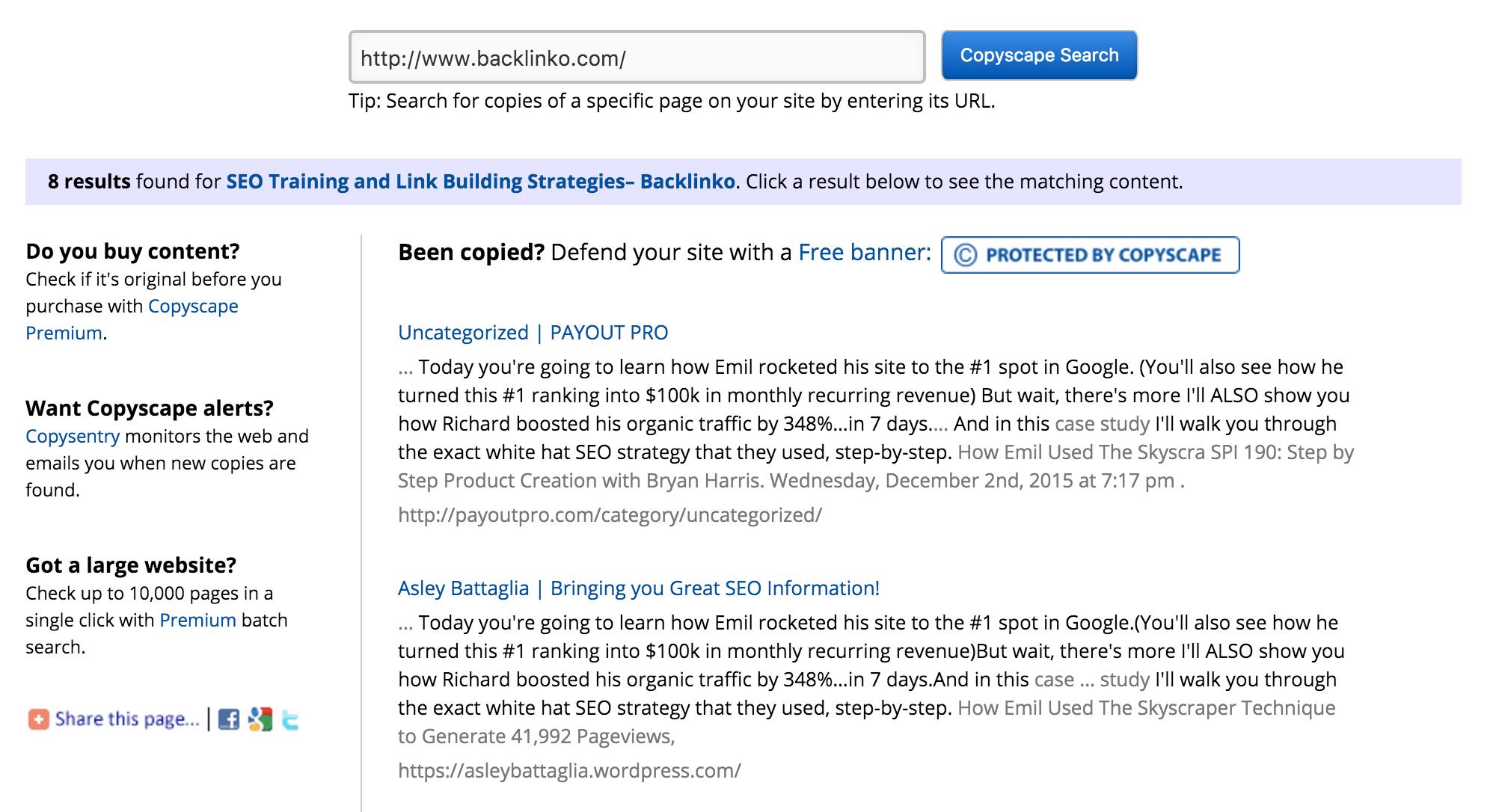
Copyscape is a great partner because it detects duplicate content outside of your blog. You can thus easily know if someone has duplicated your content without your permission or without giving you credits.
To sum this up, take a look at this video where Matt Cutts explains how Google regards duplicate content.