It is a common reality that people spend a lot of time collecting data and then finding ways to store it.
To explain this situation, let’s begin with the simplest level of computing. For example, imagine you are downloading and saving files like movies, music, and photos. You keep these on your hard drive. But when you run out of space for new data and you don’t want to remove any of your old files, what do you do? You get a larger hard drive, of course. The more data you gather, the more space you require.
There are different ways of storing files. Some people invest in large-capacity hard drives or thumb drives while others export their files onto a disc. Companies even have dedicated servers to support their entire computer system. But nowadays, some are choosing to rely on a growing trend—the Cloud. The “Cloud” is a metaphor for the Internet. You have probably been involved in Cloud computing without even noticing, like logging on web-based email like Gmail and Yahoo Mail and uploading music, videos and photos on the Internet.
The Cloud has many applications and of which is hosting. How different is Cloud hosting from other types of hosting services? Read on to find out.
On the red corner: Traditional Hosting
Traditional hosting comes in mainly two forms: Dedicated and Shared hosting.
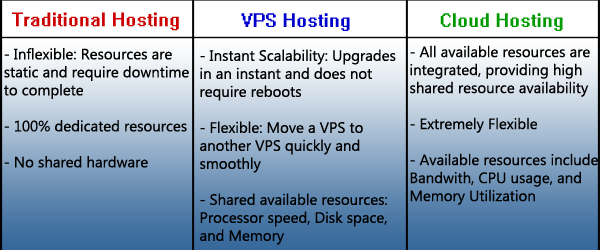
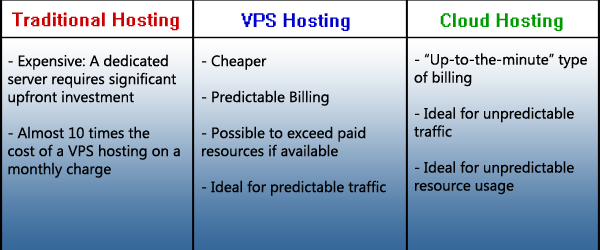
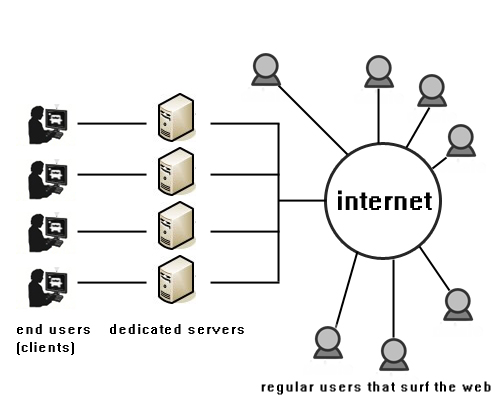
In Dedicated server hosting, a whole server caters only to one client. The company pays for the complete package, a server or servers with a dedicated amount of bandwidth, CPU, RAM and drive space. With dedicated hosting, you have complete control of your server and you don’t share it with others, but it can get very expensive especially with hardware upgrades and maintenance.
With shared hosting, the client pays for a set amount of storage on a single server and that server’s resources are shared by other websites. It’s a cost-efficient, low-maintenance way to host a website or application. The hosting company maintains, manages and updates the units. However, since thousands of websites use shared hosting, you are competing with them to gain access to the server. This may result in slow performance, especially if other websites crash or create heavy traffic.
On the blue corner: VPS Hosting
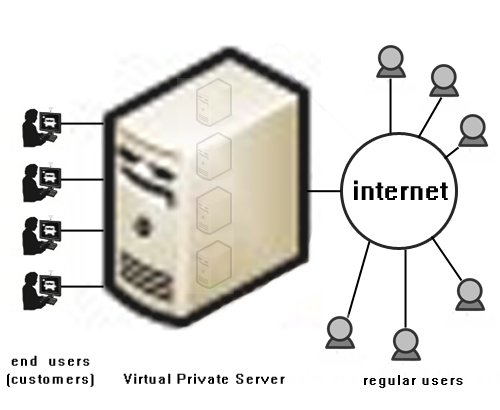
Virtual Private Server Hosting or VPS Hosting is a term used to refer to a virtual machine. Instead of having an actual physical computer as a server, VPS runs as a software in a user’s personal computer but functions like a separate computer dedicated to the individual customer’s I.T. needs. In reality, VPS is just a slice of an actual server that is partitioned virtually to appear and function to the user as a dedicated server.
With virtualization, you are provided with a dedicated space on the server as well as a dedicated amount of resources. This gives more control and reliability. But it still has a single point of failure because it is still just one server after all.
With both dedicated and shared hosting, you are paying for a set amount of storage and processing power. If you have an unpredictable flow of traffic, you may be constrained by the amount of storage space you have. The only way to adapt is to buy more server space to add to the storage space and processing power. But if traffic suddenly goes down, you will still be paying for space that you are not using.
On the green corner: Cloud Hosting
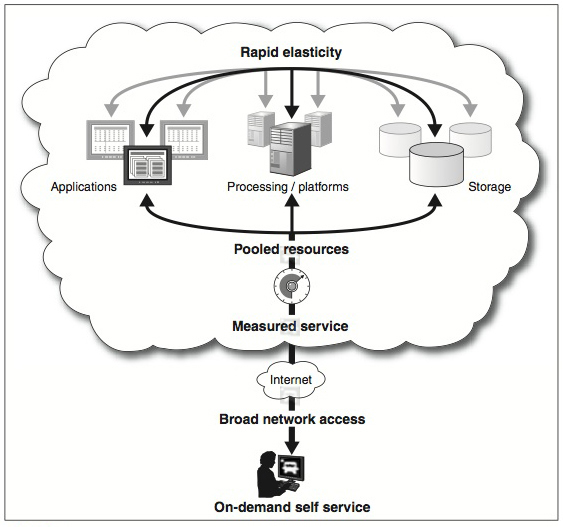
Slowly becoming the most popular web hosting service, Cloud hosting relies on a network of servers that make up the Cloud. Because it uses a number of different servers, there is virtually no downtime for your site. There will always be one server available from the Cloud to cope with your needs.
Cloud hosting offers more flexibility to clients. If you need more computing power, the Cloud can easily provide that. And if you don’t need it anymore, you can easily release it into the Cloud. There is no need to buy expensive hardware and set it up because the Cloud hosting provider takes care of it for you. You just pay for the services you use from the provider.
The most prevalent criticism for Cloud hosting is security and privacy since all the information can be seen and accessed by the service provider.
This is an Infographic representation on the impact of Cloud to businesses and the amount of storage that people use regarding their data.
Let the Battle begin!
Round 1: Flexibility and Optimization
Round 2: Control, Customization and Security
Round 3: Cost
Decision Round:
Which hosting type is the best?
Cloud hosting is a growing trend at present because it offers a level of scalability that traditional hosting cannot provide. With cloud hosting, virtual space is provided on an on-demand, as-needed basis.
It is also reliable because information is stored and mirrored across different servers. Because of this redundancy, the user is protected from loss of information and poor performance when a server crashes.Cloud hosting is a growing trend at present because it offers a level of scalability that traditional hosting cannot provide. With Cloud hosting, virtual space is provided on an on-demand, as-needed basis.
What type of hosting is for you?
It’s a case-to-case basis. If you are just a small business with not much resource, a good starting point will be the shared hosting. If your website has consistent heavy traffic, dedicated hosting might work as long as you have the resources to support it. It’s all a matter of what works for you and the company. Generally, the hosting type you should choose will depend on your needs and the resources you have to support it.
For this round, I will leave it up to you on which type of hosting gets a knockout and which one earns the championship belt.
Read more: